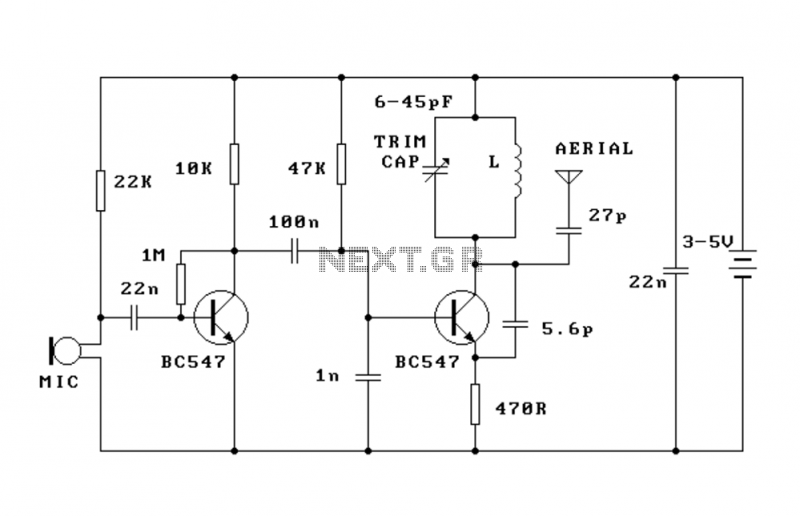
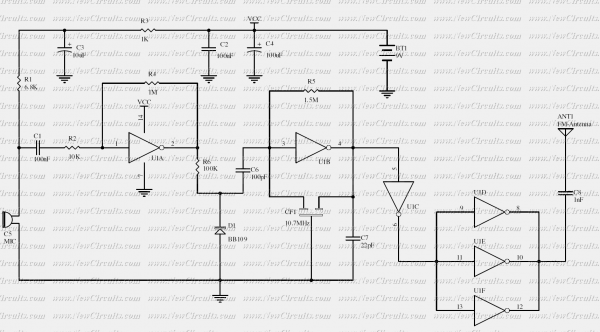
stable guitar FM transmitter
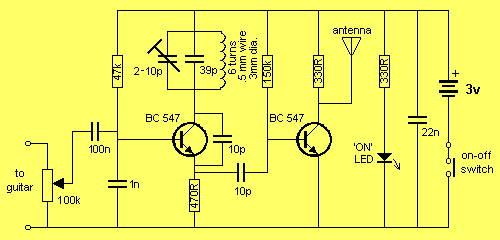
This FM transmitter has a number of features, with a volume control to adjust the input level and a small, neat box to make it easier to attach to a guitar. The volume control is positioned at the end and when turned up fully, the transmitter provides fuzz (distortion). More: The circuit takes the signal from a guitar, radio or tape-recorder and injects it into an oscillator operating at 90MHz. This produces a carrier frequency - also called a Radio Frequency (RF). This frequency is capable of being radiated to the surrounding.
The FM transmitter circuit is designed to facilitate wireless audio transmission from musical instruments such as guitars, as well as other audio sources like radios or tape recorders. The core of the transmitter is an oscillator that operates at a frequency of 90 MHz, which is within the FM band. The circuit typically includes a few key components: an audio input stage, a modulation stage, and an RF output stage.
The audio input stage includes a volume control potentiometer that allows the user to adjust the input level of the audio signal. This control is essential for preventing distortion and ensuring optimal audio quality. When the volume control is turned to its maximum setting, the circuit can introduce intentional distortion, creating a "fuzz" effect that is often desirable in electric guitar applications.
The modulation stage is responsible for mixing the audio signal with the carrier frequency generated by the oscillator. This is typically achieved using a transistor or operational amplifier configured to modulate the amplitude of the RF signal based on the audio input. The result is an FM modulated signal that can be transmitted wirelessly.
The RF output stage consists of an antenna, which is crucial for radiating the modulated signal into the surrounding environment. The antenna design can vary, but it is often a simple wire or a small PCB trace that is tuned to the operating frequency of 90 MHz to ensure efficient radiation.
The entire circuit is housed in a compact enclosure, designed for easy attachment to a guitar or other audio sources. This portability enhances the usability of the transmitter, making it suitable for live performances or practice sessions. Overall, the FM transmitter circuit represents a versatile solution for wireless audio transmission, combining functionality with ease of use.This FM transmitter has a number of features, with a volume control to adjust the input level and a small, neat box to make it easier to attach to a guitar. The volume control is positioned at the end and when turned up fully, the transmitter provides fuzz (distortion).
The circuit takes the signal from a guitar, radio or tape-recorder and injects it into an oscillator operating at 90MHz. This produces a carrier frequency - also called a Radio Frequency (RF). This frequency is capable of being radiated to the surroundin 🔗 External reference
The FM transmitter circuit is designed to facilitate wireless audio transmission from musical instruments such as guitars, as well as other audio sources like radios or tape recorders. The core of the transmitter is an oscillator that operates at a frequency of 90 MHz, which is within the FM band. The circuit typically includes a few key components: an audio input stage, a modulation stage, and an RF output stage.
The audio input stage includes a volume control potentiometer that allows the user to adjust the input level of the audio signal. This control is essential for preventing distortion and ensuring optimal audio quality. When the volume control is turned to its maximum setting, the circuit can introduce intentional distortion, creating a "fuzz" effect that is often desirable in electric guitar applications.
The modulation stage is responsible for mixing the audio signal with the carrier frequency generated by the oscillator. This is typically achieved using a transistor or operational amplifier configured to modulate the amplitude of the RF signal based on the audio input. The result is an FM modulated signal that can be transmitted wirelessly.
The RF output stage consists of an antenna, which is crucial for radiating the modulated signal into the surrounding environment. The antenna design can vary, but it is often a simple wire or a small PCB trace that is tuned to the operating frequency of 90 MHz to ensure efficient radiation.
The entire circuit is housed in a compact enclosure, designed for easy attachment to a guitar or other audio sources. This portability enhances the usability of the transmitter, making it suitable for live performances or practice sessions. Overall, the FM transmitter circuit represents a versatile solution for wireless audio transmission, combining functionality with ease of use.This FM transmitter has a number of features, with a volume control to adjust the input level and a small, neat box to make it easier to attach to a guitar. The volume control is positioned at the end and when turned up fully, the transmitter provides fuzz (distortion).
The circuit takes the signal from a guitar, radio or tape-recorder and injects it into an oscillator operating at 90MHz. This produces a carrier frequency - also called a Radio Frequency (RF). This frequency is capable of being radiated to the surroundin 🔗 External reference