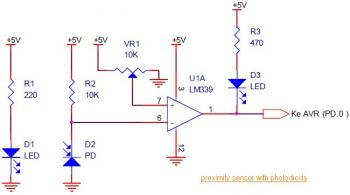
Robot shield for Arduino
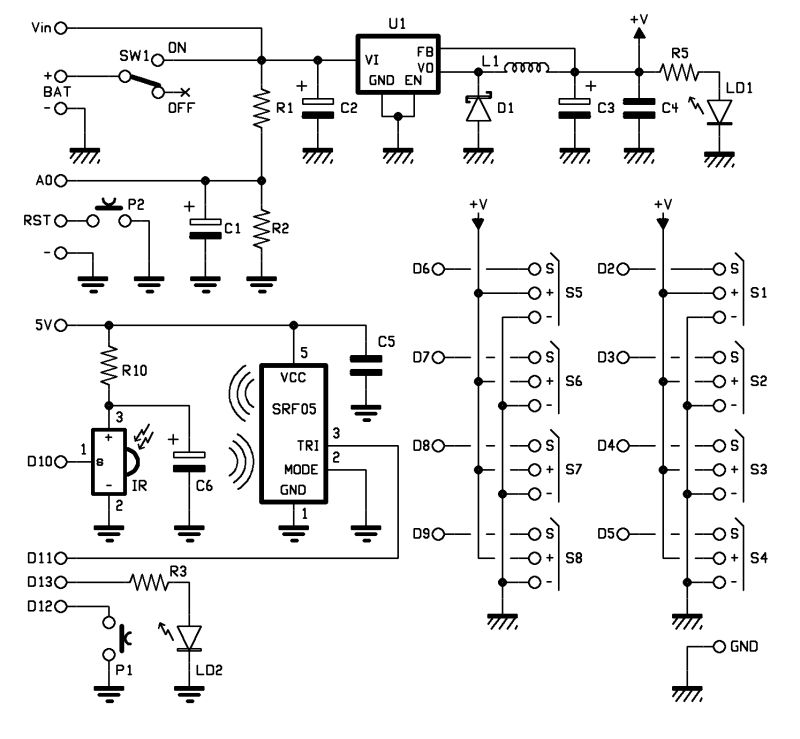
The objective of this post is to consolidate various robot designs and transform them into a new device featuring updated hardware and standardized software, specifically using Arduino, to enhance usability. These robots share three common elements: a mechanical structure, hardware, and software.
The proposed device aims to integrate several existing robotic designs into a unified platform. This new device will utilize a robust mechanical structure that can accommodate various components and configurations, allowing for flexibility in design and function. The hardware will be based on Arduino, providing a versatile and widely supported environment for development. This choice of microcontroller enables easy programming and modification, catering to users with different levels of expertise.
The software aspect will leverage the Arduino ecosystem, which includes a vast library of pre-existing code and tools that facilitate rapid development. The integration of these elements will not only streamline the building process but also ensure that users can easily customize their robotic devices according to specific requirements. The combination of a well-defined mechanical structure, reliable hardware, and accessible software will provide a comprehensive foundation for creating innovative robotic solutions that are both functional and user-friendly.
By focusing on these core components, the new device aims to simplify the robotics design process, making it more accessible to hobbyists, educators, and professionals alike. The result will be a versatile platform capable of supporting a wide range of robotic applications, from simple educational projects to complex automated systems.The idea behind this post is to bring together some robot designs and trasform them in a new device with new hardware and standard software (arduino of course) and so easier to use. These robots have three things in common: a mechanical structure, the hardware and the software. While the. 🔗 External reference
The proposed device aims to integrate several existing robotic designs into a unified platform. This new device will utilize a robust mechanical structure that can accommodate various components and configurations, allowing for flexibility in design and function. The hardware will be based on Arduino, providing a versatile and widely supported environment for development. This choice of microcontroller enables easy programming and modification, catering to users with different levels of expertise.
The software aspect will leverage the Arduino ecosystem, which includes a vast library of pre-existing code and tools that facilitate rapid development. The integration of these elements will not only streamline the building process but also ensure that users can easily customize their robotic devices according to specific requirements. The combination of a well-defined mechanical structure, reliable hardware, and accessible software will provide a comprehensive foundation for creating innovative robotic solutions that are both functional and user-friendly.
By focusing on these core components, the new device aims to simplify the robotics design process, making it more accessible to hobbyists, educators, and professionals alike. The result will be a versatile platform capable of supporting a wide range of robotic applications, from simple educational projects to complex automated systems.The idea behind this post is to bring together some robot designs and trasform them in a new device with new hardware and standard software (arduino of course) and so easier to use. These robots have three things in common: a mechanical structure, the hardware and the software. While the. 🔗 External reference