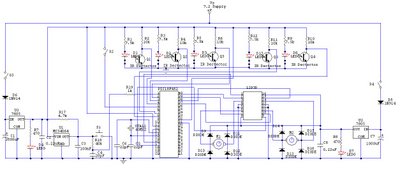
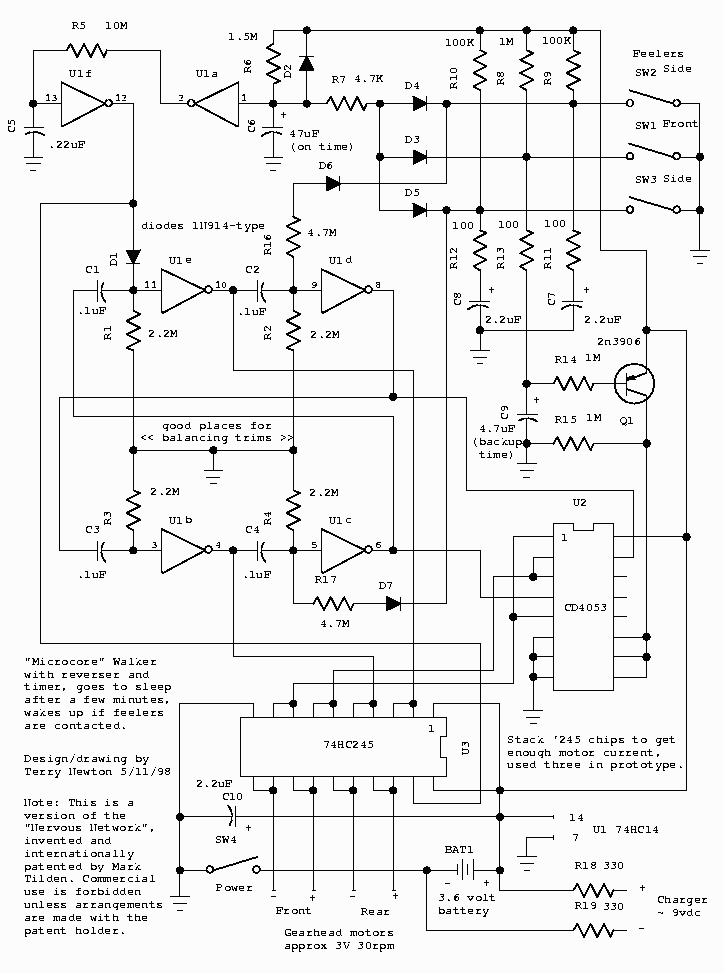
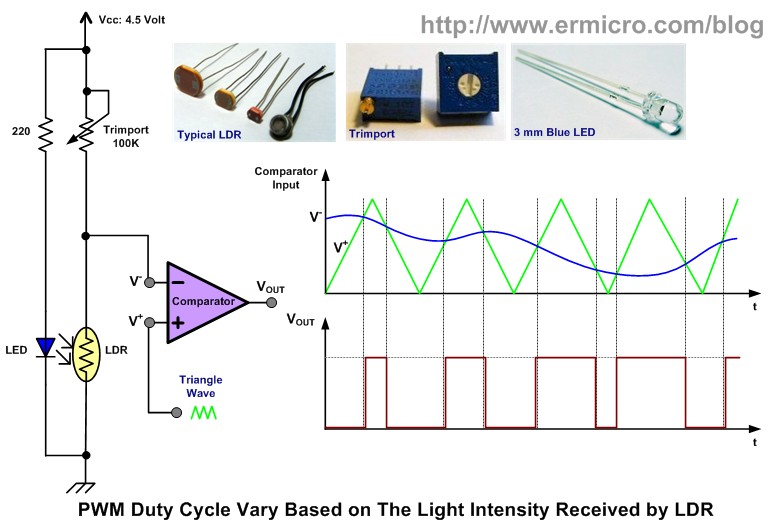
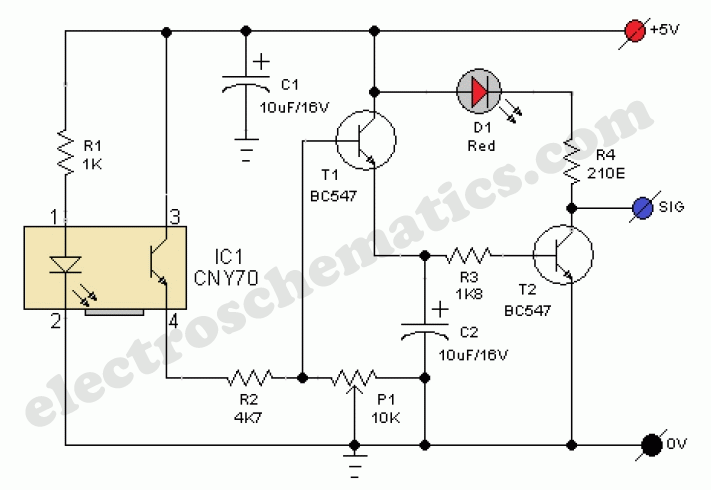
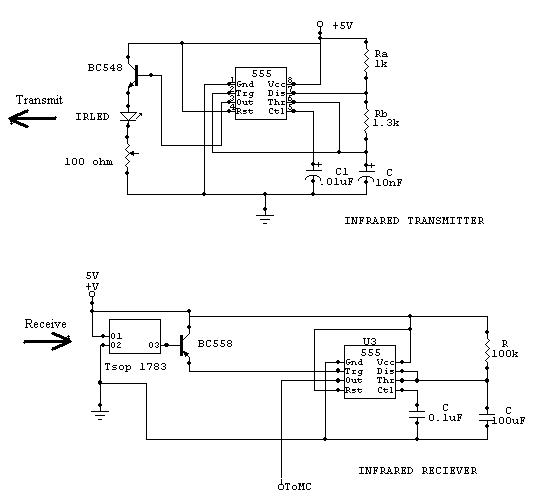
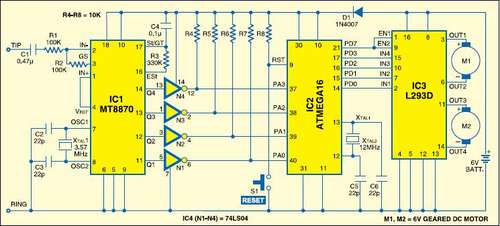
robot sense sensors
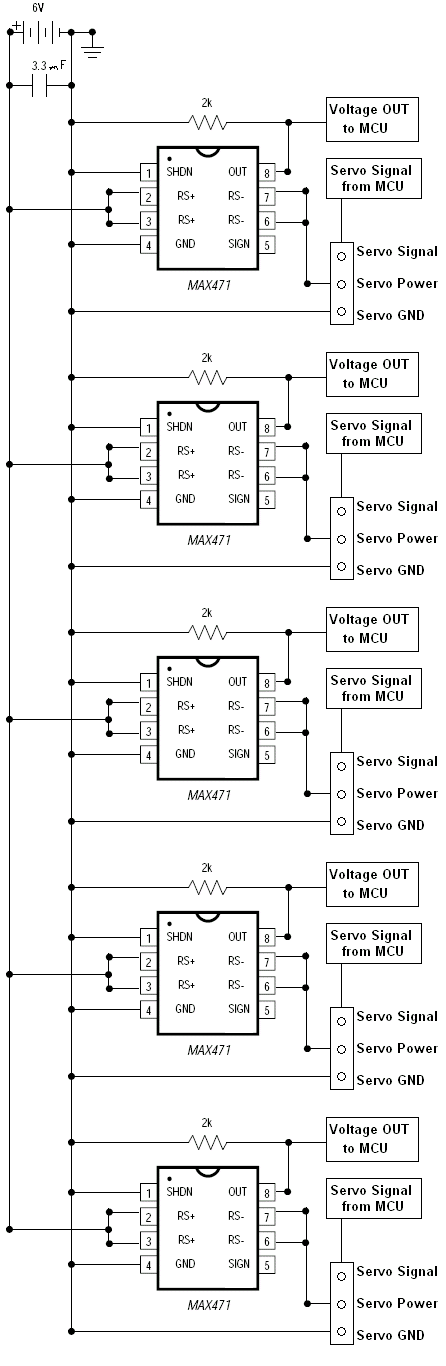
Sensors are utilized in various everyday objects, including touch-sensitive elevator buttons (tactile sensors) and lamps that adjust brightness through touch. The applications of sensors are vast, many of which are unknown to the general public. These applications span across industries such as automotive, machinery, aerospace, healthcare, manufacturing, and robotics. A sensor is defined as a device that receives and responds to specific stimuli.
