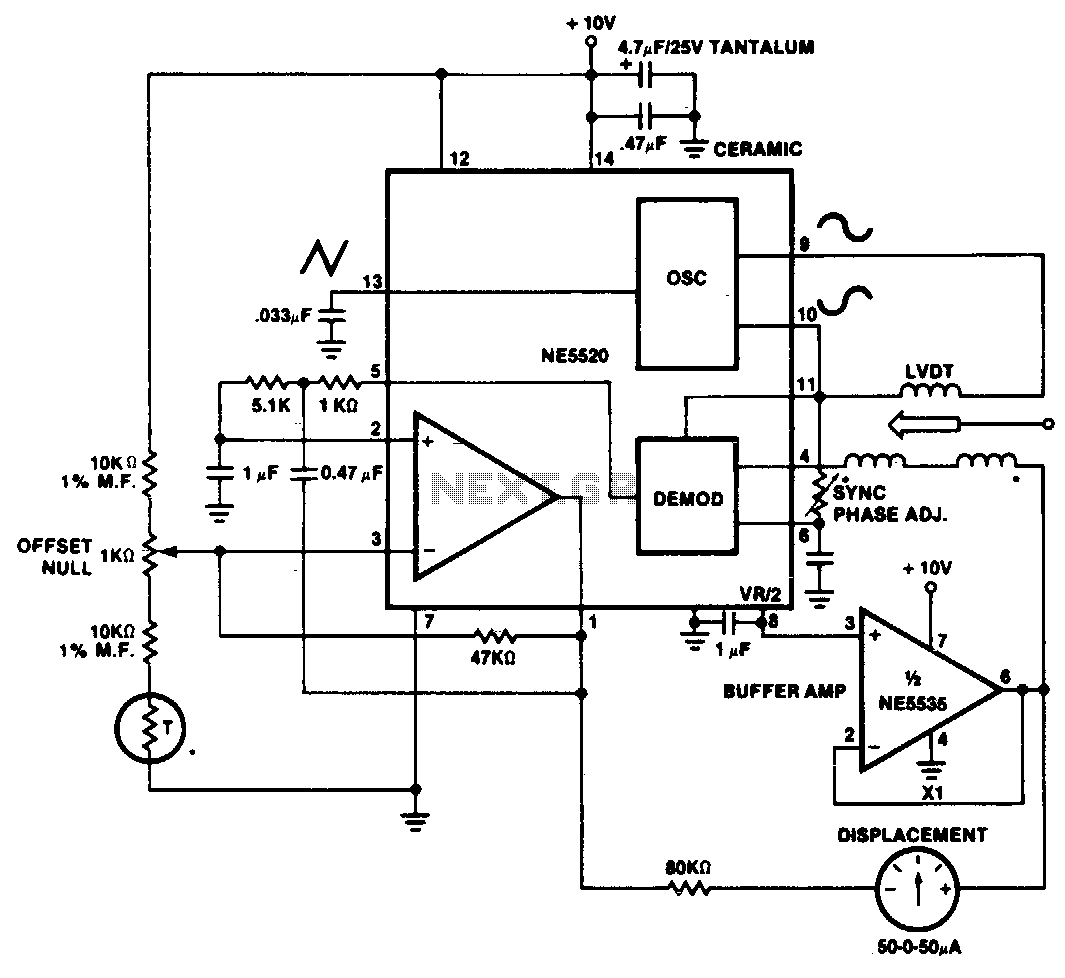
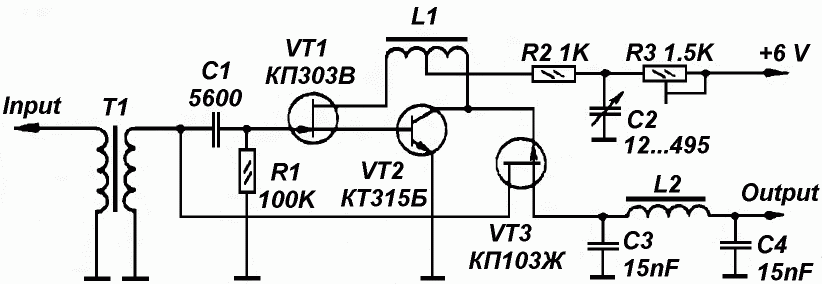
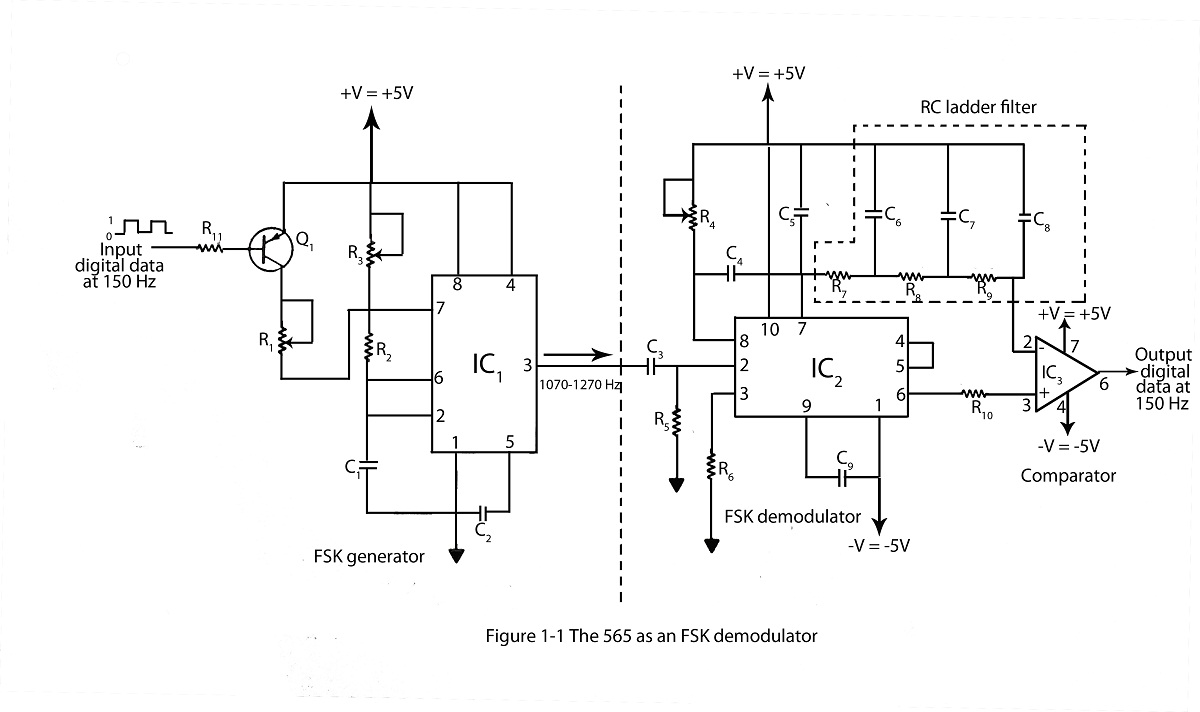
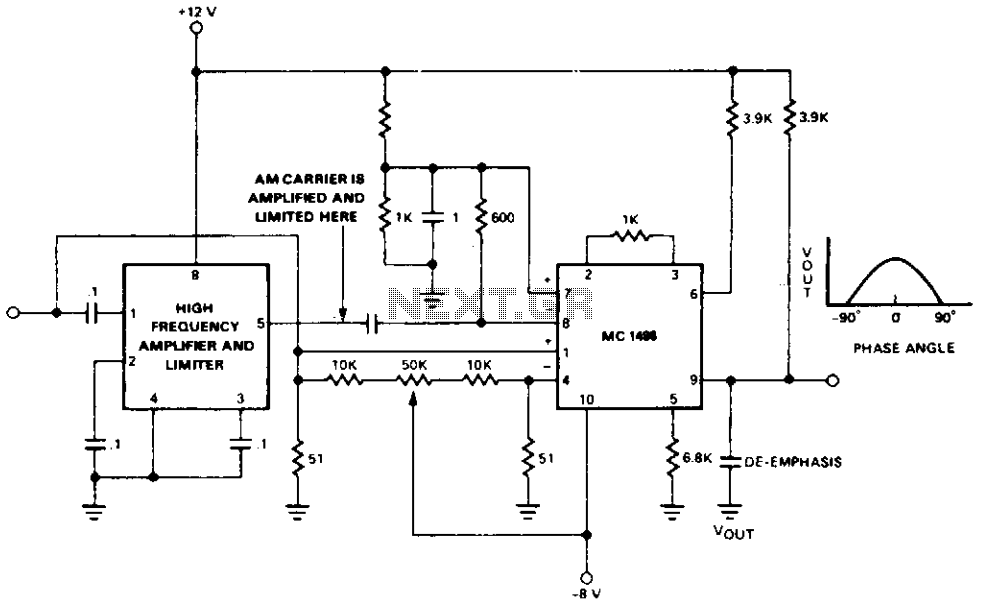
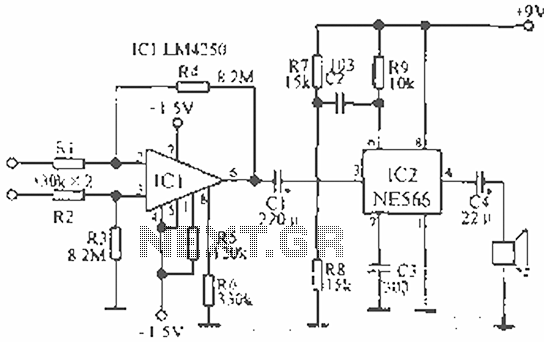
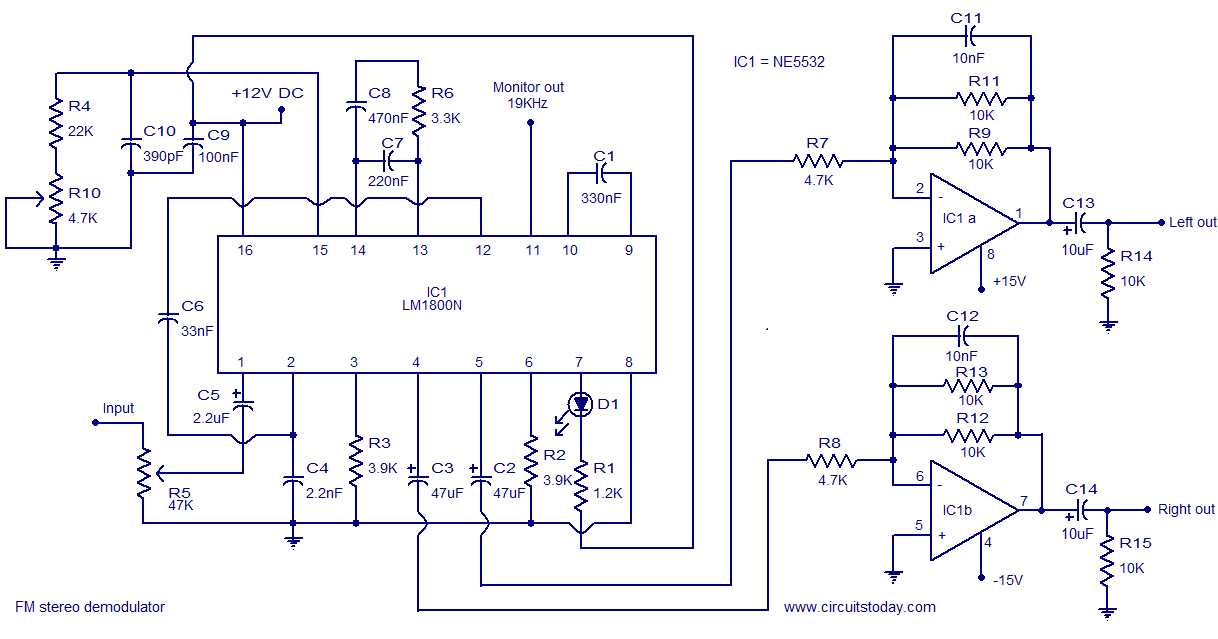
Telemetry demodulator
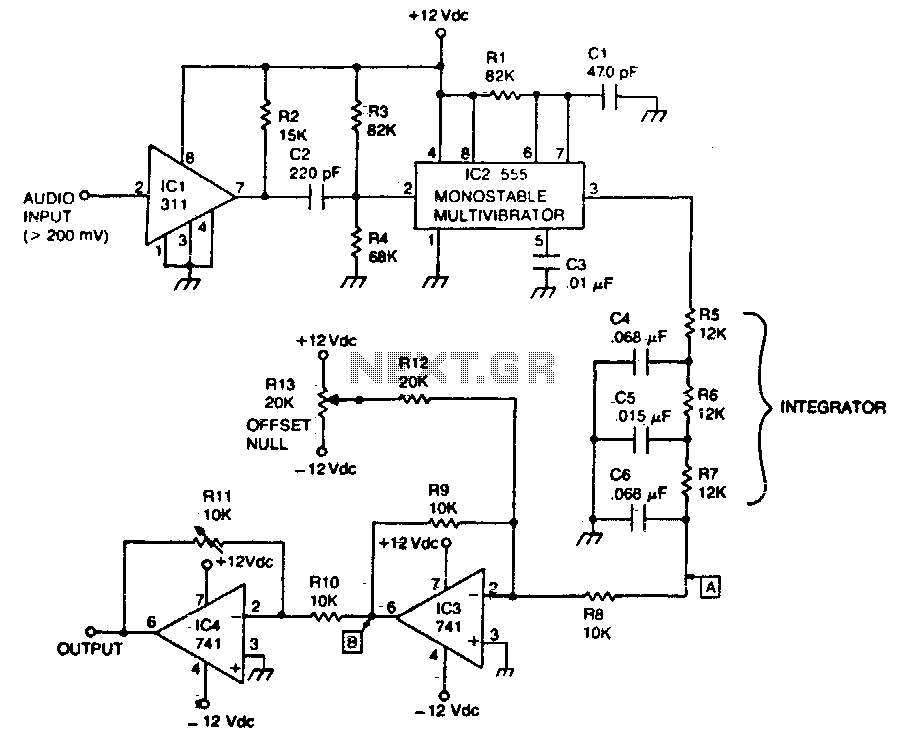
The circuit recovers an FM audio signal that varies from less than 1 kHz to about 10 kHz.
The circuit is designed to demodulate frequency-modulated (FM) audio signals within the frequency range of less than 1 kHz to approximately 10 kHz. The primary function of this circuit is to extract the original audio information from the modulated carrier wave, allowing for playback or further processing of the audio signal.
To achieve this, the circuit typically includes several key components: an antenna for receiving the FM signal, a radio frequency (RF) amplifier to boost the signal strength, and a demodulator