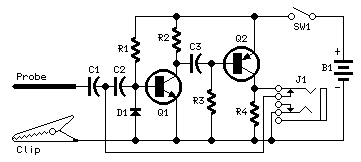
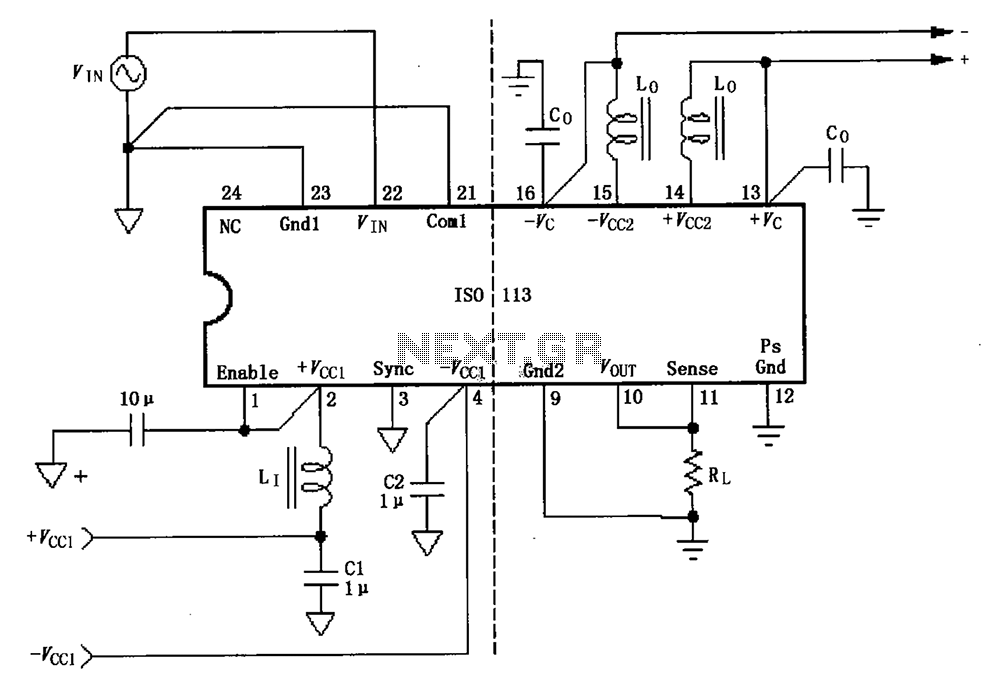
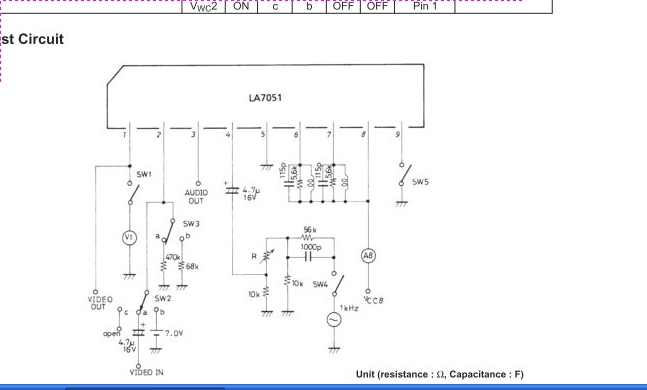
signal tracer and injector
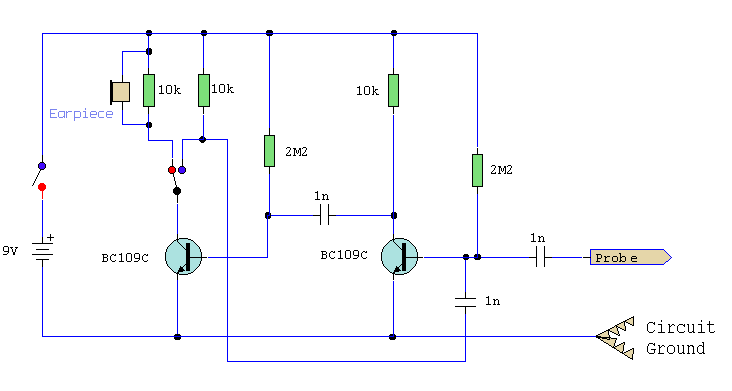
A simple test circuit to fault-find audio and radio equipment. It can be used to inject a square wave signal, rich in harmonics, or used with headphones as an audio tracer.
This test circuit is designed to assist in diagnosing faults in audio and radio equipment by providing a reliable method of signal injection. The circuit primarily generates a square wave signal, which is characterized by its sharp transitions and rich harmonic content. This feature allows for effective testing of the frequency response and linearity of audio devices, as the harmonics can reveal distortion and other anomalies in the equipment under test.
The circuit typically includes a function generator or an oscillator that produces the square wave output. This output can be connected to various points within the audio or radio circuit to evaluate performance. Additionally, the circuit may incorporate an adjustable amplitude control to vary the signal strength, ensuring compatibility with different devices and preventing damage to sensitive components.
For audio tracing, the circuit can be adapted to include a headphone output. This allows the technician to listen to the audio signals directly, facilitating the identification of faults such as intermittent connections, noise, or distortion. The use of headphones also provides a convenient way to monitor the audio signal without requiring additional equipment.
In summary, this simple test circuit serves as an essential tool for audio and radio equipment troubleshooting, offering both signal injection capabilities and audio monitoring through headphones. Its design emphasizes versatility and ease of use, making it suitable for both professional technicians and hobbyists alike.A simple test circuit to fault find audio and radio equipment. Can be used to inject a square wave signal, rich in harmonics, or used with headphones as an audio tracer.. 🔗 External reference
This test circuit is designed to assist in diagnosing faults in audio and radio equipment by providing a reliable method of signal injection. The circuit primarily generates a square wave signal, which is characterized by its sharp transitions and rich harmonic content. This feature allows for effective testing of the frequency response and linearity of audio devices, as the harmonics can reveal distortion and other anomalies in the equipment under test.
The circuit typically includes a function generator or an oscillator that produces the square wave output. This output can be connected to various points within the audio or radio circuit to evaluate performance. Additionally, the circuit may incorporate an adjustable amplitude control to vary the signal strength, ensuring compatibility with different devices and preventing damage to sensitive components.
For audio tracing, the circuit can be adapted to include a headphone output. This allows the technician to listen to the audio signals directly, facilitating the identification of faults such as intermittent connections, noise, or distortion. The use of headphones also provides a convenient way to monitor the audio signal without requiring additional equipment.
In summary, this simple test circuit serves as an essential tool for audio and radio equipment troubleshooting, offering both signal injection capabilities and audio monitoring through headphones. Its design emphasizes versatility and ease of use, making it suitable for both professional technicians and hobbyists alike.A simple test circuit to fault find audio and radio equipment. Can be used to inject a square wave signal, rich in harmonics, or used with headphones as an audio tracer.. 🔗 External reference