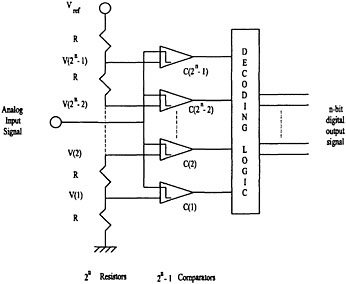
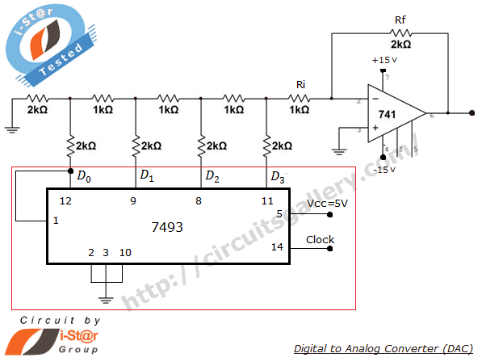
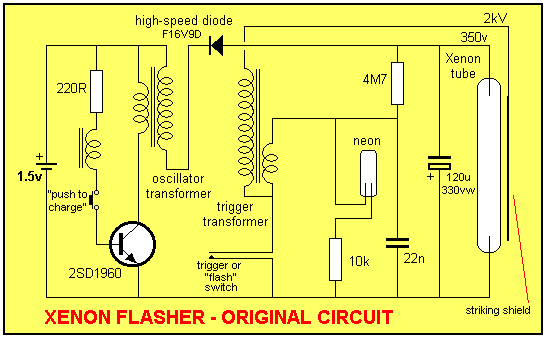
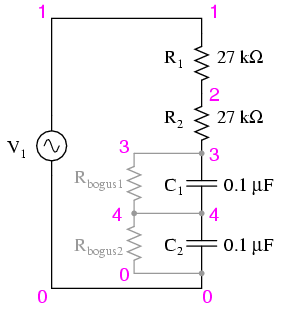
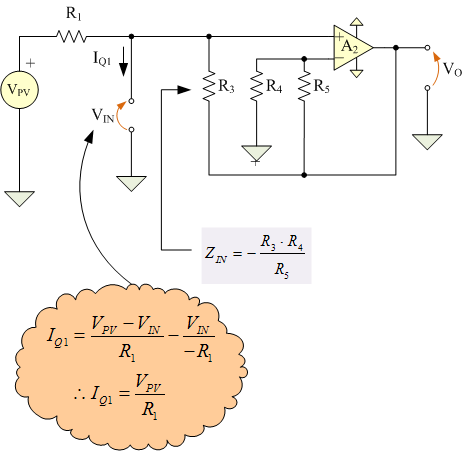
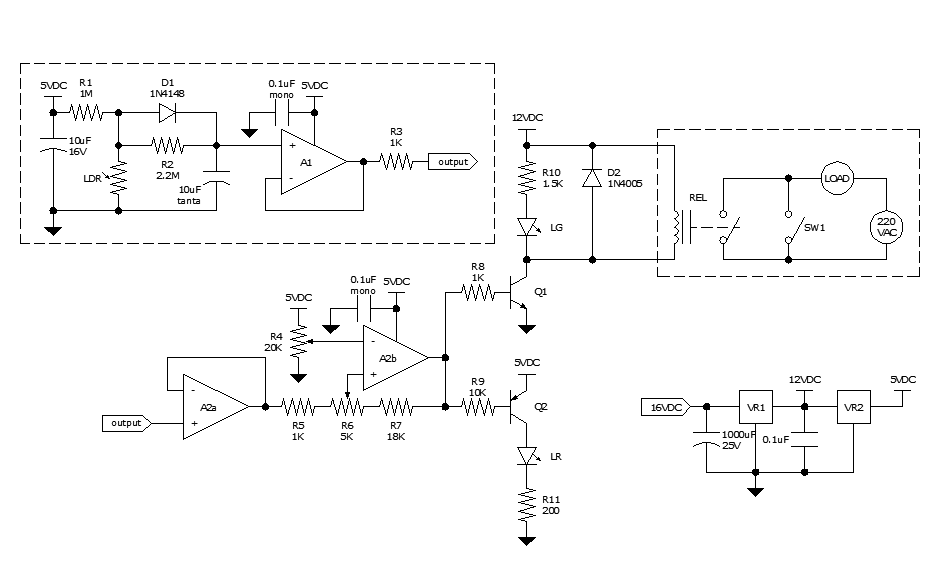
Qualitative Analysis of Analog Circuits
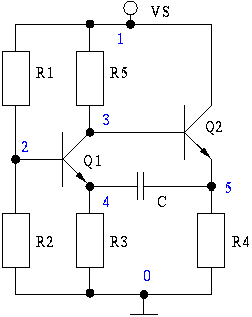
At the beginning of the design process, the designer must determine which circuit structure is appropriate for a specific purpose. During this phase, numerical and symbolic analysis are of limited utility. There are no numerical values available for conventional simulations using programs like SPICE, and symbolic analysis would yield large symbolic expressions. Further approximation of these expressions is not feasible due to the absence of numerical values. However, an experienced designer can analyze the behavior of an unknown circuit. Qualitative Analysis replicates this skill on computers by introducing qualitative states such as positive, zero, or negative. The applet serves as a graphical user interface to the Qualitative Analysis (QA) Server, which performs computations and operates on the same computer (SUN Ultra450) as the World Wide Web (WWW) Server.
