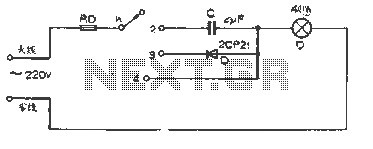
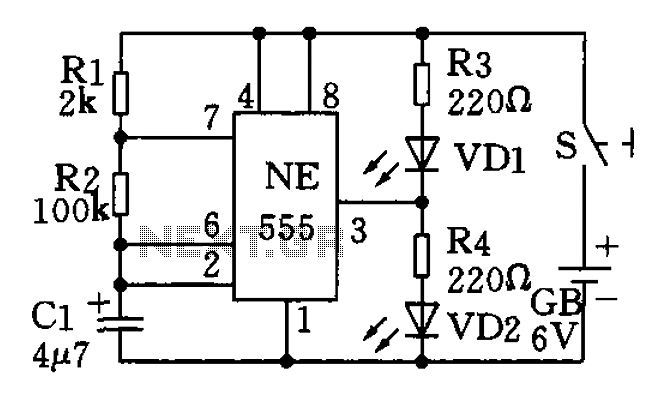
oscillator circuit with opamp and zener diode
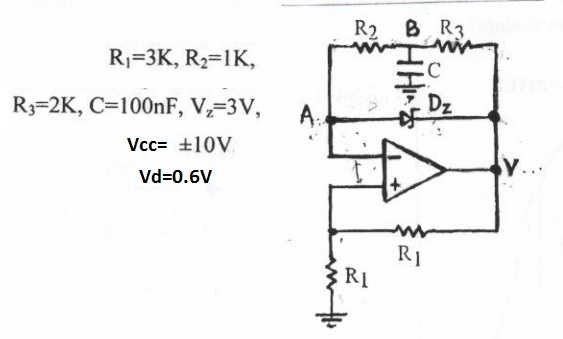
This circuit appears to be a Schmitt trigger oscillator. Based on the configuration of the resistors and capacitor, it is likely functioning as a sawtooth wave generator, with resistors R2 and R3 influencing the slope of the rising and falling edges. The Zener diode aids in regulating the amplitude between 0 to 3V or may truncate the peaks of the sawtooth waveform, resulting in an output with a trapezoidal shape.
The circuit utilizes a Schmitt trigger, which is known for its ability to provide hysteresis in the input signal, allowing for clean transitions between high and low states. The sawtooth wave generator aspect is achieved through the charging and discharging of a capacitor, which is influenced by the resistors R2 and R3. The values of these resistors determine the rate at which the capacitor charges and discharges, thereby affecting the frequency and duty cycle of the output waveform.
The Zener diode plays a crucial role in this configuration. By clamping the voltage at a specified level, it ensures that the output does not exceed a certain amplitude, thereby protecting downstream components from potential damage due to overvoltage. If the Zener diode is indeed truncating the waveform, it modifies the output from a pure sawtooth to a trapezoidal shape, which may be beneficial in applications requiring a more controlled voltage profile.
In practical applications, this type of oscillator can be used in signal generation, timing circuits, and waveform shaping. The precise control over the output waveform characteristics makes it suitable for various electronic applications, including audio synthesis and modulation. The design's simplicity and effectiveness make it an excellent choice for engineers looking to implement a reliable waveform generator in their projects.Looks like a schmitt trigger oscillator. By the way the resistors and capacitor are used it is probably a saw-tooth wave generator with R2 & R3 determining the slope of the rising and trailing edges. The zener helps control the amplitude between 0 to 3V OR maybe it chops off the tops of the sawtooth wave thereby creating an output that has a trapezoidal waveform.
🔗 External reference
The circuit utilizes a Schmitt trigger, which is known for its ability to provide hysteresis in the input signal, allowing for clean transitions between high and low states. The sawtooth wave generator aspect is achieved through the charging and discharging of a capacitor, which is influenced by the resistors R2 and R3. The values of these resistors determine the rate at which the capacitor charges and discharges, thereby affecting the frequency and duty cycle of the output waveform.
The Zener diode plays a crucial role in this configuration. By clamping the voltage at a specified level, it ensures that the output does not exceed a certain amplitude, thereby protecting downstream components from potential damage due to overvoltage. If the Zener diode is indeed truncating the waveform, it modifies the output from a pure sawtooth to a trapezoidal shape, which may be beneficial in applications requiring a more controlled voltage profile.
In practical applications, this type of oscillator can be used in signal generation, timing circuits, and waveform shaping. The precise control over the output waveform characteristics makes it suitable for various electronic applications, including audio synthesis and modulation. The design's simplicity and effectiveness make it an excellent choice for engineers looking to implement a reliable waveform generator in their projects.Looks like a schmitt trigger oscillator. By the way the resistors and capacitor are used it is probably a saw-tooth wave generator with R2 & R3 determining the slope of the rising and trailing edges. The zener helps control the amplitude between 0 to 3V OR maybe it chops off the tops of the sawtooth wave thereby creating an output that has a trapezoidal waveform.
🔗 External reference