rf detector electronic project circuit design using 2n2222 transistors
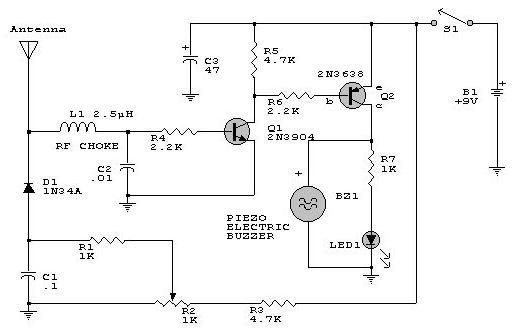
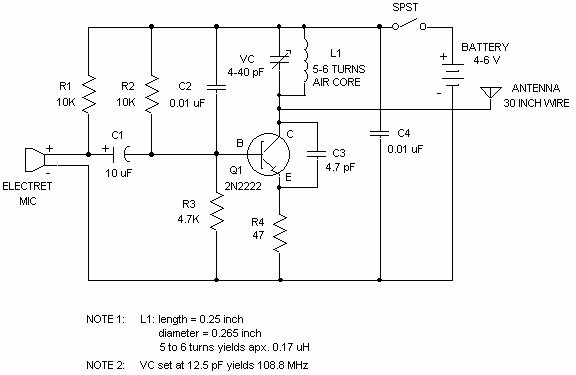
This electronic RF detector project is designed using common transistors and a few standard electronic components. The RF detector responds to RF signals below the standard broadcast band and well over 500 MHz, providing both visual and audible indications when a signal is received. By adjusting the bias of D2 with the R2 potentiometer, the circuit can detect both low-power and strong signals. The circuit can be powered using a simple 9-volt battery or any other 9-volt DC power supply. If the RF detector lacks sensitivity, a wideband RF amplifier can be connected between the antenna and the detector diode. It is essential to keep the leads of the diode and capacitor (C1) short to minimize stray inductance. The transistors used can be: 2N3906, 2N2907, or other PNP high-gain transistors for Q2, and PN2222A, 2N3904, or other NPN high-gain transistors for Q1.
This RF detector circuit utilizes a straightforward design that leverages common electronic components, making it accessible for hobbyists and engineers alike. The primary function of the circuit is to detect radio frequency signals across a broad frequency range, from below the standard AM broadcast band to frequencies exceeding 500 MHz. The inclusion of both visual and audible indicators enhances usability, allowing users to easily identify the presence of RF signals.
The circuit's sensitivity can be adjusted through the biasing of diode D2 via the potentiometer R2, enabling the detection of varying signal strengths. This versatility is particularly useful in applications where the RF signal may vary significantly in power. The power supply requirements are minimal, as the circuit operates effectively with a 9-volt battery or a similar DC power source, ensuring portability and ease of use.
For enhanced performance, particularly in environments with weak RF signals, the addition of a wideband RF amplifier is recommended. This amplifier should be connected between the antenna and the detector diode, which will significantly improve the circuit's sensitivity. Careful attention to the physical layout of the circuit is crucial; keeping the leads of the diode and capacitor (C1) short helps to reduce stray inductance, which can adversely affect performance and accuracy.
The choice of transistors is also important for optimizing the circuit's performance. The PNP transistors, such as the 2N3906 or 2N2907, are suitable for Q2, while NPN transistors like the PN2222A or 2N3904 serve well for Q1. These transistors are known for their high gain characteristics, which are essential for amplifying weak RF signals effectively. Overall, this RF detector circuit exemplifies a practical and efficient design suitable for a variety of RF detection applications.This electronic rf detector electronic project is designed using common transistors and other few common electronic parts. This rf detector responds to RF signals bellow the standard broadcast band to well over 500 MHz and provides an visual, and audible indication when the signal is received.
By adjusting the bias of D2 with the R2 potentiomete r the circuit can detect low power or strong signals. The circuit can be powered using a simple 9 volts battery or any other 9 volts DC power supply circuit. If the rf detector is not enough sensitive you can connect a good wideband RF amp between the antenna and the detector diode.
Keep diode and capacitor (C1) leads short to minimize stray inductance. The used transistors can be : 2N3906, 2N2907 or other PNP high gain transistor for Q2 and PN2222A, 2N3904 or other NPN high gain transistor for Q1. 🔗 External reference
This RF detector circuit utilizes a straightforward design that leverages common electronic components, making it accessible for hobbyists and engineers alike. The primary function of the circuit is to detect radio frequency signals across a broad frequency range, from below the standard AM broadcast band to frequencies exceeding 500 MHz. The inclusion of both visual and audible indicators enhances usability, allowing users to easily identify the presence of RF signals.
The circuit's sensitivity can be adjusted through the biasing of diode D2 via the potentiometer R2, enabling the detection of varying signal strengths. This versatility is particularly useful in applications where the RF signal may vary significantly in power. The power supply requirements are minimal, as the circuit operates effectively with a 9-volt battery or a similar DC power source, ensuring portability and ease of use.
For enhanced performance, particularly in environments with weak RF signals, the addition of a wideband RF amplifier is recommended. This amplifier should be connected between the antenna and the detector diode, which will significantly improve the circuit's sensitivity. Careful attention to the physical layout of the circuit is crucial; keeping the leads of the diode and capacitor (C1) short helps to reduce stray inductance, which can adversely affect performance and accuracy.
The choice of transistors is also important for optimizing the circuit's performance. The PNP transistors, such as the 2N3906 or 2N2907, are suitable for Q2, while NPN transistors like the PN2222A or 2N3904 serve well for Q1. These transistors are known for their high gain characteristics, which are essential for amplifying weak RF signals effectively. Overall, this RF detector circuit exemplifies a practical and efficient design suitable for a variety of RF detection applications.This electronic rf detector electronic project is designed using common transistors and other few common electronic parts. This rf detector responds to RF signals bellow the standard broadcast band to well over 500 MHz and provides an visual, and audible indication when the signal is received.
By adjusting the bias of D2 with the R2 potentiomete r the circuit can detect low power or strong signals. The circuit can be powered using a simple 9 volts battery or any other 9 volts DC power supply circuit. If the rf detector is not enough sensitive you can connect a good wideband RF amp between the antenna and the detector diode.
Keep diode and capacitor (C1) leads short to minimize stray inductance. The used transistors can be : 2N3906, 2N2907 or other PNP high gain transistor for Q2 and PN2222A, 2N3904 or other NPN high gain transistor for Q1. 🔗 External reference