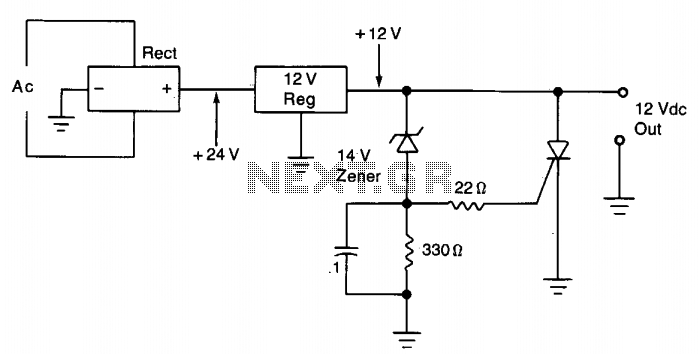
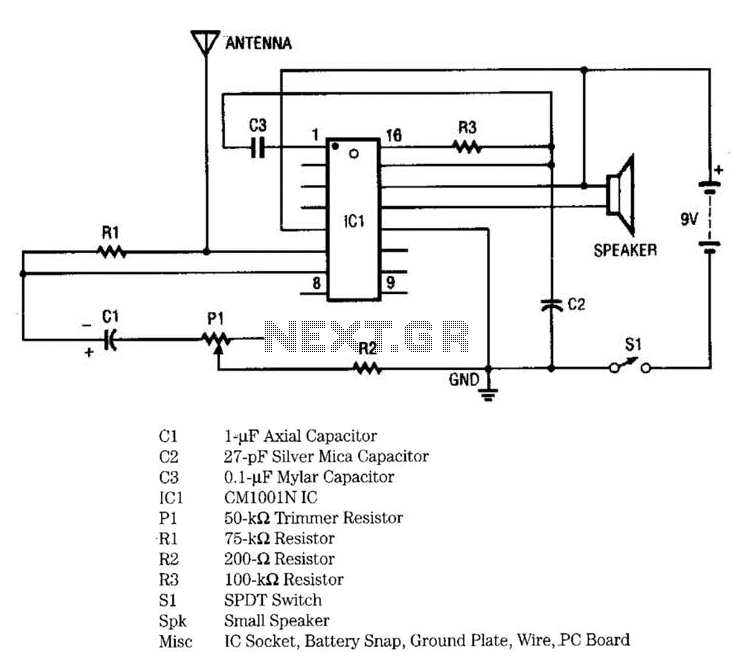
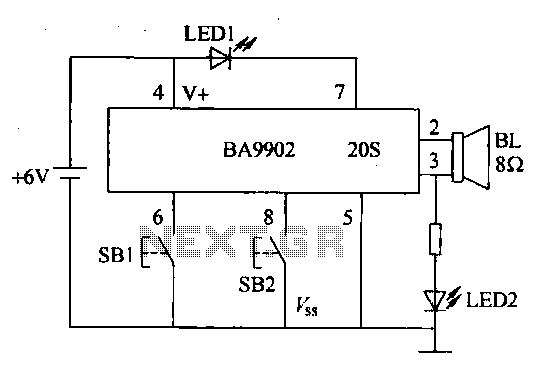
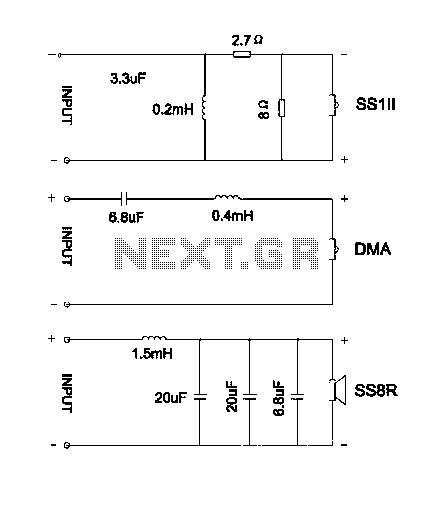
Speech Scrambler Circuit
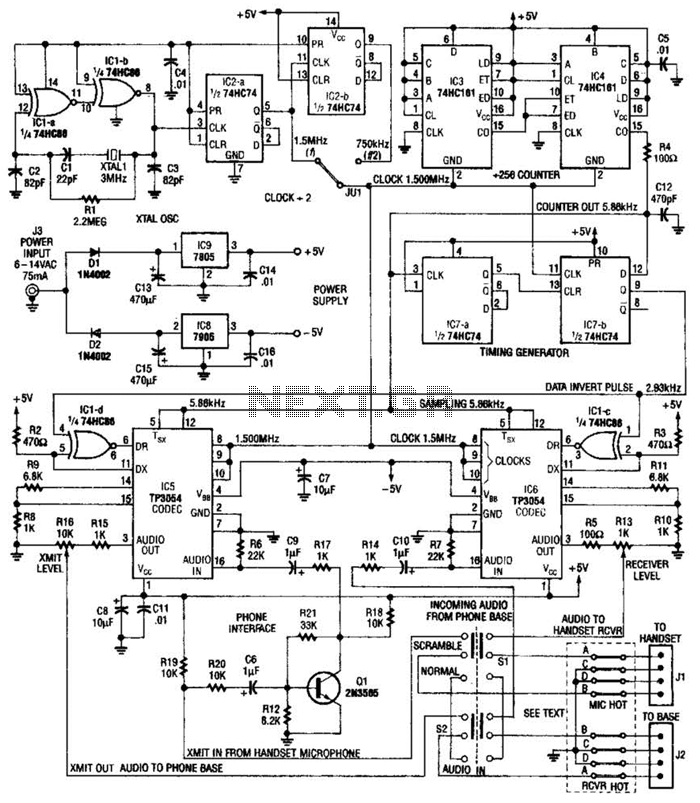
This circuit utilizes digital techniques to implement the frequency-inversion algorithm by digitizing the audio, inverting the sign of every alternate sample, and performing D/A conversion on the resulting data. The outcome is an inverted frequency spectrum. Additionally, the circuit features two channels, allowing it to function as a full duplex two-way telephone scrambler.
The described circuit operates on the principle of frequency inversion, a technique commonly used in secure communications to obscure voice signals. The initial audio input is digitized, converting the analog signal into a series of discrete digital samples. This is typically achieved using an Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC), which captures the amplitude of the audio waveform at regular intervals, producing a digital representation of the sound.
Once digitized, the algorithm processes the digital samples by inverting the sign of every alternate sample. This means that for a sequence of samples, the second, fourth, sixth, and so on, will have their values multiplied by -1. This inversion alters the frequency characteristics of the audio signal, effectively scrambling it.
Following this manipulation, the altered digital data is converted back into an analog signal using a Digital-to-Analog Converter (DAC). The DAC reconstructs the audio waveform from the modified digital samples, resulting in an audio output that has an inverted frequency spectrum compared to the original input.
The dual-channel design of the circuit allows it to operate in a full duplex mode, meaning that both parties in a telephone conversation can speak and be heard simultaneously without interruption. This is particularly useful for telephone scramblers, as it ensures that both ends of the communication can transmit scrambled audio effectively. The implementation of this circuit in telephone systems enhances privacy and security by making it difficult for unauthorized listeners to interpret the transmitted audio signals.
