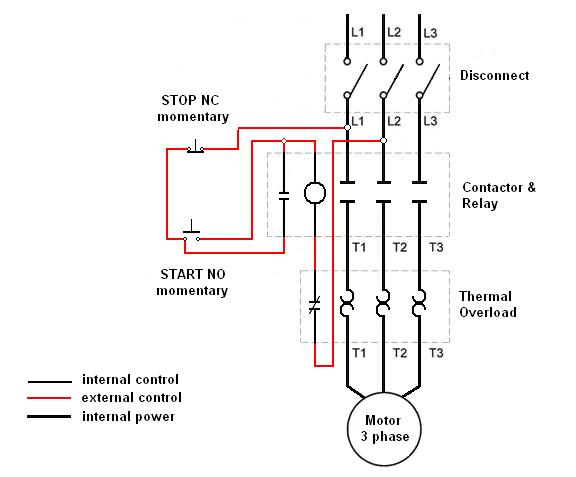
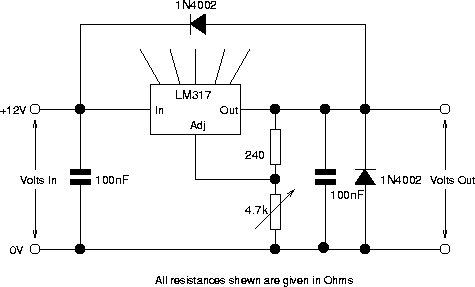
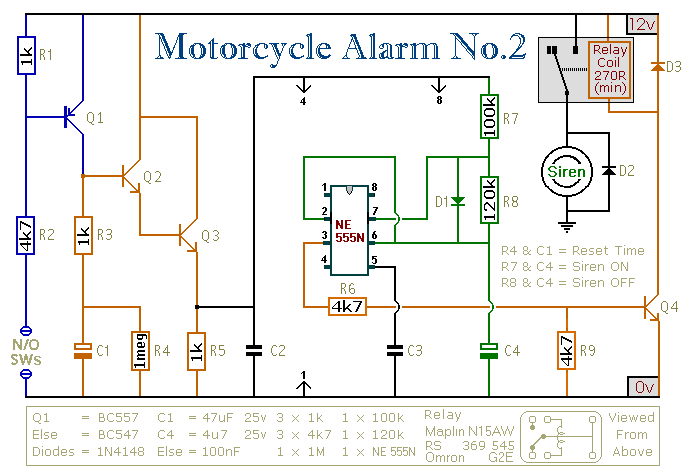
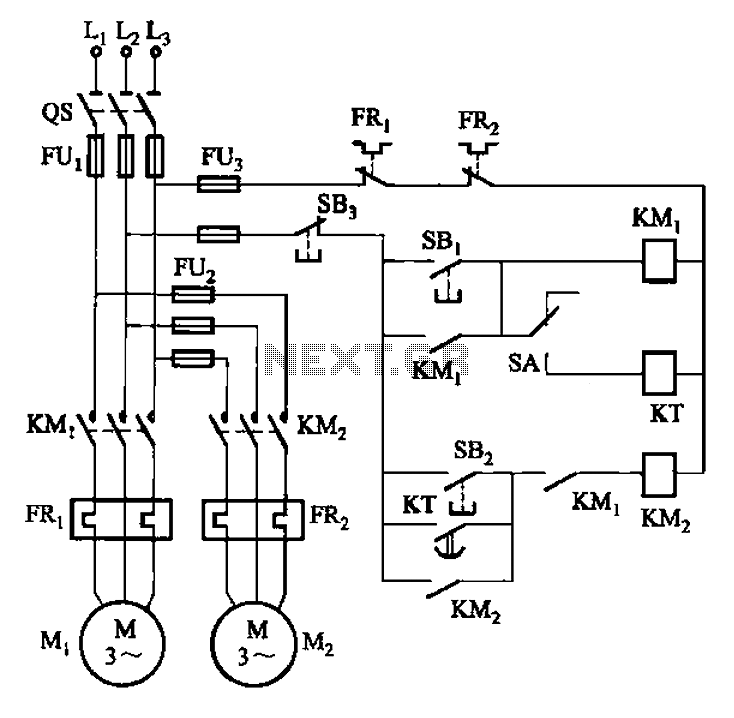
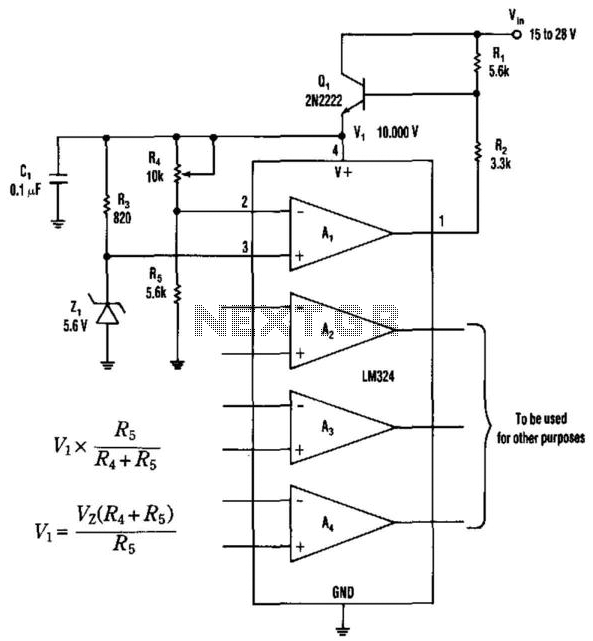
Small DC Motor Speed Regulator
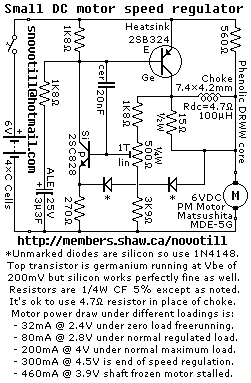
Reverse engineered circuit diagram of a motor speed regulator out of a portable pocket tape recorder containing a single motor for all functions. This circuit works amazingly well, keeping the motor speed constant regardless of shaft load and battery voltage.
The circuit diagram of the motor speed regulator is designed to maintain a consistent motor speed in a portable tape recorder, irrespective of variations in load and supply voltage. The primary components of the circuit typically include an operational amplifier, a variable resistor (potentiometer), a transistor, and feedback mechanisms.
The operational amplifier is configured to monitor the voltage across the motor. It compares the actual speed of the motor, indicated by the voltage, with a reference voltage set by the potentiometer. This reference voltage can be adjusted to set the desired motor speed.
When the load on the motor changes, causing the speed to deviate from the set point, the operational amplifier outputs a control signal. This signal drives the transistor, which acts as a switch to adjust the power supplied to the motor. The transistor's duty cycle is modulated based on the feedback from the operational amplifier, ensuring that the motor receives the appropriate amount of power to maintain the desired speed.
Additionally, the circuit may include protective components such as diodes to prevent back EMF from the motor, which could potentially damage the circuit. Capacitors may also be present to filter noise and stabilize the voltage supply.
The overall design emphasizes efficiency and reliability, allowing the tape recorder to function optimally under various operational conditions. This motor speed regulator circuit exemplifies a robust solution for applications requiring precise speed control in small electronic devices.Reverse engineered circuit diagram of a motor speed regulator out of a portable pocket tape recorder containing a single motor for all functions. This circuit works amazingly well, keeping the motor speed constant regardless of shaft load and battery voltage.
