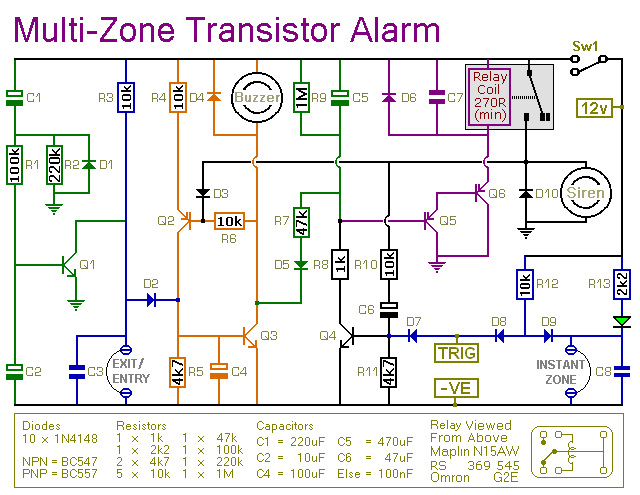
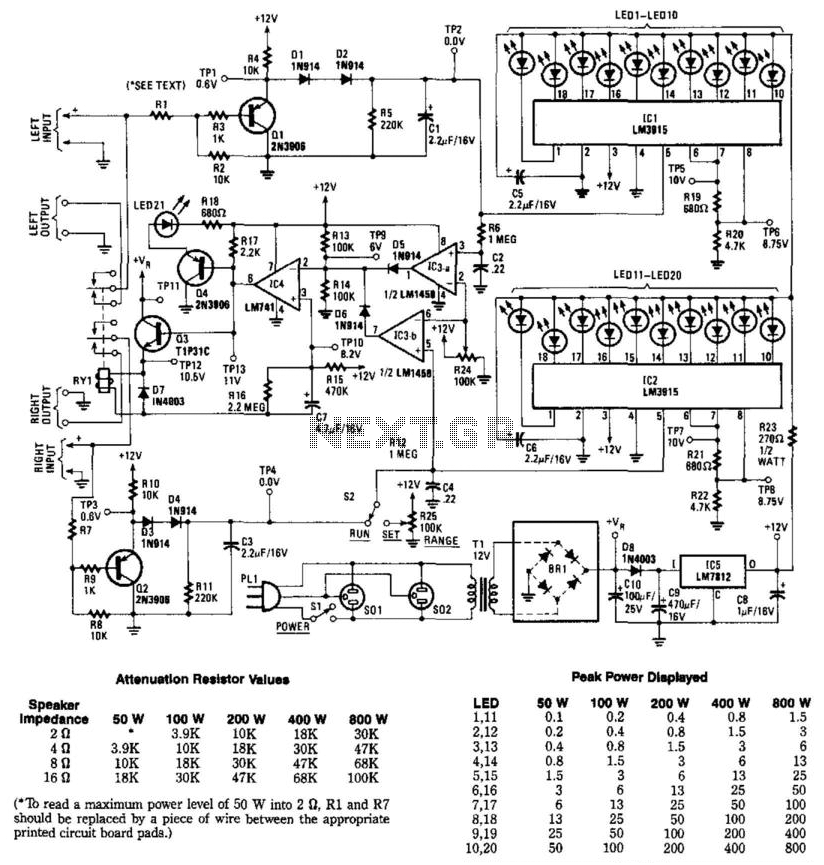
stereo to mono converter based on fet
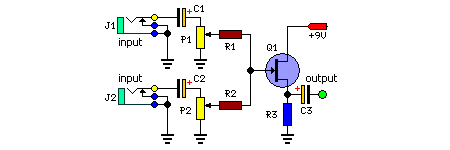
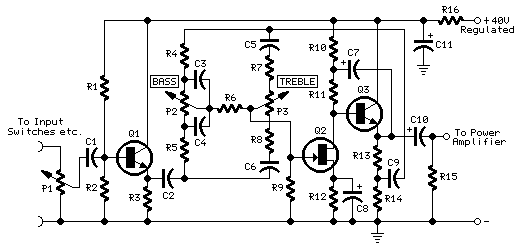
This circuit combines two or more audio channels into a single channel (for example, converting stereo to mono). It is designed to handle any number of channels while consuming minimal power. The schematic illustrates two input channels, but additional channels can be easily incorporated by duplicating the input sections that are clearly marked.
The audio mixing circuit is an essential component in various audio applications, enabling the integration of multiple audio sources into a unified output. The basic configuration typically consists of resistive mixing, where each input channel is connected to a summing point through resistors. This method ensures that the audio signals from different sources can be blended without significant distortion or loss of quality.
The circuit can be constructed using operational amplifiers (op-amps) to achieve a high degree of fidelity. In this case, each input channel is fed into an inverting summing amplifier configuration, where the op-amp combines the signals. The resistors connected to each input determine the weight of each channel in the final output, allowing for precise control over the mix.
Power consumption is minimal due to the low-voltage operation of the op-amps, making the circuit suitable for battery-powered devices or applications where energy efficiency is paramount. The layout of the circuit should ensure that the input sections are easily accessible for modifications, enabling the user to add or remove channels as needed.
For practical implementation, it is advisable to include decoupling capacitors near the power supply pins of the op-amps to filter out any noise that may affect the audio quality. Additionally, output coupling capacitors can be used to block any DC offset, ensuring that only the AC audio signal is delivered to the next stage of the audio system.
Overall, this circuit serves as a versatile tool for audio processing, allowing for flexible channel mixing while maintaining a low power profile.This simple circuit mixes two or more channels into one channel (e.g. stereo into mono). The circuit can mix as many or as few channels as you like and consume very little power. The mixer is shown with two inputs, but you can add as many as you want by just duplicating the ""input sections"" which are clearly visible on the schematic.. 🔗 External reference
The audio mixing circuit is an essential component in various audio applications, enabling the integration of multiple audio sources into a unified output. The basic configuration typically consists of resistive mixing, where each input channel is connected to a summing point through resistors. This method ensures that the audio signals from different sources can be blended without significant distortion or loss of quality.
The circuit can be constructed using operational amplifiers (op-amps) to achieve a high degree of fidelity. In this case, each input channel is fed into an inverting summing amplifier configuration, where the op-amp combines the signals. The resistors connected to each input determine the weight of each channel in the final output, allowing for precise control over the mix.
Power consumption is minimal due to the low-voltage operation of the op-amps, making the circuit suitable for battery-powered devices or applications where energy efficiency is paramount. The layout of the circuit should ensure that the input sections are easily accessible for modifications, enabling the user to add or remove channels as needed.
For practical implementation, it is advisable to include decoupling capacitors near the power supply pins of the op-amps to filter out any noise that may affect the audio quality. Additionally, output coupling capacitors can be used to block any DC offset, ensuring that only the AC audio signal is delivered to the next stage of the audio system.
Overall, this circuit serves as a versatile tool for audio processing, allowing for flexible channel mixing while maintaining a low power profile.This simple circuit mixes two or more channels into one channel (e.g. stereo into mono). The circuit can mix as many or as few channels as you like and consume very little power. The mixer is shown with two inputs, but you can add as many as you want by just duplicating the ""input sections"" which are clearly visible on the schematic.. 🔗 External reference