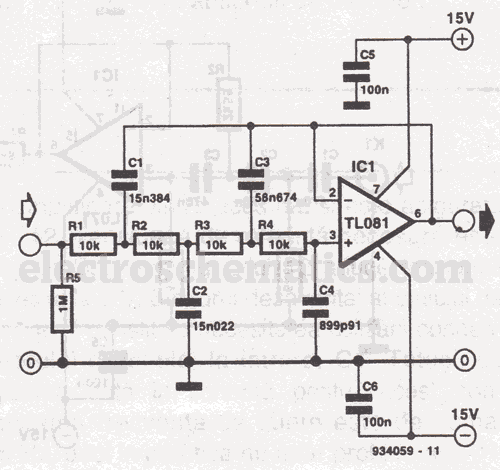
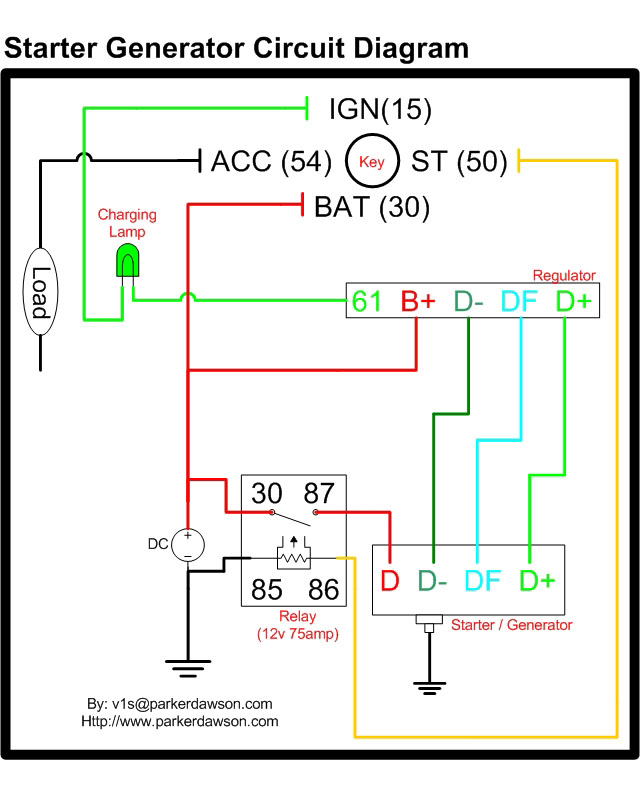
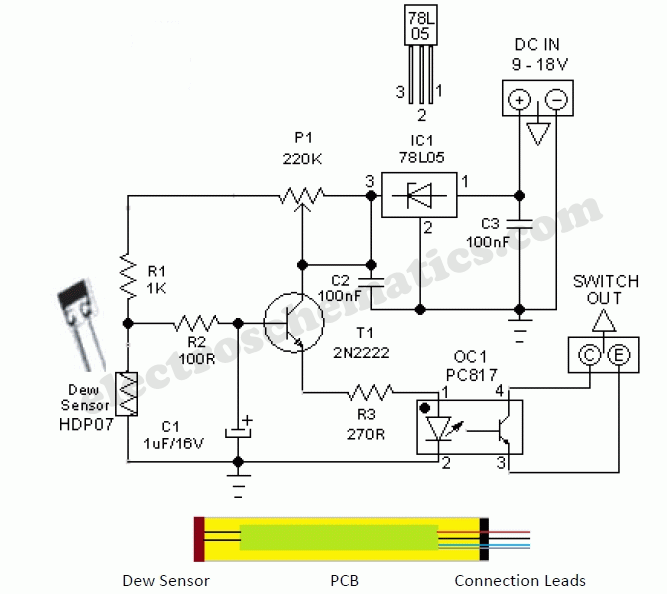
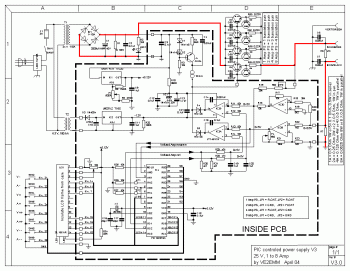
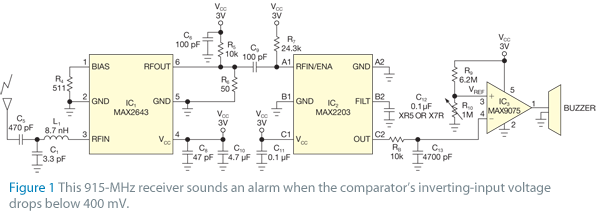
Single nozzle tracker circuit diagram
The calibration circuit operates in inject mode, generating a square wave output in the audio range, where power harmonics can be detected at several Hertz. In tracking mode, the amplifier detects non-linear operation by filtering a modulated RF signal using a 0.01 µF capacitor before sending it to the headset.
The circuit is designed to facilitate audio signal calibration and modulation detection. In inject mode, the calibration circuit produces a square wave output within the audio frequency range, allowing for the analysis and detection of harmonic distortions. These harmonics, which manifest as variations in frequency, can be observed at low frequencies, typically in the range of several Hertz. This feature is crucial for evaluating the performance of audio systems and ensuring they operate within specified parameters.
In tracking mode, the circuit transitions to detect non-linear operations of the amplifier. This is achieved by applying a 0.01 µF capacitor as a filter for the modulated RF signal. The capacitor serves to isolate the desired frequency components while attenuating unwanted high-frequency noise, thus enhancing the clarity of the received signal. The filtered signal is then routed to a headset, allowing for real-time monitoring of the audio output. This mode is particularly useful for applications requiring the detection of signal variations and quality assessment in communication systems.
Overall, the circuit's dual functionality in inject and tracking modes enables comprehensive testing and evaluation of audio and RF signal integrity, making it a valuable tool in electronic engineering applications. Circuit Description: Under inject mode, the calibration circuit provided in the audio range square wave output, power harmonics can be heard several Hertz. Under Tracking mode, the amplifier non-linear operation detecting modulated RF signal by 0.01 F capacitor filter and then input to the headset.
The circuit is designed to facilitate audio signal calibration and modulation detection. In inject mode, the calibration circuit produces a square wave output within the audio frequency range, allowing for the analysis and detection of harmonic distortions. These harmonics, which manifest as variations in frequency, can be observed at low frequencies, typically in the range of several Hertz. This feature is crucial for evaluating the performance of audio systems and ensuring they operate within specified parameters.
In tracking mode, the circuit transitions to detect non-linear operations of the amplifier. This is achieved by applying a 0.01 µF capacitor as a filter for the modulated RF signal. The capacitor serves to isolate the desired frequency components while attenuating unwanted high-frequency noise, thus enhancing the clarity of the received signal. The filtered signal is then routed to a headset, allowing for real-time monitoring of the audio output. This mode is particularly useful for applications requiring the detection of signal variations and quality assessment in communication systems.
Overall, the circuit's dual functionality in inject and tracking modes enables comprehensive testing and evaluation of audio and RF signal integrity, making it a valuable tool in electronic engineering applications. Circuit Description: Under inject mode, the calibration circuit provided in the audio range square wave output, power harmonics can be heard several Hertz. Under Tracking mode, the amplifier non-linear operation detecting modulated RF signal by 0.01 F capacitor filter and then input to the headset.