Simple crowbar
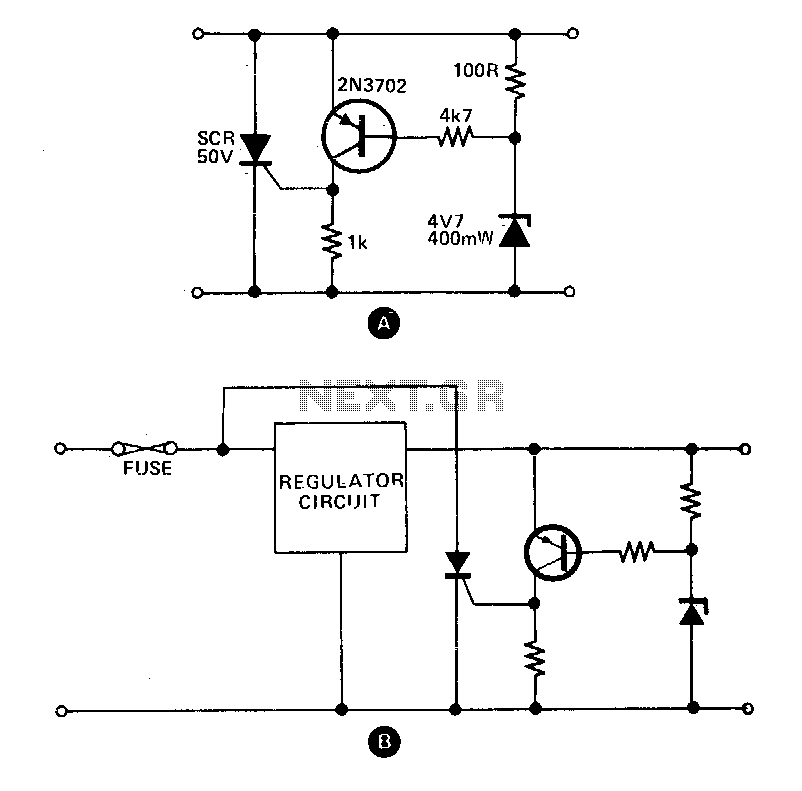
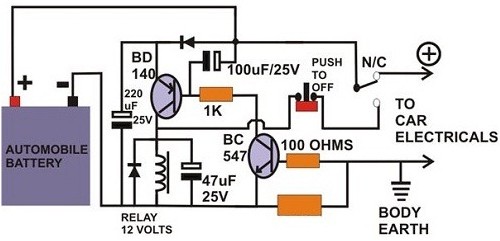
These circuits provide overvoltage protection in the event of a voltage regulator failure or the application of an external voltage. They are designed to be used with a power supply that includes some form of short circuit protection, such as foldback, current limiting, or a simple fuse. The most common application is in a 5 V logic supply, as TTL components are particularly susceptible to damage from excess voltage. The component values specified are for a 5 V supply; however, any supply voltage up to approximately 25 V can be protected by selecting an appropriate zener diode. When the supply voltage exceeds the zener voltage, the transistor activates and triggers the thyristor. This action effectively shorts the supply, preventing any further increase in voltage. In systems with only fuse protection, it is advisable to connect the thyristor to the regulator circuit when the crowbar function is activated. The thyristor should have a current rating approximately double that of the anticipated short circuit current and a maximum voltage rating higher than the supply voltage. The circuit can be reset by either turning off the power supply or by interrupting the thyristor circuit with a switch.
