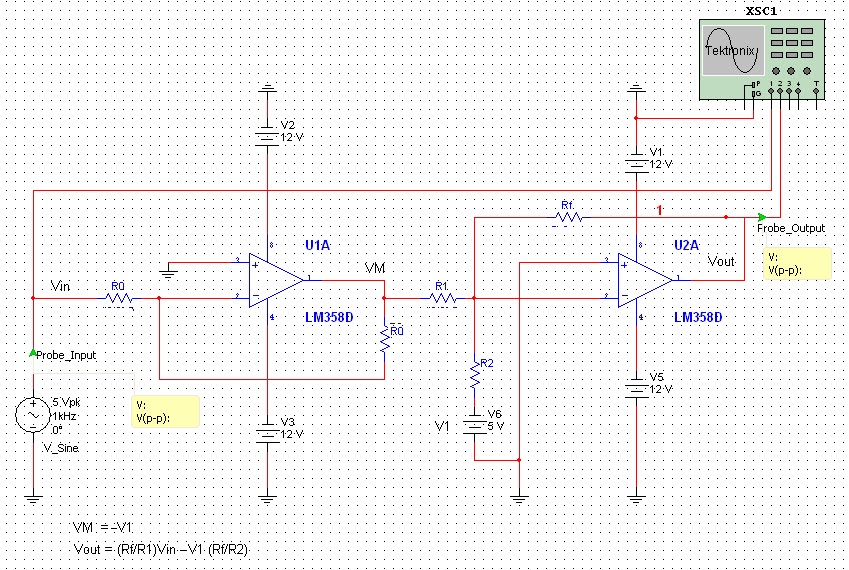
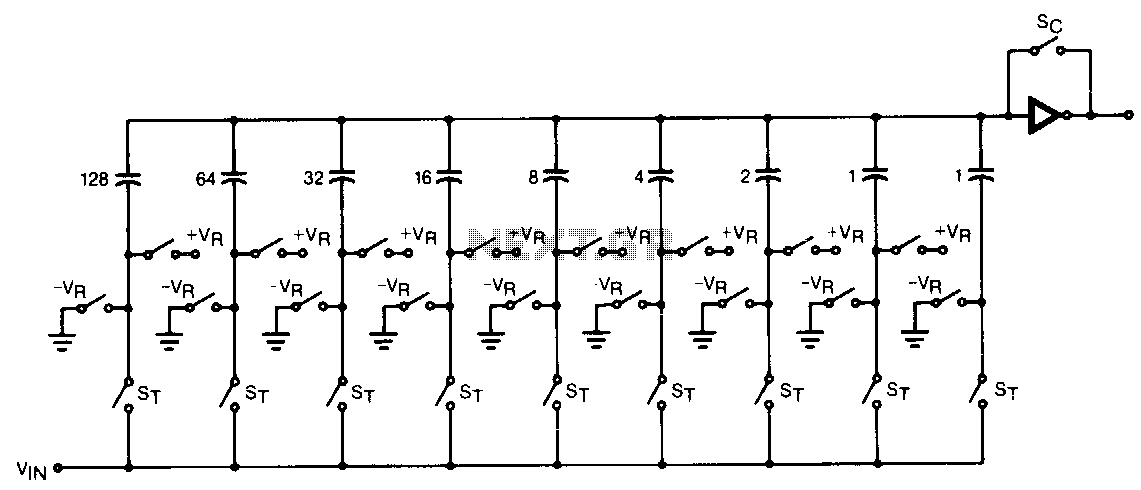
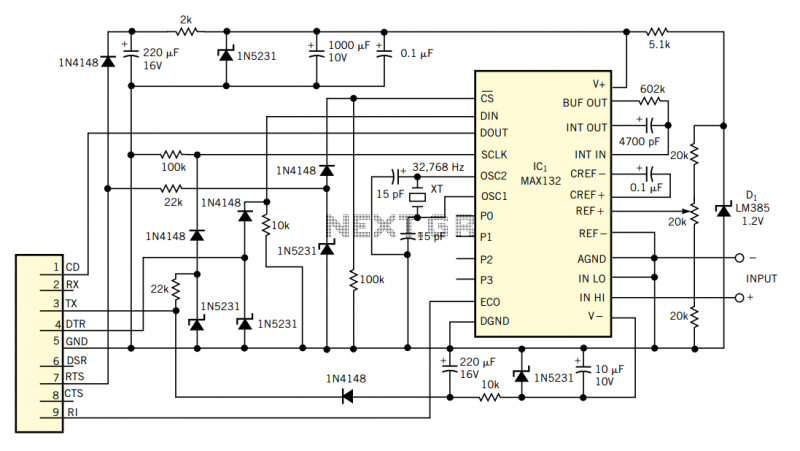
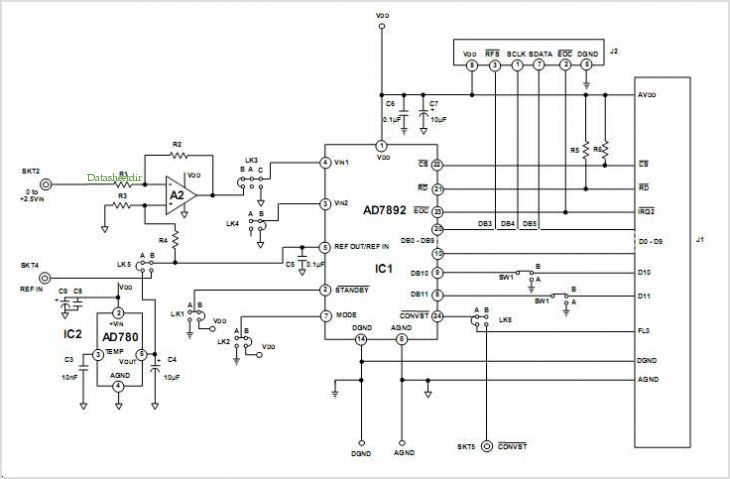
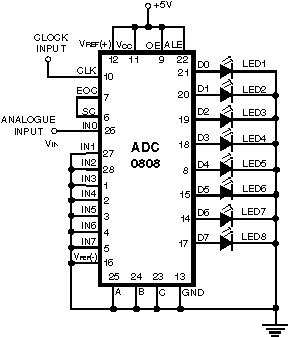
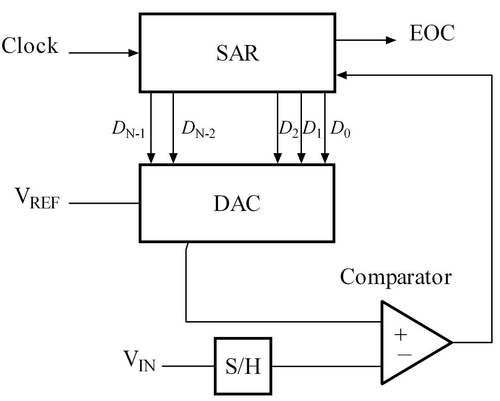
Successive Approximation ADC
An analog-to-digital converter is a device that converts a continuous quantity to a discrete time digital representation. An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement. An analog signal is any continuous signal where the time-varying feature represents another time-varying quantity. It differs from a digital signal, which is characterized by discrete values. Quantization is the process of mapping a large set of input values to a smaller set, such as rounding values to a specific unit of precision. A quantizer is a device or algorithm that performs this function. Voltage, or electrical potential difference, is the difference in electric potential between two points. In electronics, a digital-to-analog converter converts a digital code to an analog signal, while an analog-to-digital converter performs the reverse operation. In computer architecture, a processor register is a small storage space in a CPU or digital processor that can be accessed more quickly than main memory. A comparator is a device that compares two voltages or currents and indicates which is larger, commonly used in analog-to-digital converters.
An analog-to-digital converter (ADC) is a critical component in modern electronic systems, facilitating the transformation of continuous analog signals into discrete digital representations. This conversion process is essential in applications such as audio processing, sensor data acquisition, and digital communication systems. The ADC typically operates by sampling the input analog signal at regular intervals and quantizing the sampled values into a finite number of discrete levels, which are then encoded into a binary format.
