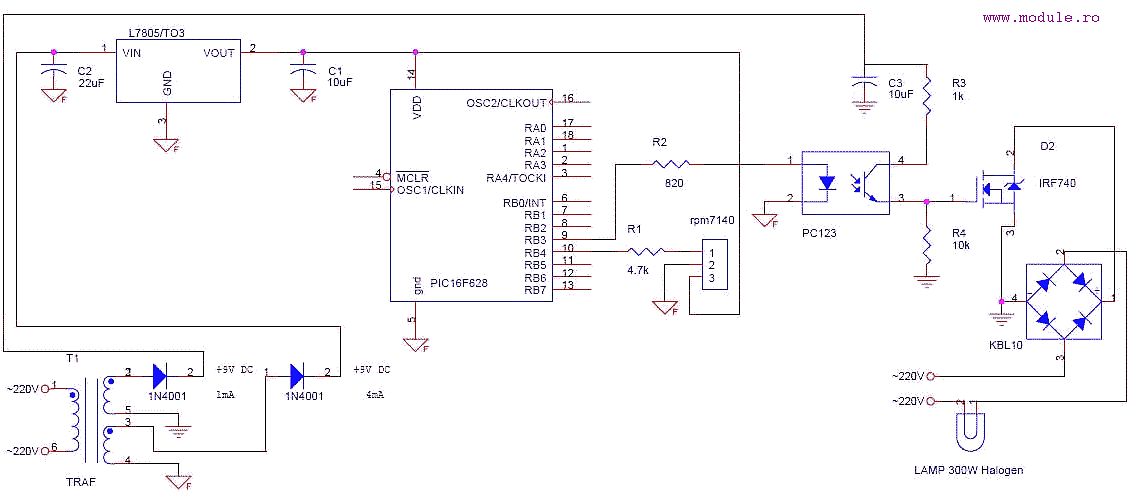
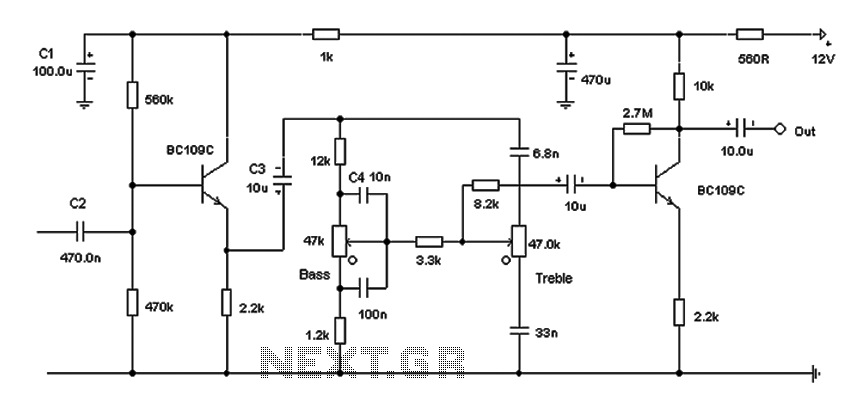
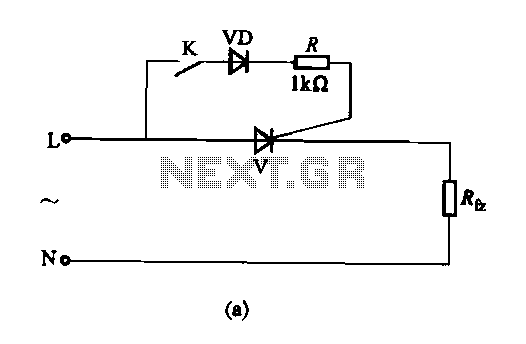
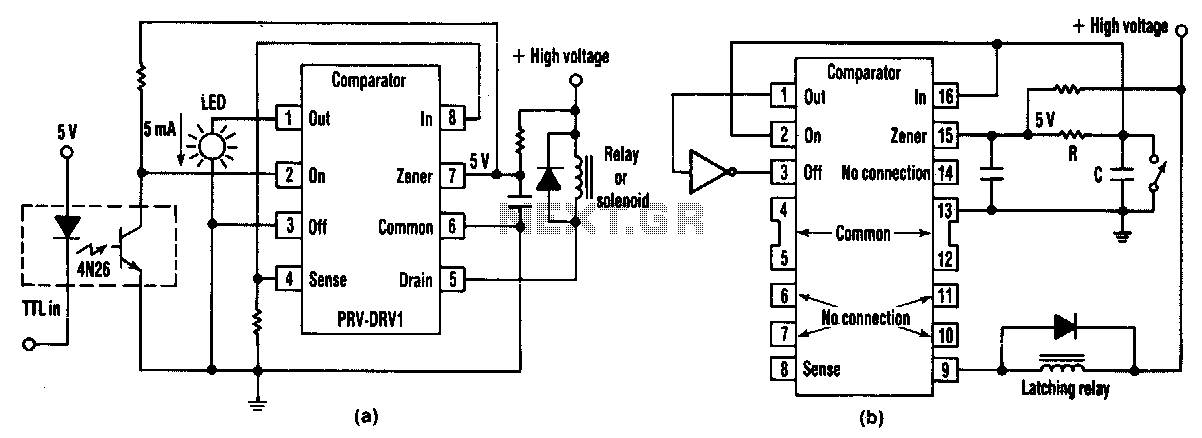
Satellite receiver antenna servo control circuit diagram
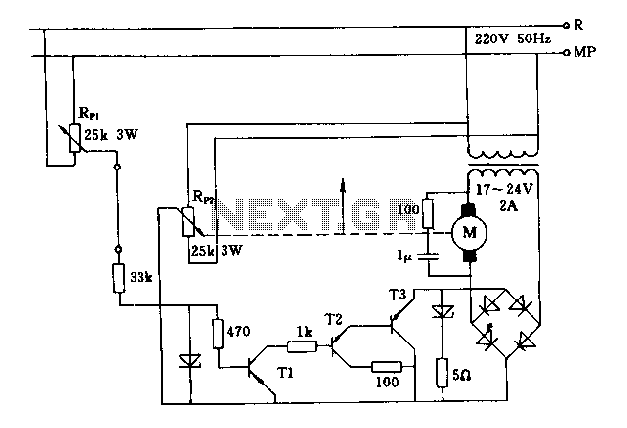
The FIG potentiometer RP2 has a sliding contact that is directly connected to the antenna. The system operates such that only when potentiometers RP1 and RP2 are positioned identically, do the non-conductive transistors and rectifier bridge remain off, resulting in no voltage being supplied to the motor, which keeps the antenna stationary. If the positions of the potentiometers differ, the motor or antenna will rotate in synchronization with the reference potentiometer.
The described circuit involves a dual potentiometer setup, specifically RP1 and RP2, which are critical for controlling the position of an antenna through a motor. The sliding contact of potentiometer RP2 is mechanically linked to the antenna, allowing for direct positional feedback.
In this configuration, both potentiometers must be aligned to ensure that the system remains inactive, meaning that no power is supplied to the motor. This is achieved through the use of non-conductive transistors that are controlled by the voltage output from the potentiometers. The rectifier bridge plays a vital role in converting AC to DC voltage, but in this scenario, it remains off when the potentiometers are not in the same position.
When the potentiometers are not aligned, the system activates the motor, allowing the antenna to adjust its position in accordance with the reference set by the potentiometers. This synchronous rotation mechanism ensures that the antenna can follow the desired positional reference accurately. The design emphasizes the importance of maintaining alignment between the two potentiometers to prevent unintended movement of the antenna, which could lead to misalignment in applications such as radio frequency transmission or reception.
This circuit exemplifies a feedback control system where precise adjustments can be made based on the relative positions of the potentiometers, ensuring that the antenna remains in the optimal position for its intended function. The careful arrangement of components, including the potentiometers, transistors, and rectifier bridge, is crucial for the reliable operation of the