stage that converts the FM signal back into an audio frequency (AF) signal. The demodulation process often employs a phase-locked loop (PLL) or a discriminator circuit, which can effectively track the variations in frequency of the incoming FM signal.
After demodulation, the audio signal may undergo additional processing, such as filtering to remove any residual RF components and amplification to bring the signal to a suitable level for output. The final output stage may include a low-pass filter to ensure that only the desired audio frequencies are passed through, effectively eliminating any high-frequency noise that may have been introduced during the transmission.
The circuit's design must also consider factors such as signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), distortion, and the overall bandwidth to ensure high-quality audio reproduction. Proper layout and component selection are critical to minimize interference and maintain signal integrity throughout the circuit.The circuit recovers an FM audio signal that variesfrom less than 1 kHz to about 10 kHz. 🔗 External reference
The circuit is designed to demodulate frequency-modulated (FM) audio signals within the frequency range of less than 1 kHz to approximately 10 kHz. The primary function of this circuit is to extract the original audio information from the modulated carrier wave, allowing for playback or further processing of the audio signal.
To achieve this, the circuit typically includes several key components: an antenna for receiving the FM signal, a radio frequency (RF) amplifier to boost the signal strength, and a demodulator stage that converts the FM signal back into an audio frequency (AF) signal. The demodulation process often employs a phase-locked loop (PLL) or a discriminator circuit, which can effectively track the variations in frequency of the incoming FM signal.
After demodulation, the audio signal may undergo additional processing, such as filtering to remove any residual RF components and amplification to bring the signal to a suitable level for output. The final output stage may include a low-pass filter to ensure that only the desired audio frequencies are passed through, effectively eliminating any high-frequency noise that may have been introduced during the transmission.
The circuit's design must also consider factors such as signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), distortion, and the overall bandwidth to ensure high-quality audio reproduction. Proper layout and component selection are critical to minimize interference and maintain signal integrity throughout the circuit.The circuit recovers an FM audio signal that variesfrom less than 1 kHz to about 10 kHz. 🔗 External reference