The quantization process involves mapping a continuous range of input values to a limited set of output values, which can introduce quantization error. This error is a fundamental aspect of ADC performance and is influenced by the resolution of the converter, typically measured in bits. Higher resolution ADCs can represent finer distinctions in the input signal, reducing quantization error.
Voltage measurement is a crucial aspect of ADC functionality, as the input analog signal is often represented as a voltage level. The ADC's input voltage range must be carefully defined to ensure accurate conversion, as exceeding this range can lead to signal clipping and distortion. In many cases, ADCs incorporate features such as input signal conditioning and isolation to enhance measurement accuracy and protect against noise and interference.
The output of an ADC can be directly interfaced with digital systems, such as microcontrollers and digital signal processors (DSPs), where the digital data can be stored, processed, or transmitted. Additionally, the integration of comparators within ADC architectures allows for efficient signal comparison and threshold detection, further enhancing the functionality of the device.
In summary, the analog-to-digital converter is a vital component in bridging the gap between the analog world and digital processing systems, enabling a wide range of applications in electronics and communication. Its design considerations, including quantization, voltage range, and integration with digital components, are key to achieving optimal performance in various applications.An analog-to-digital converter is a device that converts a continuous quantity to a discrete time digital representation. An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement. An analog or analogue signal is any continuous signal for which the time varying feature of the signal is a representation of some other time varying quantity, i.
e. , analogous to another time varying signal. It differs from a digital signal in terms of small fluctuations in the signal which are. A digital system is a data technology that uses discrete values. By contrast, non-digital systems use a continuous range of values to represent information. Quantization, in mathematics and digital signal processing, is the process of mapping a large set of input values to a smaller set such as rounding values to some unit of precision. A device or algorithmic function that performs quantization is called a quantizer. The error introduced by. Voltage, otherwise known as electrical potential difference or electric tension is the difference in electric potential between two points ” or the difference in electric potential energy per unit charge between two points.
In electronics, a digital-to-analog converter is a device that converts a digital code to an analog signal. An analog-to-digital converter performs the reverse operation. In computer architecture, a processor register is a small amount of storage available as part of a CPU or other digital processor.
Such registers are addressed by mechanisms other than main memory and can be accessed more quickly. In electronics, a comparator is a device that compares two voltages or currents and switches its output to indicate which is larger. They are commonly used in devices such as Analog-to-digital converters. - Input voltage range :. A digital system is a data technology that uses discrete values. By contrast, non-digital systems use a continuous range of values to represent information. An analog-to-digital converter is a device that converts a continuous quantity to a discrete time digital representation.
An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement. An analog or analogue signal is any continuous signal for which the time varying feature of the signal is a representation of some other time varying quantity, i. e. , analogous to another time varying signal. It differs from a digital signal in terms of small fluctuations in the signal which are. A digital system is a data technology that uses discrete values. By contrast, non-digital systems use a continuous range of values to represent information. Quantization, in mathematics and digital signal processing, is the process of mapping a large set of input values to a smaller set such as rounding values to some unit of precision.
A device or algorithmic function that performs quantization is called a quantizer. The error introduced by. Voltage, otherwise known as electrical potential difference or electric tension is the difference in electric potential between two points ” or the difference in electric potential energy per unit charge between two points. In electronics, a digital-to-analog converter is a device that converts a digital code to an analog signal.
An analog-to-digital converter performs the reverse operation. In computer architecture, a processor register is a small amount of storage available as part of a CPU or other digital processor. Such registers are addressed by mechanisms other than main memory and can be accessed more quickly. In electronics, a comparator is a device that compares two voltages or currents and switches its output to indicate which is larger.
They are commonly used in devices such as Analog-to-digital converters. - Input voltage range :. A digital system is a data technology that uses discrete values. By contrast, non-digital systems use a continuous range of values to represent information. 1. This code is fed into the DAC, which then supplies the analog equivalent 🔗 External reference
An analog-to-digital converter (ADC) is a critical component in modern electronic systems, facilitating the transformation of continuous analog signals into discrete digital representations. This conversion process is essential in applications such as audio processing, sensor data acquisition, and digital communication systems. The ADC typically operates by sampling the input analog signal at regular intervals and quantizing the sampled values into a finite number of discrete levels, which are then encoded into a binary format.