Sensors play a crucial role in modern electronic systems, facilitating interaction between the user and the device. In the context of tactile sensors, these devices detect physical pressure or touch, converting mechanical force into an electrical signal. This process typically involves a resistive or capacitive mechanism, where the change in resistance or capacitance due to pressure is measured and interpreted by a microcontroller or processing unit.
In elevator systems, tactile sensors enhance user experience by providing a responsive interface. When a user presses a button, the sensor detects the force applied and activates the corresponding elevator function, such as calling the elevator to a specific floor. This interaction is not only intuitive but also contributes to the overall efficiency of the system.
In lighting applications, touch-sensitive lamps utilize capacitive sensing technology. When a user touches the base of the lamp, the sensor detects the change in capacitance caused by the proximity of the user's hand. This signal is processed to adjust the brightness level of the lamp, allowing for a seamless and user-friendly lighting experience.
Beyond consumer products, sensors are integral to various industrial applications. In automotive systems, sensors monitor critical parameters such as temperature, pressure, and position, enabling advanced features like automatic braking and stability control. In aerospace, sensors contribute to navigation and flight control systems, ensuring safety and efficiency in air travel.
In the medical field, sensors are employed in devices that monitor vital signs, providing real-time data that is essential for patient care. In manufacturing, sensors facilitate automation and quality control, ensuring that products meet specified standards. Robotics heavily relies on sensors for navigation and interaction with the environment, allowing for the development of sophisticated autonomous systems.
Overall, the versatility and significance of sensors in diverse applications underscore their importance in enhancing functionality, safety, and user experience across various sectors.Sensors are used in everyday objects such as touch-sensitive elevator buttons (tactile sensor) and lamps which dim or brighten by touching the base. There are also innumerable applications for sensors of which most people are never aware. Applications include cars, machines, aerospace, medicine, manufacturing and robotics. A sensor is a device which receives and responds.. 🔗 External reference
Sensors play a crucial role in modern electronic systems, facilitating interaction between the user and the device. In the context of tactile sensors, these devices detect physical pressure or touch, converting mechanical force into an electrical signal. This process typically involves a resistive or capacitive mechanism, where the change in resistance or capacitance due to pressure is measured and interpreted by a microcontroller or processing unit.
In elevator systems, tactile sensors enhance user experience by providing a responsive interface. When a user presses a button, the sensor detects the force applied and activates the corresponding elevator function, such as calling the elevator to a specific floor. This interaction is not only intuitive but also contributes to the overall efficiency of the system.
In lighting applications, touch-sensitive lamps utilize capacitive sensing technology. When a user touches the base of the lamp, the sensor detects the change in capacitance caused by the proximity of the user's hand. This signal is processed to adjust the brightness level of the lamp, allowing for a seamless and user-friendly lighting experience.
Beyond consumer products, sensors are integral to various industrial applications. In automotive systems, sensors monitor critical parameters such as temperature, pressure, and position, enabling advanced features like automatic braking and stability control. In aerospace, sensors contribute to navigation and flight control systems, ensuring safety and efficiency in air travel.
In the medical field, sensors are employed in devices that monitor vital signs, providing real-time data that is essential for patient care. In manufacturing, sensors facilitate automation and quality control, ensuring that products meet specified standards. Robotics heavily relies on sensors for navigation and interaction with the environment, allowing for the development of sophisticated autonomous systems.
Overall, the versatility and significance of sensors in diverse applications underscore their importance in enhancing functionality, safety, and user experience across various sectors.Sensors are used in everyday objects such as touch-sensitive elevator buttons (tactile sensor) and lamps which dim or brighten by touching the base. There are also innumerable applications for sensors of which most people are never aware. Applications include cars, machines, aerospace, medicine, manufacturing and robotics. A sensor is a device which receives and responds.. 🔗 External reference