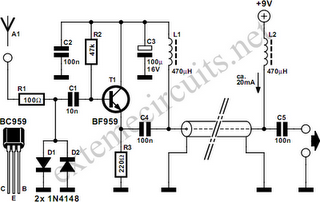
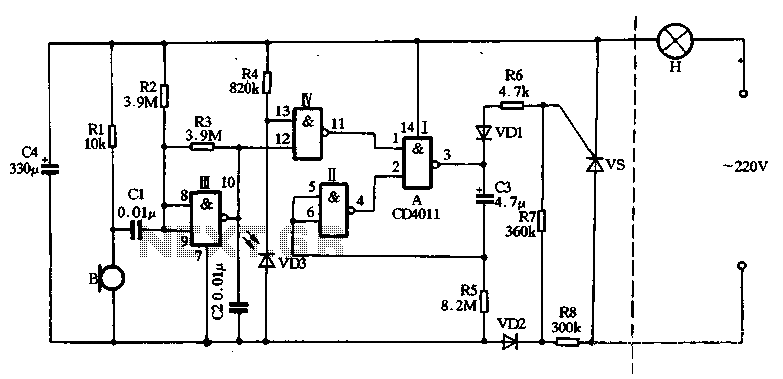
RF Probe Circuit
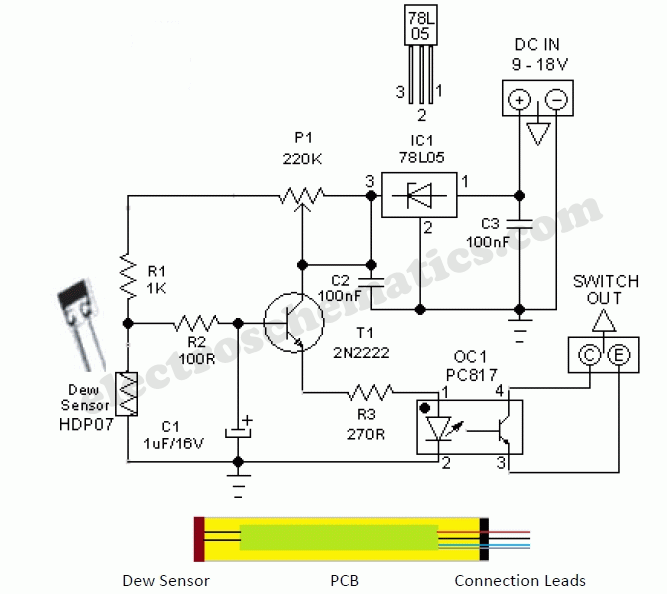
An RF probe is a circuit designed for testing equipment that converts high-frequency signals into DC voltage. This conversion facilitates the measurement of RF voltages for testing or adjusting transmitters, receivers, and modulators. The RF probe circuit outlined here is suitable for signals within the frequency range of approximately 100 kHz to 1000 MHz. Although the diode utilized can theoretically operate up to 3 GHz, the impedance of the ground connection may negatively impact measurements at very high frequencies. It is also important to use this probe exclusively on low RF power.
The RF probe circuit typically consists of a diode, a resistor, and a capacitor arranged in a configuration that allows for efficient signal detection and conversion. The diode serves as the primary component for rectifying the incoming RF signal. When the RF signal is applied to the circuit, the diode conducts during the positive half-cycle, allowing current to flow through the load resistor. The resulting voltage across the resistor is proportional to the RF signal's amplitude.
To enhance the circuit's performance, especially at higher frequencies, a bypass capacitor is often included in parallel with the load resistor. This capacitor helps to stabilize the DC voltage output by filtering out any high-frequency noise that could affect the measurement accuracy. Additionally, the choice of components, such as the diode type and the resistor value, is crucial for optimizing the probe's response across the desired frequency range.
For practical applications, the RF probe can be connected to an oscilloscope or a voltmeter to visualize or quantify the rectified signal. Calibration of the probe may be necessary to ensure accurate voltage readings, particularly when measuring signals at the upper end of the specified frequency range. It is also essential to maintain proper grounding techniques to minimize interference and ensure reliable measurements.
In summary, the RF probe circuit is a valuable tool for engineers and technicians working with RF equipment, providing a straightforward method for measuring RF voltages across a wide frequency spectrum while emphasizing the importance of component selection and proper usage to maintain measurement integrity.A RF probe is a circuit for testing equipment that converts a high frequency signal into a DC voltage. In this way it is very easy to measure RF voltages for either testing or adjustments of transmitters, receivers, modulators.
The RF probe circuit described here is suitable for signals with the frequency range from about 100 kHz to 1000 MHz. Alth ough the diode used here can, in principle, go up to 3 GHz, the impedance of the ground connection will adversely influence the measurement at very high frequencies. Also, please keep in mind to use this probe only on low RF power. 🔗 External reference
The RF probe circuit typically consists of a diode, a resistor, and a capacitor arranged in a configuration that allows for efficient signal detection and conversion. The diode serves as the primary component for rectifying the incoming RF signal. When the RF signal is applied to the circuit, the diode conducts during the positive half-cycle, allowing current to flow through the load resistor. The resulting voltage across the resistor is proportional to the RF signal's amplitude.
To enhance the circuit's performance, especially at higher frequencies, a bypass capacitor is often included in parallel with the load resistor. This capacitor helps to stabilize the DC voltage output by filtering out any high-frequency noise that could affect the measurement accuracy. Additionally, the choice of components, such as the diode type and the resistor value, is crucial for optimizing the probe's response across the desired frequency range.
For practical applications, the RF probe can be connected to an oscilloscope or a voltmeter to visualize or quantify the rectified signal. Calibration of the probe may be necessary to ensure accurate voltage readings, particularly when measuring signals at the upper end of the specified frequency range. It is also essential to maintain proper grounding techniques to minimize interference and ensure reliable measurements.
In summary, the RF probe circuit is a valuable tool for engineers and technicians working with RF equipment, providing a straightforward method for measuring RF voltages across a wide frequency spectrum while emphasizing the importance of component selection and proper usage to maintain measurement integrity.A RF probe is a circuit for testing equipment that converts a high frequency signal into a DC voltage. In this way it is very easy to measure RF voltages for either testing or adjustments of transmitters, receivers, modulators.
The RF probe circuit described here is suitable for signals with the frequency range from about 100 kHz to 1000 MHz. Alth ough the diode used here can, in principle, go up to 3 GHz, the impedance of the ground connection will adversely influence the measurement at very high frequencies. Also, please keep in mind to use this probe only on low RF power. 🔗 External reference