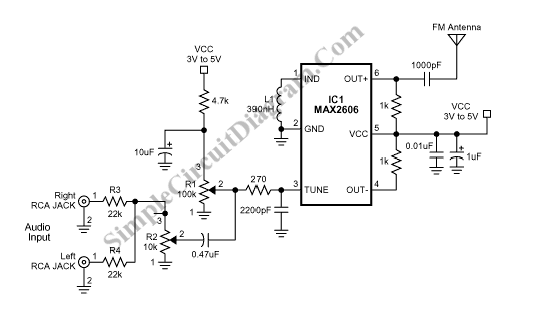
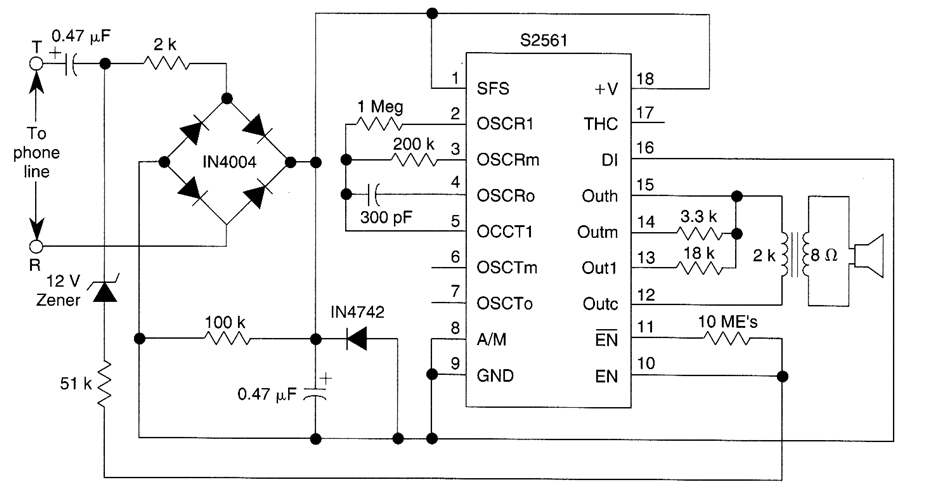
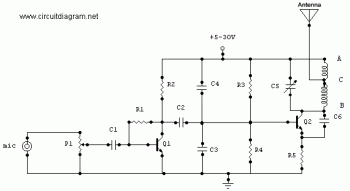
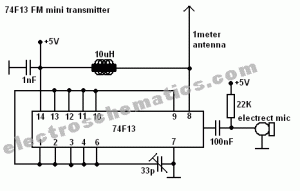
Phone Spy Transmitter
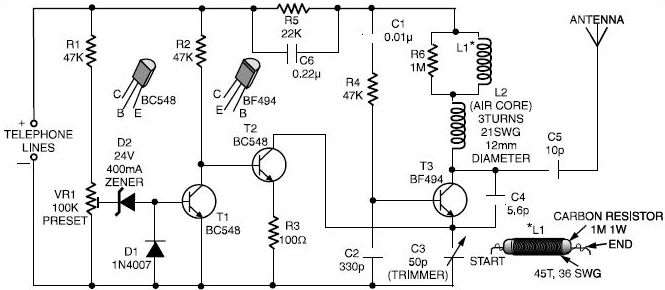
This is a straightforward telephone broadcaster transmitter designed for eavesdropping on telephone conversations. Additionally, the circuit can function as a wireless telephone amplifier. A key feature of this phone transmitter is that it draws power directly from the active telephone lines, eliminating the need for an external battery or power supply.
The telephone broadcaster transmitter circuit operates by utilizing the existing voltage present on the telephone lines, typically around 48 volts DC when the phone is on-hook. This voltage is sufficient to power the transmitter without the need for any additional power source. The circuit generally consists of a few essential components, including a microphone, an amplifier, a modulator, and an RF transmitter.
The microphone captures the audio from the telephone conversation, converting sound waves into electrical signals. These signals are then amplified to ensure they are strong enough for transmission. The modulator is responsible for encoding the audio signal onto a carrier frequency, which allows it to be transmitted wirelessly. The RF transmitter then broadcasts the modulated signal, which can be received by a compatible receiver tuned to the same frequency.
In terms of design, the circuit should include proper filtering to minimize interference and ensure clear audio quality. Additionally, it is crucial to implement appropriate safety measures to prevent damage to the telephone line or the circuit itself. The layout of the components should be compact, allowing for easy integration into existing telephone setups without causing disruption.
Overall, this telephone broadcaster transmitter circuit serves dual purposes as both an eavesdropping device and a wireless amplifier, leveraging the existing infrastructure of telephone lines for power and functionality.Here is a very simple telephone broadcaster transmitter which can be used to eavesdrop on a telephone conversation. The circuit can also be used as a wireless telephone amplifier. One important feature of this phone transmitter is that the circuit derives its power directly from the active telephone lines, and thus avoids use of any external battery or other power supplies
🔗 External reference
The telephone broadcaster transmitter circuit operates by utilizing the existing voltage present on the telephone lines, typically around 48 volts DC when the phone is on-hook. This voltage is sufficient to power the transmitter without the need for any additional power source. The circuit generally consists of a few essential components, including a microphone, an amplifier, a modulator, and an RF transmitter.
The microphone captures the audio from the telephone conversation, converting sound waves into electrical signals. These signals are then amplified to ensure they are strong enough for transmission. The modulator is responsible for encoding the audio signal onto a carrier frequency, which allows it to be transmitted wirelessly. The RF transmitter then broadcasts the modulated signal, which can be received by a compatible receiver tuned to the same frequency.
In terms of design, the circuit should include proper filtering to minimize interference and ensure clear audio quality. Additionally, it is crucial to implement appropriate safety measures to prevent damage to the telephone line or the circuit itself. The layout of the components should be compact, allowing for easy integration into existing telephone setups without causing disruption.
Overall, this telephone broadcaster transmitter circuit serves dual purposes as both an eavesdropping device and a wireless amplifier, leveraging the existing infrastructure of telephone lines for power and functionality.Here is a very simple telephone broadcaster transmitter which can be used to eavesdrop on a telephone conversation. The circuit can also be used as a wireless telephone amplifier. One important feature of this phone transmitter is that the circuit derives its power directly from the active telephone lines, and thus avoids use of any external battery or other power supplies
🔗 External reference