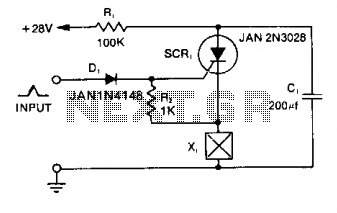
simple dimmer circuit
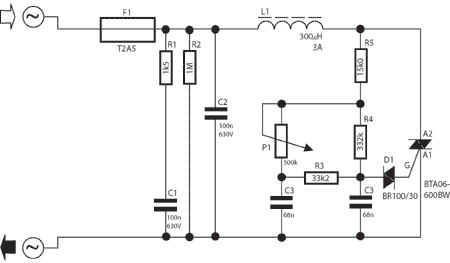
A potentiometer regulates the firing point of the triac. Capacitor C4 is charged through resistors R3, R4, P1, and R5. After a specific duration, determined by the potentiometer setting, the charge in C4 becomes sufficient for the diac D to begin conducting, resulting in a firing pulse being sent to the gate of the triac. As a result, the triac becomes conductive, allowing power to flow from the dimmer to the tungsten or LED lamp.
The described circuit employs a triac as a key component for controlling the power supplied to a load, such as a tungsten or LED lamp. The operation begins with the potentiometer, which adjusts the resistance in the circuit. This adjustment influences the charge time of capacitor C4, which is critical for the timing of the firing pulse. The resistors R3, R4, and R5, along with the potentiometer P1, form a voltage divider network that determines the charging rate of C4.
Once the voltage across C4 reaches a threshold level, the diac D transitions from a non-conductive to a conductive state. This transition generates a pulse that triggers the gate of the triac. The triac, once triggered, enters a conductive state and allows current to flow to the load, effectively controlling the power delivered to the lamp. The design enables smooth dimming of the light output by varying the phase angle of the AC waveform delivered to the lamp.
The circuit's performance can be affected by the values of the resistors and the capacitor, which need to be carefully selected to achieve the desired dimming range and response time. Additionally, the characteristics of the lamp (tungsten or LED) will influence the overall behavior of the circuit, particularly regarding the minimum load required for stable operation. Proper thermal management and component ratings are essential to ensure reliability and prevent overheating during extended use.A potentiometer is controlling the firing point of the triac. Capacitor C4 is charged via resistors R3, R4, P1, and R5. After a certain time, dependant on the potentiometer, the charge contained in C4 is large enough for the dimmers diac D to start conducting, so that a firing pulse is applied to the gate of the triac. Consequently the triac conducts and power is transferred from the dimmer to the tungsten or LED lamp.
. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit employs a triac as a key component for controlling the power supplied to a load, such as a tungsten or LED lamp. The operation begins with the potentiometer, which adjusts the resistance in the circuit. This adjustment influences the charge time of capacitor C4, which is critical for the timing of the firing pulse. The resistors R3, R4, and R5, along with the potentiometer P1, form a voltage divider network that determines the charging rate of C4.
Once the voltage across C4 reaches a threshold level, the diac D transitions from a non-conductive to a conductive state. This transition generates a pulse that triggers the gate of the triac. The triac, once triggered, enters a conductive state and allows current to flow to the load, effectively controlling the power delivered to the lamp. The design enables smooth dimming of the light output by varying the phase angle of the AC waveform delivered to the lamp.
The circuit's performance can be affected by the values of the resistors and the capacitor, which need to be carefully selected to achieve the desired dimming range and response time. Additionally, the characteristics of the lamp (tungsten or LED) will influence the overall behavior of the circuit, particularly regarding the minimum load required for stable operation. Proper thermal management and component ratings are essential to ensure reliability and prevent overheating during extended use.A potentiometer is controlling the firing point of the triac. Capacitor C4 is charged via resistors R3, R4, P1, and R5. After a certain time, dependant on the potentiometer, the charge contained in C4 is large enough for the dimmers diac D to start conducting, so that a firing pulse is applied to the gate of the triac. Consequently the triac conducts and power is transferred from the dimmer to the tungsten or LED lamp.
. 🔗 External reference