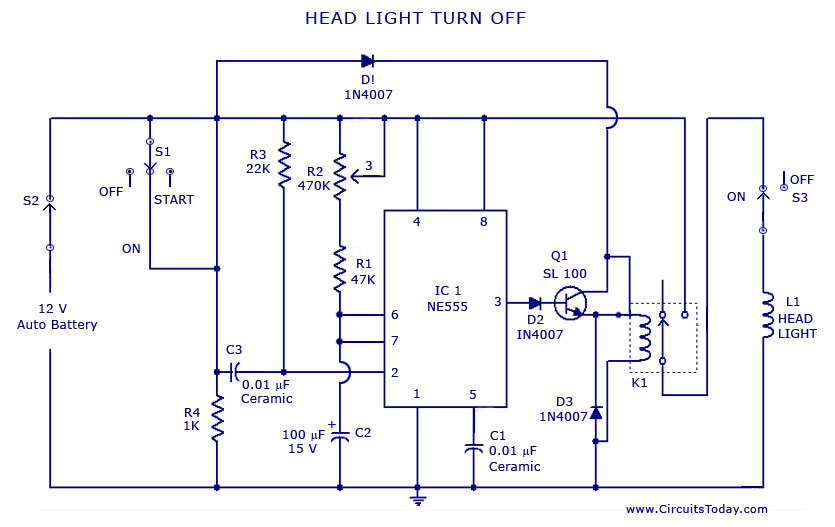
Security Light & Switch with PIR Sensor Update
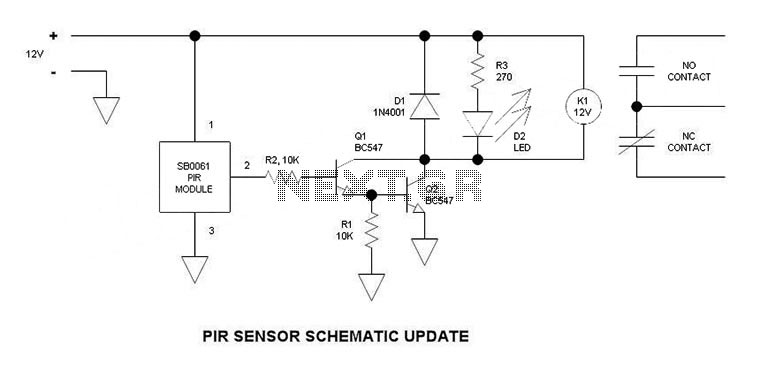
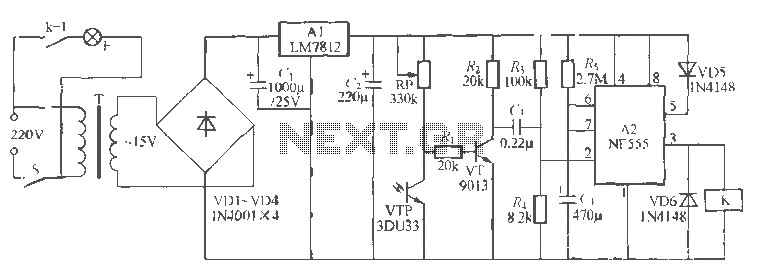
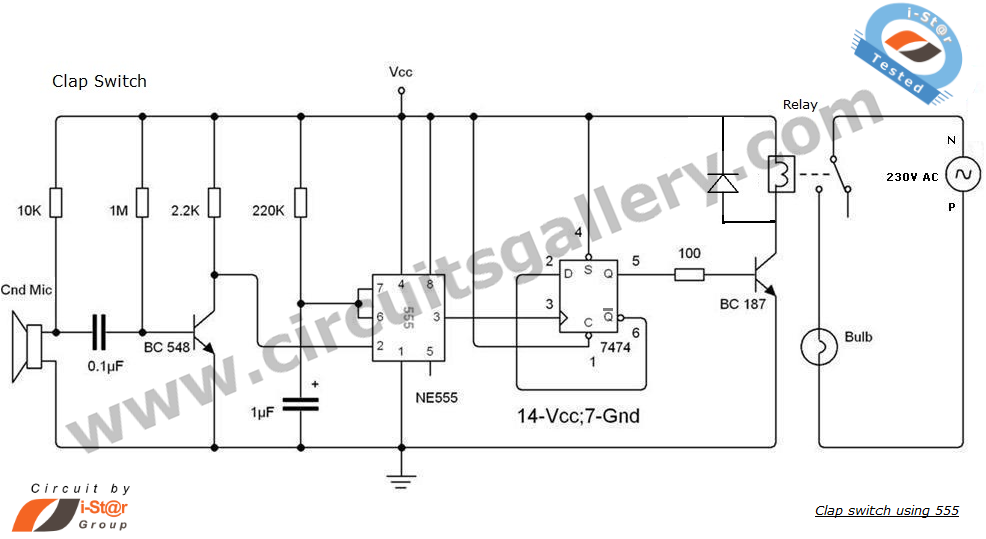
This is a simple update to Mr. Hareendran's PIR Sensor Security Light circuit. It has a shortcoming that limits the relay voltage to approximately 3.3V. While this may function with some 5V relays, it will not function with all.