The quantization process involves mapping a continuous range of input values to a limited set of output values, which can introduce quantization error. This error is a fundamental aspect of ADC performance and is influenced by the resolution of the converter, typically measured in bits. Higher resolution ADCs can represent finer distinctions in the input signal, reducing quantization error.
Voltage measurement is a crucial aspect of ADC functionality, as the input analog signal is often represented as a voltage level. The ADC's input voltage range must be carefully defined to ensure accurate conversion, as exceeding this range can lead to signal clipping and distortion. In many cases, ADCs incorporate features such as input signal conditioning and isolation to enhance measurement accuracy and protect against noise and interference.
The output of an ADC can be directly interfaced with digital systems, such as microcontrollers and digital signal processors (DSPs), where the digital data can be stored, processed, or transmitted. Additionally, the integration of comparators within ADC architectures allows for efficient signal comparison and threshold detection, further enhancing the functionality of the device.
In summary, the analog-to-digital converter is a vital component in bridging the gap between the analog world and digital processing systems, enabling a wide range of applications in electronics and communication. Its design considerations, including quantization, voltage range, and integration with digital components, are key to achieving optimal performance in various applications.An analog-to-digital converter is a device that converts a continuous quantity to a discrete time digital representation. An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement. An analog or analogue signal is any continuous signal for which the time varying feature of the signal is a representation of some other time varying quantity, i.
e. , analogous to another time varying signal. It differs from a digital signal in terms of small fluctuations in the signal which are. A digital system is a data technology that uses discrete values. By contrast, non-digital systems use a continuous range of values to represent information. Quantization, in mathematics and digital signal processing, is the process of mapping a large set of input values to a smaller set such as rounding values to some unit of precision. A device or algorithmic function that performs quantization is called a quantizer. The error introduced by. Voltage, otherwise known as electrical potential difference or electric tension is the difference in electric potential between two points ” or the difference in electric potential energy per unit charge between two points.
In electronics, a digital-to-analog converter is a device that converts a digital code to an analog signal. An analog-to-digital converter performs the reverse operation. In computer architecture, a processor register is a small amount of storage available as part of a CPU or other digital processor.
Such registers are addressed by mechanisms other than main memory and can be accessed more quickly. In electronics, a comparator is a device that compares two voltages or currents and switches its output to indicate which is larger. They are commonly used in devices such as Analog-to-digital converters. - Input voltage range :. A digital system is a data technology that uses discrete values. By contrast, non-digital systems use a continuous range of values to represent information. An analog-to-digital converter is a device that converts a continuous quantity to a discrete time digital representation.
An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement. An analog or analogue signal is any continuous signal for which the time varying feature of the signal is a representation of some other time varying quantity, i. e. , analogous to another time varying signal. It differs from a digital signal in terms of small fluctuations in the signal which are. A digital system is a data technology that uses discrete values. By contrast, non-digital systems use a continuous range of values to represent information. Quantization, in mathematics and digital signal processing, is the process of mapping a large set of input values to a smaller set such as rounding values to some unit of precision.
A device or algorithmic function that performs quantization is called a quantizer. The error introduced by. Voltage, otherwise known as electrical potential difference or electric tension is the difference in electric potential between two points ” or the difference in electric potential energy per unit charge between two points. In electronics, a digital-to-analog converter is a device that converts a digital code to an analog signal.
An analog-to-digital converter performs the reverse operation. In computer architecture, a processor register is a small amount of storage available as part of a CPU or other digital processor. Such registers are addressed by mechanisms other than main memory and can be accessed more quickly. In electronics, a comparator is a device that compares two voltages or currents and switches its output to indicate which is larger.
They are commonly used in devices such as Analog-to-digital converters. - Input voltage range :. A digital system is a data technology that uses discrete values. By contrast, non-digital systems use a continuous range of values to represent information. 1. This code is fed into the DAC, which then supplies the analog equivalent 🔗 External reference