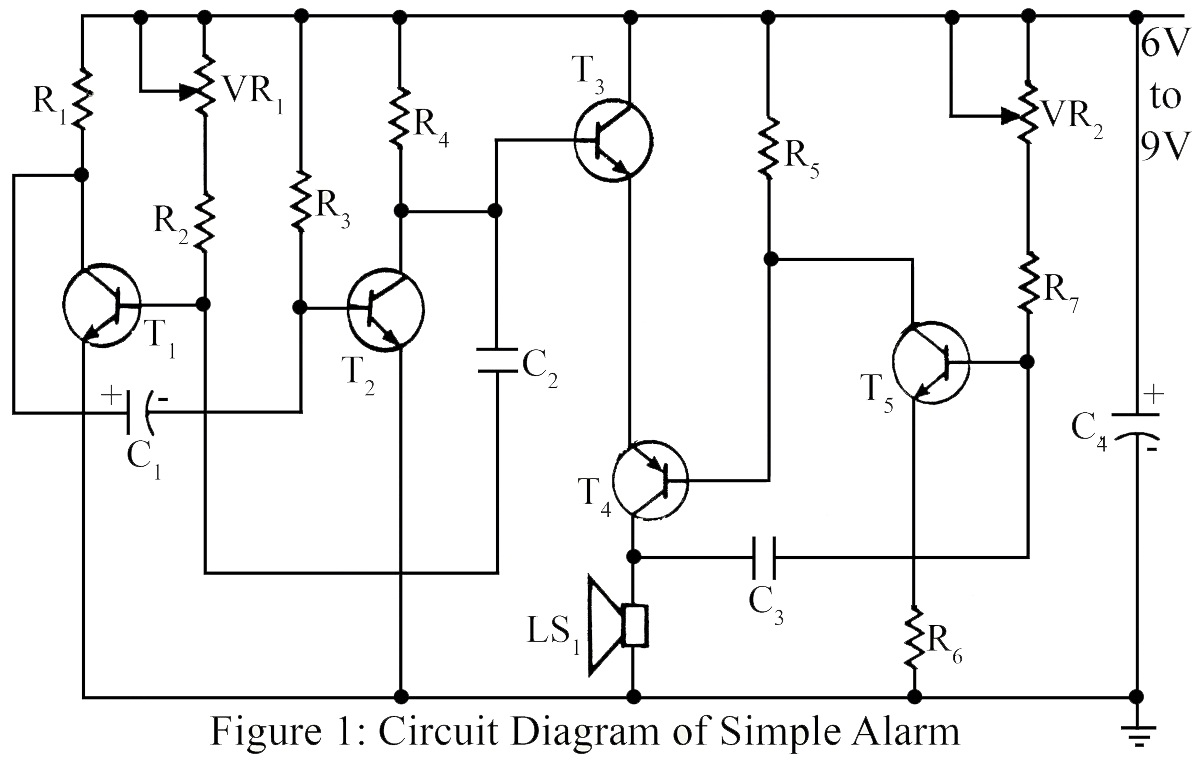
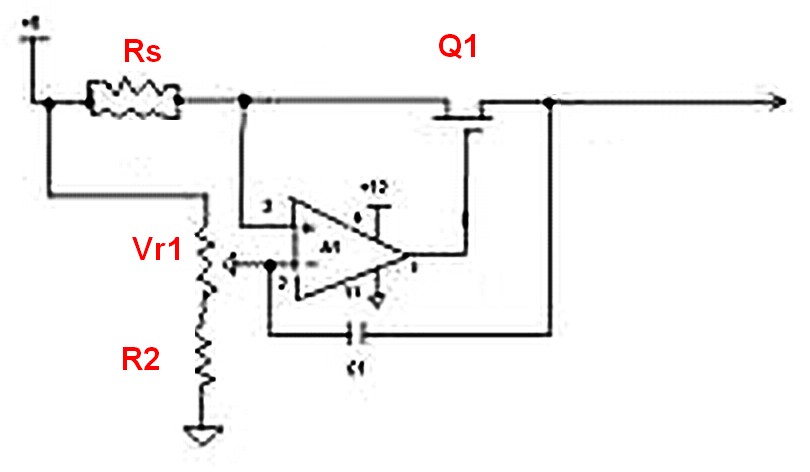
The overvoltage protection circuit is a critical component in safeguarding sensitive electronic devices from voltage spikes that could lead to catastrophic failures. The circuit typically comprises a zener diode, a transistor, and a thyristor, each playing a vital role in the operation of the protection mechanism.
The zener diode is selected based on the desired clamping voltage, which should correspond to the maximum allowable voltage for the application. When the input voltage exceeds this threshold, the zener diode conducts, allowing current to flow into the base of the transistor. This action turns on the transistor, which, in turn, triggers the thyristor. The thyristor acts as a switch that effectively short circuits the supply voltage, diverting the excess current away from the load and protecting the downstream components.
