Solid State Relay Required Only 50uA Drive Current

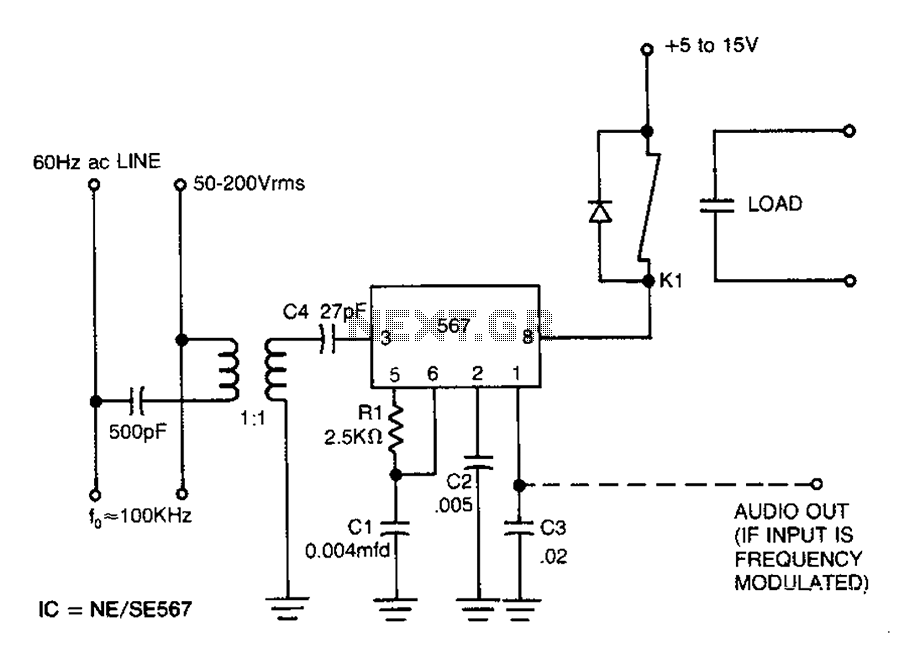
This circuit requires a control current that is 100 times smaller than that required by standard optically isolated solid-state relays. It is particularly suitable for battery-powered systems. By utilizing a combination of a high-current TRIAC and a very sensitive low-current SCR, the circuit can manage approximately 600 watts of power to the load while ensuring complete electrical isolation and transient protection.
The described circuit is designed to operate efficiently in environments where minimizing control current is critical, such as in battery-operated devices. The use of a high-current TRIAC allows for the handling of significant power loads, while the sensitive low-current SCR ensures that the control requirements are minimal. This combination not only enhances the efficiency of the circuit but also extends the life of the power source, making it ideal for applications where energy conservation is paramount.
The circuit achieves full isolation, which is essential in protecting sensitive components from voltage spikes and transients that may occur in the load circuit. The transient protection feature is vital for safeguarding against potential damage caused by sudden changes in current or voltage, which can be common in inductive loads.
In practical applications, this circuit can be employed in various scenarios, including remote control systems, automation in industrial settings, or any application where reliable power control is necessary without compromising on safety or efficiency. The design should incorporate appropriate heat dissipation mechanisms for the TRIAC and SCR to ensure stable operation under high load conditions. Additionally, careful consideration of component ratings and circuit layout will further enhance the reliability and performance of the overall system.This circuit demands a control current that is 100 times smaller than that needed by a typical optically isolated solid state relays. It is ideal for battery-powered systems. Using a combination of a high current TRIAC and a very sensitive low current SCR, the circuit can control about 600 watts of power to load while providing full isolation and
transient protection. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit is designed to operate efficiently in environments where minimizing control current is critical, such as in battery-operated devices. The use of a high-current TRIAC allows for the handling of significant power loads, while the sensitive low-current SCR ensures that the control requirements are minimal. This combination not only enhances the efficiency of the circuit but also extends the life of the power source, making it ideal for applications where energy conservation is paramount.
The circuit achieves full isolation, which is essential in protecting sensitive components from voltage spikes and transients that may occur in the load circuit. The transient protection feature is vital for safeguarding against potential damage caused by sudden changes in current or voltage, which can be common in inductive loads.
In practical applications, this circuit can be employed in various scenarios, including remote control systems, automation in industrial settings, or any application where reliable power control is necessary without compromising on safety or efficiency. The design should incorporate appropriate heat dissipation mechanisms for the TRIAC and SCR to ensure stable operation under high load conditions. Additionally, careful consideration of component ratings and circuit layout will further enhance the reliability and performance of the overall system.This circuit demands a control current that is 100 times smaller than that needed by a typical optically isolated solid state relays. It is ideal for battery-powered systems. Using a combination of a high current TRIAC and a very sensitive low current SCR, the circuit can control about 600 watts of power to load while providing full isolation and
transient protection. 🔗 External reference