Simple Dc/Ac Inverter Circuit
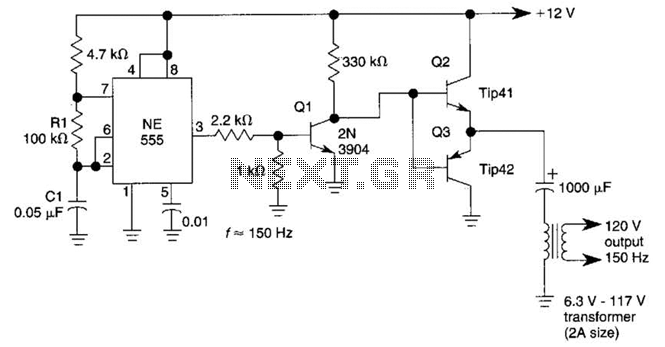
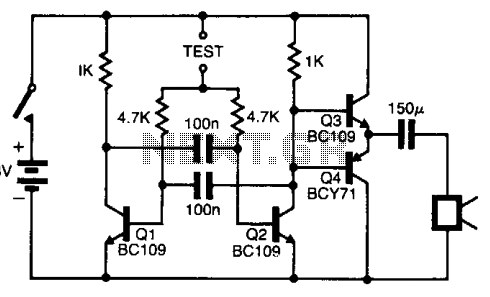
This DC-to-AC inverter utilizes the well-known 555 timer IC. A 555 oscillator circuit drives a buffer amplifier composed of transistors Q1, Q2, and Q3. The circuit operates at a frequency range of 150 to 160 Hz. Transformer T1 can be a 6.3-V or 12.6-V filament transformer, depending on the application. The operating frequency can be adjusted by modifying the values of resistor R1 and/or capacitor C1.
The circuit functions by converting direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC) using the 555 timer as an oscillator. The 555 timer is configured in astable mode, generating a square wave output that oscillates between high and low states. This output drives the buffer amplifier, where transistors Q1, Q2, and Q3 amplify the signal to a suitable level for driving the transformer.
The choice of transformer T1 is critical, as it determines the output voltage and current characteristics of the inverter. A 6.3-V transformer is typically used for low-power applications, while a 12.6-V transformer can be employed for higher power needs. The output frequency of the inverter is predominantly determined by the timing components R1 and C1. By adjusting these components, the user can fine-tune the frequency to match specific requirements of the load being powered.
The design of this inverter is advantageous for applications requiring low-cost and lightweight solutions for AC power generation from a DC source. It is commonly used in small electronic devices, battery-operated equipment, and other applications where a compact inverter is necessary. The simplicity of the circuit allows for easy troubleshooting and modifications, making it a popular choice among hobbyists and engineers alike. This dc-to-ac inverter is based on the popular 555. A 555 oscillator circuit drives a buffer amplifier consisting of Ql, Q2, and Q3. The circuit operates at 150 to 160 Hz. Tl can be a 6.3-V or 12.6-V filament transformer as applicable. The frequency can be changed by changing the values of Rl and/or Cl. 🔗 External reference
The circuit functions by converting direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC) using the 555 timer as an oscillator. The 555 timer is configured in astable mode, generating a square wave output that oscillates between high and low states. This output drives the buffer amplifier, where transistors Q1, Q2, and Q3 amplify the signal to a suitable level for driving the transformer.
The choice of transformer T1 is critical, as it determines the output voltage and current characteristics of the inverter. A 6.3-V transformer is typically used for low-power applications, while a 12.6-V transformer can be employed for higher power needs. The output frequency of the inverter is predominantly determined by the timing components R1 and C1. By adjusting these components, the user can fine-tune the frequency to match specific requirements of the load being powered.
The design of this inverter is advantageous for applications requiring low-cost and lightweight solutions for AC power generation from a DC source. It is commonly used in small electronic devices, battery-operated equipment, and other applications where a compact inverter is necessary. The simplicity of the circuit allows for easy troubleshooting and modifications, making it a popular choice among hobbyists and engineers alike. This dc-to-ac inverter is based on the popular 555. A 555 oscillator circuit drives a buffer amplifier consisting of Ql, Q2, and Q3. The circuit operates at 150 to 160 Hz. Tl can be a 6.3-V or 12.6-V filament transformer as applicable. The frequency can be changed by changing the values of Rl and/or Cl. 🔗 External reference