Overall, this frequency-inversion circuit exemplifies the application of digital signal processing techniques to achieve secure communication through audio scrambling. Using digital techniques, this circuit accomplishes the frequency-inversion algorithm via digitization of the audio, inversion of the sign of every alternate sample, and D/A conversion of the resultant data. The result is an inverted frequency spectrum. Because the circuit has two channels, this system can be used in a full duplex two-way telephone scrambler.
The described circuit operates on the principle of frequency inversion, a technique commonly used in secure communications to obscure voice signals. The initial audio input is digitized, converting the analog signal into a series of discrete digital samples. This is typically achieved using an Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC), which captures the amplitude of the audio waveform at regular intervals, producing a digital representation of the sound.
Once digitized, the algorithm processes the digital samples by inverting the sign of every alternate sample. This means that for a sequence of samples, the second, fourth, sixth, and so on, will have their values multiplied by -1. This inversion alters the frequency characteristics of the audio signal, effectively scrambling it.
Following this manipulation, the altered digital data is converted back into an analog signal using a Digital-to-Analog Converter (DAC). The DAC reconstructs the audio waveform from the modified digital samples, resulting in an audio output that has an inverted frequency spectrum compared to the original input.
The dual-channel design of the circuit allows it to operate in a full duplex mode, meaning that both parties in a telephone conversation can speak and be heard simultaneously without interruption. This is particularly useful for telephone scramblers, as it ensures that both ends of the communication can transmit scrambled audio effectively. The implementation of this circuit in telephone systems enhances privacy and security by making it difficult for unauthorized listeners to interpret the transmitted audio signals.
Overall, this frequency-inversion circuit exemplifies the application of digital signal processing techniques to achieve secure communication through audio scrambling. Using digital techniques, this circuit accomplishes the frequency-inversion algorithm via digitization of the audio, inversion of the sign of every alternate sample, and D/A conversion of the resultant data. The result is an inverted frequency spectrum. Because the circuit has two channels, this system can be used in a full duplex two-way telephone scrambler.