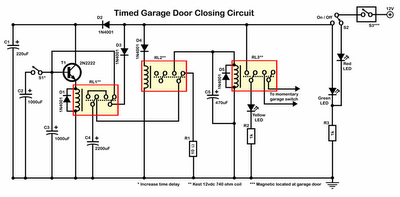
switching power supply schematic
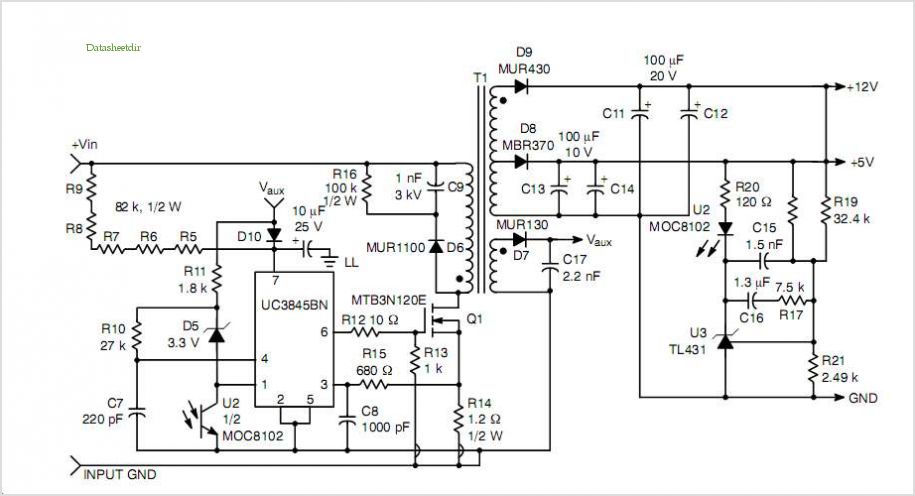
This post summarizes the work of experts in switching power supply schematic diagrams who are thoroughly knowledgeable about all aspects of the subject.
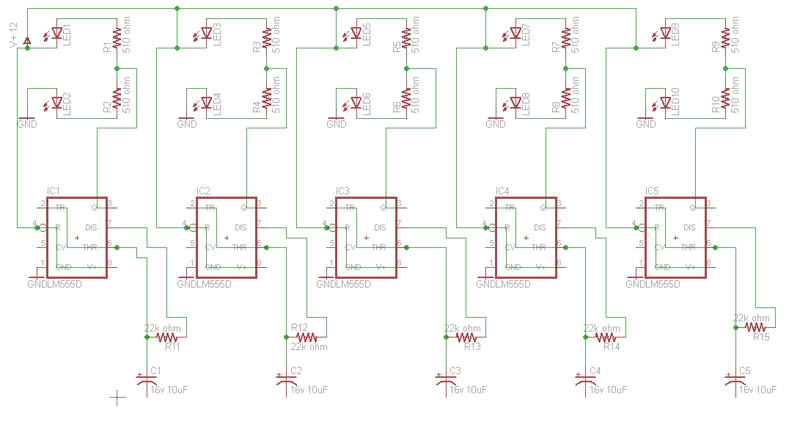
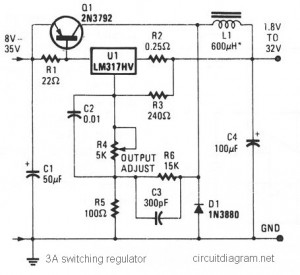
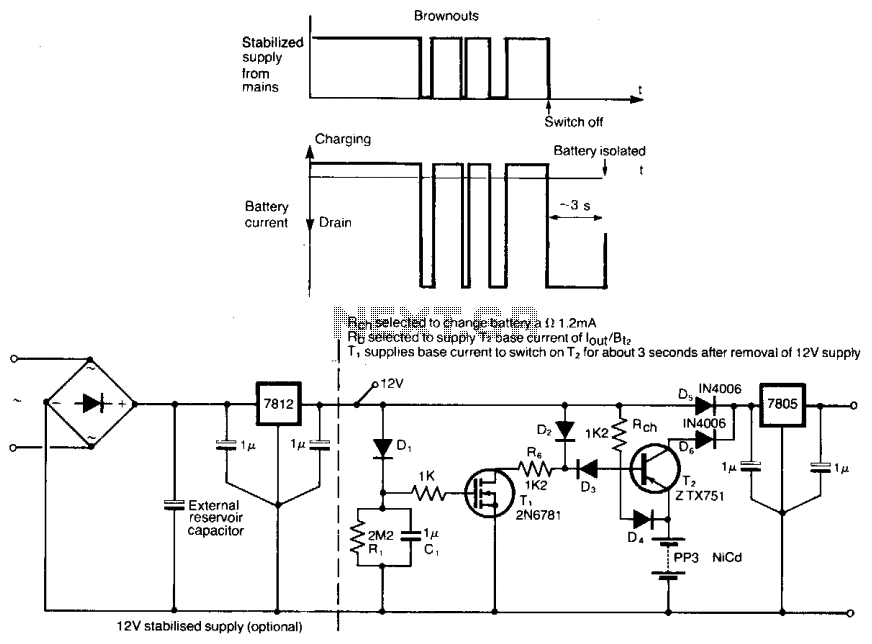
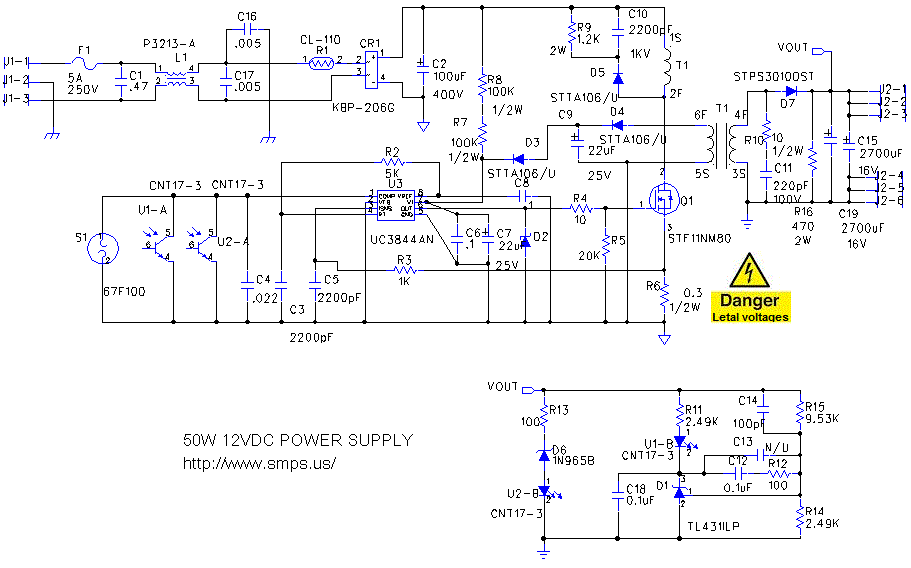
Switching power supplies are crucial components in modern electronic devices, providing efficient voltage regulation and power conversion. The schematic diagram of a switching power supply typically includes several key components: an input filter, a power switch (usually a MOSFET or IGBT), a transformer, a rectifier, an output filter, and control circuitry.
The input filter is designed to reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI) and protect the power supply from voltage spikes. It typically consists of capacitors and inductors arranged to form a low-pass filter. The power switch operates by rapidly turning on and off, allowing energy to be transferred to the transformer during the 'on' state and preventing energy flow during the 'off' state.
The transformer in a switching power supply serves to step up or step down the voltage while isolating the input from the output. It operates at high frequencies, which allows for smaller and lighter components compared to linear power supplies. The output side usually features a rectifier, which converts the AC output of the transformer back into DC, and an output filter that smooths the voltage to ensure a stable output.
Control circuitry is essential for regulating the output voltage and current. It typically uses feedback mechanisms to compare the output voltage with a reference voltage and adjust the duty cycle of the power switch accordingly. This feedback loop ensures that the output remains stable under varying load conditions.
