Practical differentiator
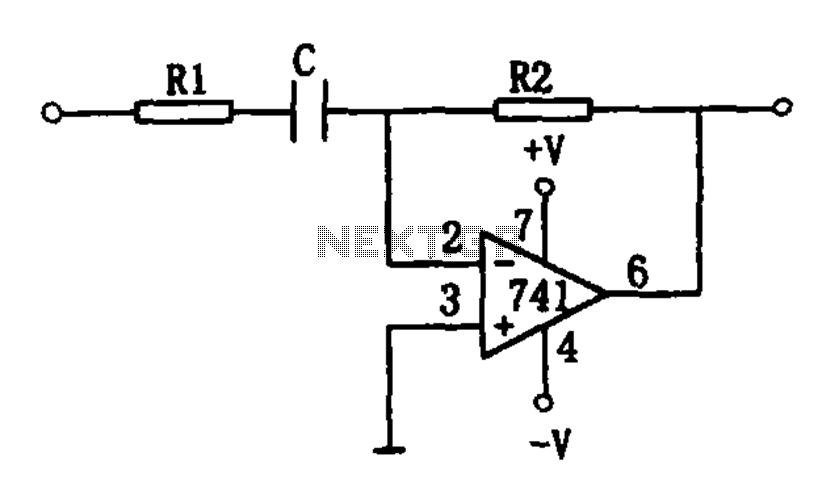
The circuit functions as a differentiating circuit designed for utility applications. It employs an operational amplifier (op-amp) configuration. When a triangular wave is applied as the differential input, the output is a square wave. The frequency of the input signal is influenced by the circuit's resistors R1, R2, and the capacitor C. The circuit requires the resistance values of R1 and R2 to be in a specific ratio, where R1 is ten times the value of R2 (R1 = R2/10). The capacitor C's value is determined in conjunction with R2 and the input frequency (fin), following the relationship C = 1/(R2 * fin). Conversely, if the value of C is known, R2 can be calculated using the formula R2 = 1/(C * fin).
The differentiating circuit utilizes an operational amplifier to convert a triangular wave input into a square wave output. This transformation is achieved through the differentiation process, where the op-amp amplifies the rate of change of the input signal. The circuit design requires careful selection of resistors R1 and R2, as their values directly impact the circuit's frequency response and stability. Specifically, R1 should be ten times the value of R2 to ensure proper functionality.
The capacitor C plays a crucial role in determining the circuit's behavior, as it works in conjunction with R2 to set the time constant of the differentiating circuit. The relationship C = 1/(R2 * fin) indicates that for a given input frequency fin, the capacitor value must be chosen to achieve the desired differentiation effect. Alternatively, if the capacitance is predetermined, R2 can be adjusted according to the formula R2 = 1/(C * fin) to maintain the circuit's operational integrity.
In practical applications, the circuit can be used in signal processing tasks where the conversion of waveform shapes is essential, such as in waveform generators or signal conditioning circuits. Proper implementation of this differentiating circuit requires attention to component tolerances and characteristics to ensure reliable performance across varying input frequencies.Differentiating circuit as shown for the utility. The op amp circuit constituted by Universal. When the differential input a triangular wave, square wave output, while the inpu t signal frequency by the circuit resistors R1, R2 and capacitor C decision. The circuit requires about one-tenth of the value of R1 R2, namely:R1 R2/10 The value of the capacitor C is jointly determined by the R2 value of the input frequency fin, their relationship: C 1/R2fin Similarly, if the known value C, then R. Values calculated by the following formula:R2 1/Cfin
The differentiating circuit utilizes an operational amplifier to convert a triangular wave input into a square wave output. This transformation is achieved through the differentiation process, where the op-amp amplifies the rate of change of the input signal. The circuit design requires careful selection of resistors R1 and R2, as their values directly impact the circuit's frequency response and stability. Specifically, R1 should be ten times the value of R2 to ensure proper functionality.
The capacitor C plays a crucial role in determining the circuit's behavior, as it works in conjunction with R2 to set the time constant of the differentiating circuit. The relationship C = 1/(R2 * fin) indicates that for a given input frequency fin, the capacitor value must be chosen to achieve the desired differentiation effect. Alternatively, if the capacitance is predetermined, R2 can be adjusted according to the formula R2 = 1/(C * fin) to maintain the circuit's operational integrity.
In practical applications, the circuit can be used in signal processing tasks where the conversion of waveform shapes is essential, such as in waveform generators or signal conditioning circuits. Proper implementation of this differentiating circuit requires attention to component tolerances and characteristics to ensure reliable performance across varying input frequencies.Differentiating circuit as shown for the utility. The op amp circuit constituted by Universal. When the differential input a triangular wave, square wave output, while the inpu t signal frequency by the circuit resistors R1, R2 and capacitor C decision. The circuit requires about one-tenth of the value of R1 R2, namely:R1 R2/10 The value of the capacitor C is jointly determined by the R2 value of the input frequency fin, their relationship: C 1/R2fin Similarly, if the known value C, then R. Values calculated by the following formula:R2 1/Cfin