The design process of electronic circuits often begins with the selection of an appropriate circuit structure tailored to the intended application. During the initial stages, traditional numerical and symbolic analysis techniques may not be applicable due to the absence of specific numerical values. This limitation poses challenges for conventional simulation tools such as SPICE, which rely on numerical inputs to model circuit behavior accurately. Furthermore, symbolic analysis can result in complex expressions that are cumbersome and impractical to manage without numerical values for simplification.
To address these challenges, experienced designers utilize their intuition and knowledge to assess the behavior of unknown circuits qualitatively. This approach is formalized through Qualitative Analysis (QA), which introduces qualitative states (positive, zero, and negative) to characterize circuit components and their interactions. By employing these qualitative states, the analysis can yield insights into circuit behavior without requiring precise numerical data.
The QA Server is a dedicated computational engine that performs the necessary calculations to facilitate qualitative analysis. It is designed to run on the same hardware as the World Wide Web Server, specifically the SUN Ultra450, allowing for efficient data processing and seamless integration with a graphical user interface (GUI) applet. This GUI provides users with an accessible platform to interact with the QA Server, enabling them to input circuit parameters and receive qualitative insights into circuit performance.
This innovative approach to circuit analysis enhances the designer's ability to explore various configurations and predict their behavior, ultimately leading to more informed design decisions in the early stages of the development process. The combination of qualitative analysis and user-friendly interfaces represents a significant advancement in the field of electronic circuit design, bridging the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application.At the beginning of a design process the designer has to verify which circuit structure is suitable for a given purpose. At this stage numerical and symbolic analysis are of little use. There are no numerical values for conventional simulation with programs like SPICE and a Symbolic Analysis would produce large symbolic expressions.
No further app roximation of these expressions can be performed due to the lack of numerical values. An experienced designer however, is able to analyze the behavior of an unknown circuit. The Qualitative Analysis reproduces this ability on computers by introducing qualitative states such as positive, zero, or negative. The applet is a graphical user interface to the QA Server. The QA Server performs the computations and runs on the same computer (, SUN Ultra450) as the WWW Server.
🔗 External reference
The design process of electronic circuits often begins with the selection of an appropriate circuit structure tailored to the intended application. During the initial stages, traditional numerical and symbolic analysis techniques may not be applicable due to the absence of specific numerical values. This limitation poses challenges for conventional simulation tools such as SPICE, which rely on numerical inputs to model circuit behavior accurately. Furthermore, symbolic analysis can result in complex expressions that are cumbersome and impractical to manage without numerical values for simplification.
To address these challenges, experienced designers utilize their intuition and knowledge to assess the behavior of unknown circuits qualitatively. This approach is formalized through Qualitative Analysis (QA), which introduces qualitative states (positive, zero, and negative) to characterize circuit components and their interactions. By employing these qualitative states, the analysis can yield insights into circuit behavior without requiring precise numerical data.
The QA Server is a dedicated computational engine that performs the necessary calculations to facilitate qualitative analysis. It is designed to run on the same hardware as the World Wide Web Server, specifically the SUN Ultra450, allowing for efficient data processing and seamless integration with a graphical user interface (GUI) applet. This GUI provides users with an accessible platform to interact with the QA Server, enabling them to input circuit parameters and receive qualitative insights into circuit performance.
This innovative approach to circuit analysis enhances the designer's ability to explore various configurations and predict their behavior, ultimately leading to more informed design decisions in the early stages of the development process. The combination of qualitative analysis and user-friendly interfaces represents a significant advancement in the field of electronic circuit design, bridging the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application.At the beginning of a design process the designer has to verify which circuit structure is suitable for a given purpose. At this stage numerical and symbolic analysis are of little use. There are no numerical values for conventional simulation with programs like SPICE and a Symbolic Analysis would produce large symbolic expressions.
No further app roximation of these expressions can be performed due to the lack of numerical values. An experienced designer however, is able to analyze the behavior of an unknown circuit. The Qualitative Analysis reproduces this ability on computers by introducing qualitative states such as positive, zero, or negative. The applet is a graphical user interface to the QA Server. The QA Server performs the computations and runs on the same computer (, SUN Ultra450) as the WWW Server.
🔗 External reference