Overall, the design and implementation of switching power supply schematic diagrams require a deep understanding of electronics, including circuit theory, component specifications, and electromagnetic compatibility considerations.Greeting, This post summarize the work of switching power supply schematic diagram experts who are completely familiar with all the aspects of.. 🔗 External reference
Switching power supplies are crucial components in modern electronic devices, providing efficient voltage regulation and power conversion. The schematic diagram of a switching power supply typically includes several key components: an input filter, a power switch (usually a MOSFET or IGBT), a transformer, a rectifier, an output filter, and control circuitry.
The input filter is designed to reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI) and protect the power supply from voltage spikes. It typically consists of capacitors and inductors arranged to form a low-pass filter. The power switch operates by rapidly turning on and off, allowing energy to be transferred to the transformer during the 'on' state and preventing energy flow during the 'off' state.
The transformer in a switching power supply serves to step up or step down the voltage while isolating the input from the output. It operates at high frequencies, which allows for smaller and lighter components compared to linear power supplies. The output side usually features a rectifier, which converts the AC output of the transformer back into DC, and an output filter that smooths the voltage to ensure a stable output.
Control circuitry is essential for regulating the output voltage and current. It typically uses feedback mechanisms to compare the output voltage with a reference voltage and adjust the duty cycle of the power switch accordingly. This feedback loop ensures that the output remains stable under varying load conditions.
Overall, the design and implementation of switching power supply schematic diagrams require a deep understanding of electronics, including circuit theory, component specifications, and electromagnetic compatibility considerations.Greeting, This post summarize the work of switching power supply schematic diagram experts who are completely familiar with all the aspects of.. 🔗 External reference