Power-Off Time Delay Relay
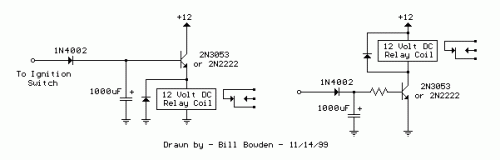
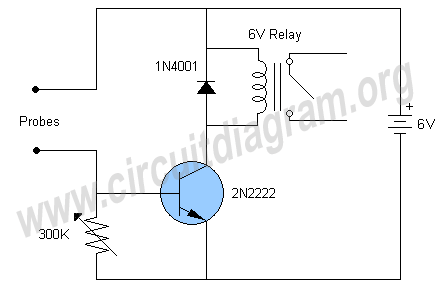
The two circuits demonstrate the operation of opening a relay contact shortly after the ignition or light switch is turned off. The capacitor becomes charged, and the relay remains closed until the voltage at the diode anode reaches 12 volts.
The described circuits utilize a relay mechanism to control the disconnection of a load after a specified delay. When the ignition or light switch is turned off, the capacitor begins to charge through a resistor connected to the power supply. This charging process allows the relay to remain in a closed state, thereby maintaining the connection of the load.
As the capacitor charges, the voltage across it increases. The diode is positioned in such a manner that it allows current to flow into the capacitor while preventing it from discharging back into the circuit. When the voltage at the anode of the diode reaches 12 volts, it triggers the relay to open, disconnecting the load. This delay in opening the relay contact can be adjusted by changing the resistor and capacitor values, allowing for customization based on the specific requirements of the application.
The relay used in this circuit should be rated appropriately for the load it will control, ensuring safe operation. Additionally, the capacitor must have a voltage rating higher than 12 volts to prevent breakdown during operation. The circuit can be further enhanced by incorporating additional components such as a Zener diode for voltage regulation or a transistor for improved switching performance. Overall, this configuration provides a reliable method to control electrical loads with a timed delay, enhancing the functionality of automotive and lighting systems.The two circuits illustrate opening a relay contact a short time after the ignition or ligh switch is turned off. The capacitor is charged and the relay is closed when the voltage at the diode anode rises to 12 volts
🔗 External reference
The described circuits utilize a relay mechanism to control the disconnection of a load after a specified delay. When the ignition or light switch is turned off, the capacitor begins to charge through a resistor connected to the power supply. This charging process allows the relay to remain in a closed state, thereby maintaining the connection of the load.
As the capacitor charges, the voltage across it increases. The diode is positioned in such a manner that it allows current to flow into the capacitor while preventing it from discharging back into the circuit. When the voltage at the anode of the diode reaches 12 volts, it triggers the relay to open, disconnecting the load. This delay in opening the relay contact can be adjusted by changing the resistor and capacitor values, allowing for customization based on the specific requirements of the application.
The relay used in this circuit should be rated appropriately for the load it will control, ensuring safe operation. Additionally, the capacitor must have a voltage rating higher than 12 volts to prevent breakdown during operation. The circuit can be further enhanced by incorporating additional components such as a Zener diode for voltage regulation or a transistor for improved switching performance. Overall, this configuration provides a reliable method to control electrical loads with a timed delay, enhancing the functionality of automotive and lighting systems.The two circuits illustrate opening a relay contact a short time after the ignition or ligh switch is turned off. The capacitor is charged and the relay is closed when the voltage at the diode anode rises to 12 volts
🔗 External reference