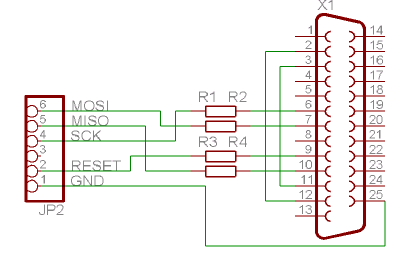
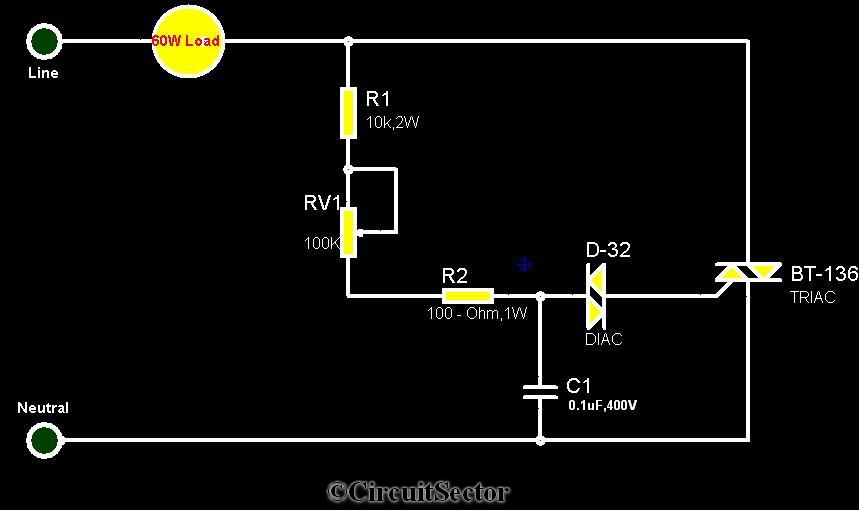
Sim card to PC adapter cable
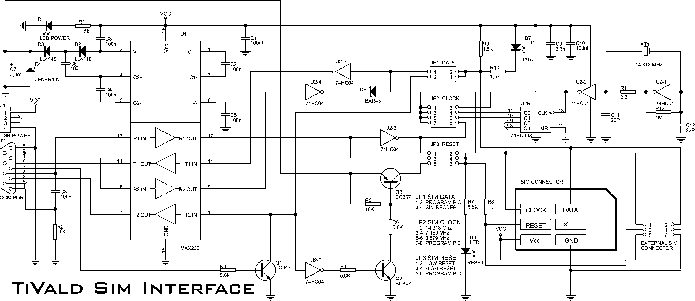
The electronic adapter derives its power supply from the VCC line of the smartcard reader device, or alternatively, an external 5 V supply can be utilized. The RST line of the card slot is connected to one of the TTL to RS-232 drivers in the MAX232, which interfaces with the DCD line. This setup enables the software and the reader to resynchronize easily in the event of a protocol error. The circuit can be tested using a terminal emulator and an external +5 V supply by disabling local echo. If every character typed appears immediately on the screen, the interface is functioning correctly. Additionally, this adapter circuit can facilitate a PC in monitoring the data traffic between a reader and an actual card. To achieve this, the real card and the adapter should be connected in parallel to the reader, ensuring that the PC software does not transmit any data.
The electronic adapter is designed to interface with smartcard readers, providing flexibility in power supply options and ensuring robust communication. It can be powered from the smartcard reader's VCC line, which simplifies the setup, or an external 5 V source can be employed if a more stable supply is required. The integration of the MAX232 device is critical for converting TTL logic levels to RS-232 standards, which is essential for reliable communication between the smartcard reader and the connected devices.
The connection of the RST line to the MAX232 allows for effective error handling and resynchronization. In scenarios where protocol errors occur, this setup ensures that the communication can be reestablished without manual intervention, thus enhancing the system's reliability. Testing the circuit with a terminal emulator is straightforward; by turning off local echo, the user can verify that the interface is operational based on the immediate display of typed characters.
Moreover, the adapter circuit serves a dual purpose by enabling a PC to monitor the data exchange between the smartcard reader and an actual smartcard. This feature is particularly useful for debugging and development purposes, as it allows for observation of the communication protocol in real-time. The requirement to connect the real card and the adapter in parallel to the reader ensures that the data flow remains intact while preventing any interference from the PC software. This capability makes the adapter a versatile tool in the field of smartcard technology and electronic communication.The adapter electronic gets its power supply from the smartcard reader device VCC line or you can use an external 5 V supply if you wish. The card slot"s RST line is connected using one of the TTL->RS-232 drivers in the MAX232 to DCD, so that the software and the reader can easily resynchronize in case of a protocol error.
You can test the circuit with a terminal emulator and external +5 V supply by switching of local echo if you still see every typed character immediately on the screen, the interface should be all right. You can also use this adapter circuit to allow a PC to listen to the data traffic between a reader and a real card.
Just connect the real card and the adapter parallel to the reader and don"t let the PC software transmit anything. 🔗 External reference
The electronic adapter is designed to interface with smartcard readers, providing flexibility in power supply options and ensuring robust communication. It can be powered from the smartcard reader's VCC line, which simplifies the setup, or an external 5 V source can be employed if a more stable supply is required. The integration of the MAX232 device is critical for converting TTL logic levels to RS-232 standards, which is essential for reliable communication between the smartcard reader and the connected devices.
The connection of the RST line to the MAX232 allows for effective error handling and resynchronization. In scenarios where protocol errors occur, this setup ensures that the communication can be reestablished without manual intervention, thus enhancing the system's reliability. Testing the circuit with a terminal emulator is straightforward; by turning off local echo, the user can verify that the interface is operational based on the immediate display of typed characters.
Moreover, the adapter circuit serves a dual purpose by enabling a PC to monitor the data exchange between the smartcard reader and an actual smartcard. This feature is particularly useful for debugging and development purposes, as it allows for observation of the communication protocol in real-time. The requirement to connect the real card and the adapter in parallel to the reader ensures that the data flow remains intact while preventing any interference from the PC software. This capability makes the adapter a versatile tool in the field of smartcard technology and electronic communication.The adapter electronic gets its power supply from the smartcard reader device VCC line or you can use an external 5 V supply if you wish. The card slot"s RST line is connected using one of the TTL->RS-232 drivers in the MAX232 to DCD, so that the software and the reader can easily resynchronize in case of a protocol error.
You can test the circuit with a terminal emulator and external +5 V supply by switching of local echo if you still see every typed character immediately on the screen, the interface should be all right. You can also use this adapter circuit to allow a PC to listen to the data traffic between a reader and a real card.
Just connect the real card and the adapter parallel to the reader and don"t let the PC software transmit anything. 🔗 External reference