Simple Audio Mixer Circuit
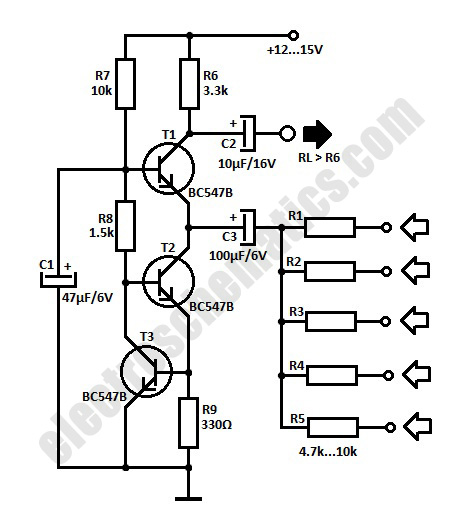
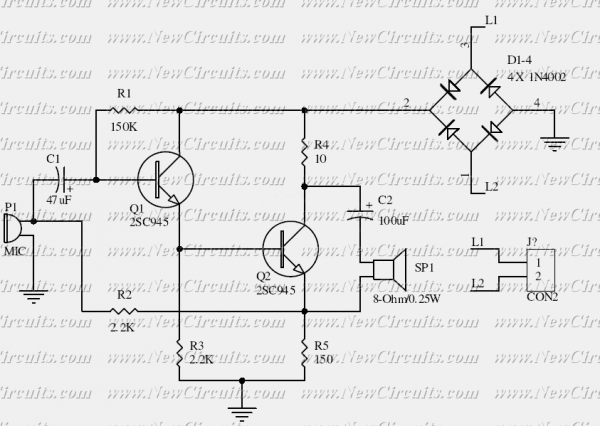
The simple audio mixer circuit is built on the common base principle, where input voltages are transformed into alternating currents which are summed to form the output.
The simple audio mixer circuit utilizes a common base configuration to achieve effective mixing of audio signals. In this design, multiple input voltage signals are fed into the circuit, where they are converted into alternating currents. The common base amplifier configuration is particularly advantageous for audio mixing applications due to its high input impedance and low output impedance, allowing for minimal loading on the preceding stages of the audio source.
The circuit typically consists of a transistor, which serves as the primary active component. The transistor is configured with its emitter connected to the ground, the base receiving the audio input signals, and the collector connected to the output. Each audio input is coupled to the base through capacitive coupling, ensuring only the AC components of the signals are processed while blocking any DC offset that might distort the output.
To achieve the summation of the input signals, resistive mixing can be employed at the collector. This involves connecting the outputs of the individual audio channels through resistors, which allows for the combination of the various audio signals into a single output. The values of these resistors are selected to control the mixing levels, thus enabling the user to adjust the balance between different audio sources.
The output of the circuit can be further processed or amplified before being sent to speakers or recording devices. Additional components such as capacitors may be included in the circuit to filter out unwanted frequency components, ensuring a cleaner audio output. The overall design is straightforward, making it suitable for applications in small audio mixing setups, such as home studios or portable audio equipment.The simple audio mixer circuit is built on common base principle, where input voltages are transformed in alternative currents wich are summed to form the.. 🔗 External reference
The simple audio mixer circuit utilizes a common base configuration to achieve effective mixing of audio signals. In this design, multiple input voltage signals are fed into the circuit, where they are converted into alternating currents. The common base amplifier configuration is particularly advantageous for audio mixing applications due to its high input impedance and low output impedance, allowing for minimal loading on the preceding stages of the audio source.
The circuit typically consists of a transistor, which serves as the primary active component. The transistor is configured with its emitter connected to the ground, the base receiving the audio input signals, and the collector connected to the output. Each audio input is coupled to the base through capacitive coupling, ensuring only the AC components of the signals are processed while blocking any DC offset that might distort the output.
To achieve the summation of the input signals, resistive mixing can be employed at the collector. This involves connecting the outputs of the individual audio channels through resistors, which allows for the combination of the various audio signals into a single output. The values of these resistors are selected to control the mixing levels, thus enabling the user to adjust the balance between different audio sources.
The output of the circuit can be further processed or amplified before being sent to speakers or recording devices. Additional components such as capacitors may be included in the circuit to filter out unwanted frequency components, ensuring a cleaner audio output. The overall design is straightforward, making it suitable for applications in small audio mixing setups, such as home studios or portable audio equipment.The simple audio mixer circuit is built on common base principle, where input voltages are transformed in alternative currents wich are summed to form the.. 🔗 External reference