system.FIG potentiometer RP2 sliding contact with the axle shaft is directly connected to the antenna. Only when given potentiometer RP1 and RP2 refers in the same position, only non- conductive transistors, rectifier bridge off, no voltage on the motor, the antenna stationary, otherwise the motor or antenna will follow the reference potentiometer synchronous rotation.
The described circuit involves a dual potentiometer setup, specifically RP1 and RP2, which are critical for controlling the position of an antenna through a motor. The sliding contact of potentiometer RP2 is mechanically linked to the antenna, allowing for direct positional feedback.
In this configuration, both potentiometers must be aligned to ensure that the system remains inactive, meaning that no power is supplied to the motor. This is achieved through the use of non-conductive transistors that are controlled by the voltage output from the potentiometers. The rectifier bridge plays a vital role in converting AC to DC voltage, but in this scenario, it remains off when the potentiometers are not in the same position.
When the potentiometers are not aligned, the system activates the motor, allowing the antenna to adjust its position in accordance with the reference set by the potentiometers. This synchronous rotation mechanism ensures that the antenna can follow the desired positional reference accurately. The design emphasizes the importance of maintaining alignment between the two potentiometers to prevent unintended movement of the antenna, which could lead to misalignment in applications such as radio frequency transmission or reception.
This circuit exemplifies a feedback control system where precise adjustments can be made based on the relative positions of the potentiometers, ensuring that the antenna remains in the optimal position for its intended function. The careful arrangement of components, including the potentiometers, transistors, and rectifier bridge, is crucial for the reliable operation of the system.FIG potentiometer RP2 sliding contact with the axle shaft is directly connected to the antenna. Only when given potentiometer RP1 and RP2 refers in the same position, only non- conductive transistors, rectifier bridge off, no voltage on the motor, the antenna stationary, otherwise the motor or antenna will follow the reference potentiometer synchronous rotation.