The selection of the thyristor is crucial; it must be rated for a current level that is at least twice the expected short circuit current to ensure reliable operation during fault conditions. Additionally, the thyristor's voltage rating must exceed the maximum voltage of the supply to prevent breakdown during operation.
In applications where the protection circuit is integrated with a fuse, it is essential to connect the thyristor in such a way that it operates in conjunction with the fuse, providing an additional layer of safety. This configuration ensures that, in the event of an overvoltage condition, the thyristor will activate before the fuse blows, thereby minimizing the risk of damage to the connected loads.
Resetting the circuit can be achieved through two methods: either by switching off the power supply, which cuts off the current flow and allows the thyristor to turn off, or by introducing a switch to break the thyristor circuit, thus allowing for manual reset. This design allows for efficient recovery from overvoltage conditions, ensuring the continued operation of the electronic system while maintaining the integrity of sensitive components.These circuits provide overvoltage protection in case of voltage regulator failure or application of an external voltage. Intended to be used with a supply offering some form of short circuit protection, either foldback, current limiting, or a simple fuse.
The most likely application is a 5 V logic supply, since TTL is easily damaged by excess voltage. The values chosen in A are for a 5 V supply, although any supply up to about 25 V can be protected by simply choosing the appropriate zener diode. When the supply voltage exceeds the zener voltage +0 V, the transistor turns on and fires the thyristor
This shorts out the supply, and prevents the voltage rising any further. In the case of a supply with only fuse protection, it is better to connect the thyristor the regulator circuit when the crowbar operates. The thyristor should have a current rating about twice the expected short circuit current and a maximum voltage greater than the supply voltage.
The circuit can be reset by either switching off the supply, or by breaking the thyristor circuit with a switch. 🔗 External reference
The overvoltage protection circuit is a critical component in safeguarding sensitive electronic devices from voltage spikes that could lead to catastrophic failures. The circuit typically comprises a zener diode, a transistor, and a thyristor, each playing a vital role in the operation of the protection mechanism.
The zener diode is selected based on the desired clamping voltage, which should correspond to the maximum allowable voltage for the application. When the input voltage exceeds this threshold, the zener diode conducts, allowing current to flow into the base of the transistor. This action turns on the transistor, which, in turn, triggers the thyristor. The thyristor acts as a switch that effectively short circuits the supply voltage, diverting the excess current away from the load and protecting the downstream components.
The selection of the thyristor is crucial; it must be rated for a current level that is at least twice the expected short circuit current to ensure reliable operation during fault conditions. Additionally, the thyristor's voltage rating must exceed the maximum voltage of the supply to prevent breakdown during operation.
In applications where the protection circuit is integrated with a fuse, it is essential to connect the thyristor in such a way that it operates in conjunction with the fuse, providing an additional layer of safety. This configuration ensures that, in the event of an overvoltage condition, the thyristor will activate before the fuse blows, thereby minimizing the risk of damage to the connected loads.
Resetting the circuit can be achieved through two methods: either by switching off the power supply, which cuts off the current flow and allows the thyristor to turn off, or by introducing a switch to break the thyristor circuit, thus allowing for manual reset. This design allows for efficient recovery from overvoltage conditions, ensuring the continued operation of the electronic system while maintaining the integrity of sensitive components.These circuits provide overvoltage protection in case of voltage regulator failure or application of an external voltage. Intended to be used with a supply offering some form of short circuit protection, either foldback, current limiting, or a simple fuse.
The most likely application is a 5 V logic supply, since TTL is easily damaged by excess voltage. The values chosen in A are for a 5 V supply, although any supply up to about 25 V can be protected by simply choosing the appropriate zener diode. When the supply voltage exceeds the zener voltage +0 V, the transistor turns on and fires the thyristor
This shorts out the supply, and prevents the voltage rising any further. In the case of a supply with only fuse protection, it is better to connect the thyristor the regulator circuit when the crowbar operates. The thyristor should have a current rating about twice the expected short circuit current and a maximum voltage greater than the supply voltage.
The circuit can be reset by either switching off the supply, or by breaking the thyristor circuit with a switch. 🔗 External reference