The PIR (Passive Infrared) Sensor Security Light circuit is designed to activate a light source based on motion detection through infrared signals. The original design by Mr. Hareendran incorporates a relay that switches on the light when motion is detected. However, a critical limitation in the circuit arises from the relay voltage being restricted to approximately 3.3V. This voltage level may be sufficient for certain low-voltage relays, but it does not guarantee compatibility with all 5V relays, which are commonly used in similar applications.
To enhance the functionality and reliability of the circuit, it is recommended to redesign the relay driver stage to accommodate a higher voltage level. This can be achieved by integrating a transistor-based driver circuit that can handle the required current and voltage for 5V relays. The transistor can be used to switch the relay on and off based on the output from the PIR sensor, ensuring that the relay operates correctly regardless of its specifications.
Additionally, incorporating a flyback diode across the relay coil is advisable to protect the circuit from voltage spikes generated when the relay is deactivated. This diode will allow the inductive kickback to dissipate safely, preventing potential damage to the PIR sensor and other components in the circuit.
Overall, by addressing the voltage limitation and enhancing the relay driver stage, the PIR Sensor Security Light circuit can be made more versatile and reliable, ensuring compatibility with a wider range of relay types and improving the overall performance of the security light system.This is a simple update to Mr. Hareendran s PIR Sensor Security Light circuit. It has a shortcoming limits the relay voltage to approximately 3.3V. While this may function with some 5V relays, it will not function with all. The nature of.. 🔗 External reference
The PIR (Passive Infrared) Sensor Security Light circuit is designed to activate a light source based on motion detection through infrared signals. The original design by Mr. Hareendran incorporates a relay that switches on the light when motion is detected. However, a critical limitation in the circuit arises from the relay voltage being restricted to approximately 3.3V. This voltage level may be sufficient for certain low-voltage relays, but it does not guarantee compatibility with all 5V relays, which are commonly used in similar applications.
To enhance the functionality and reliability of the circuit, it is recommended to redesign the relay driver stage to accommodate a higher voltage level. This can be achieved by integrating a transistor-based driver circuit that can handle the required current and voltage for 5V relays. The transistor can be used to switch the relay on and off based on the output from the PIR sensor, ensuring that the relay operates correctly regardless of its specifications.
Additionally, incorporating a flyback diode across the relay coil is advisable to protect the circuit from voltage spikes generated when the relay is deactivated. This diode will allow the inductive kickback to dissipate safely, preventing potential damage to the PIR sensor and other components in the circuit.
Overall, by addressing the voltage limitation and enhancing the relay driver stage, the PIR Sensor Security Light circuit can be made more versatile and reliable, ensuring compatibility with a wider range of relay types and improving the overall performance of the security light system.This is a simple update to Mr. Hareendran s PIR Sensor Security Light circuit. It has a shortcoming limits the relay voltage to approximately 3.3V. While this may function with some 5V relays, it will not function with all. The nature of.. 🔗 External reference