🔗 External reference
The circuit diagram of the motor speed regulator is designed to maintain a consistent motor speed in a portable tape recorder, irrespective of variations in load and supply voltage. The primary components of the circuit typically include an operational amplifier, a variable resistor (potentiometer), a transistor, and feedback mechanisms.
The operational amplifier is configured to monitor the voltage across the motor. It compares the actual speed of the motor, indicated by the voltage, with a reference voltage set by the potentiometer. This reference voltage can be adjusted to set the desired motor speed.
When the load on the motor changes, causing the speed to deviate from the set point, the operational amplifier outputs a control signal. This signal drives the transistor, which acts as a switch to adjust the power supplied to the motor. The transistor's duty cycle is modulated based on the feedback from the operational amplifier, ensuring that the motor receives the appropriate amount of power to maintain the desired speed.
Additionally, the circuit may include protective components such as diodes to prevent back EMF from the motor, which could potentially damage the circuit. Capacitors may also be present to filter noise and stabilize the voltage supply.
The overall design emphasizes efficiency and reliability, allowing the tape recorder to function optimally under various operational conditions. This motor speed regulator circuit exemplifies a robust solution for applications requiring precise speed control in small electronic devices.Reverse engineered circuit diagram of a motor speed regulator out of a portable pocket tape recorder containing a single motor for all functions. This circuit works amazingly well, keeping the motor speed constant regardless of shaft load and battery voltage.
🔗 External reference