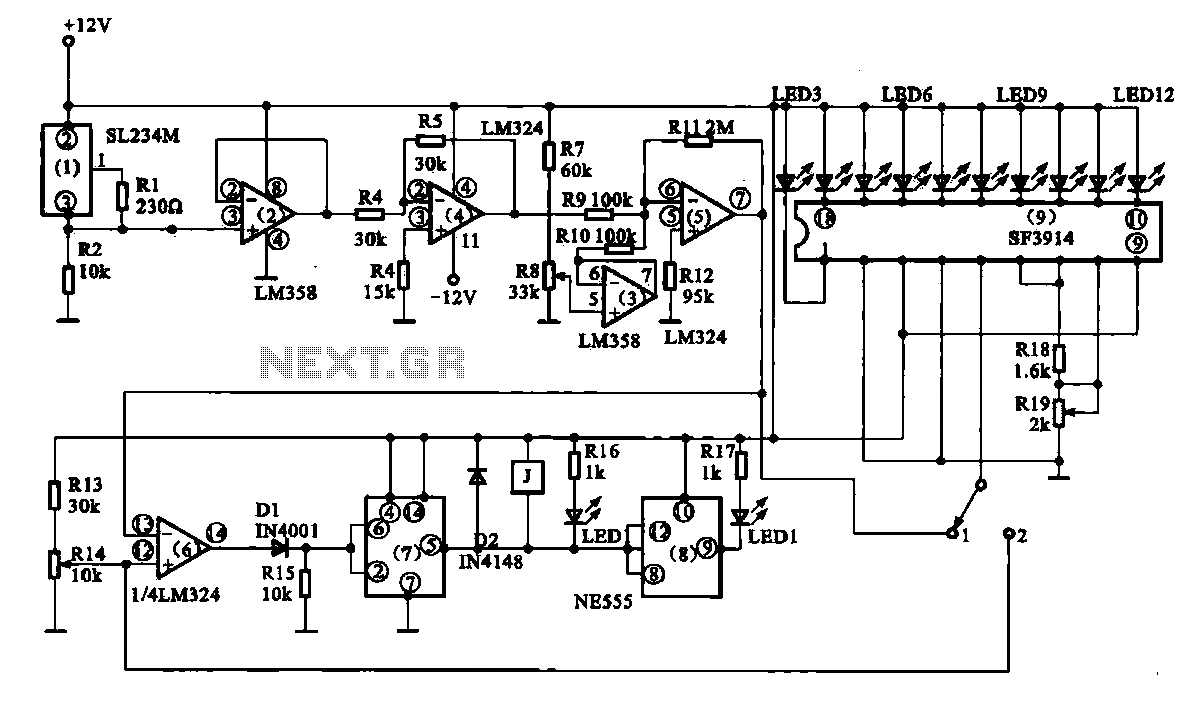
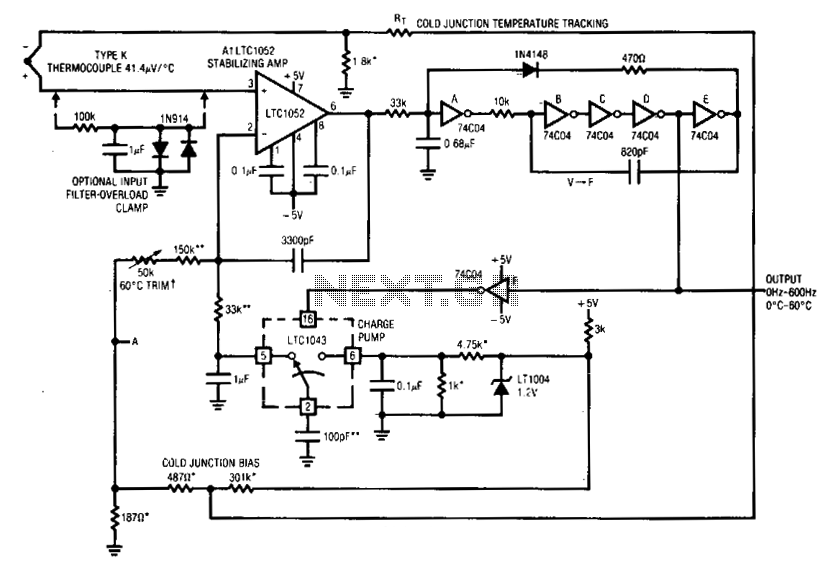
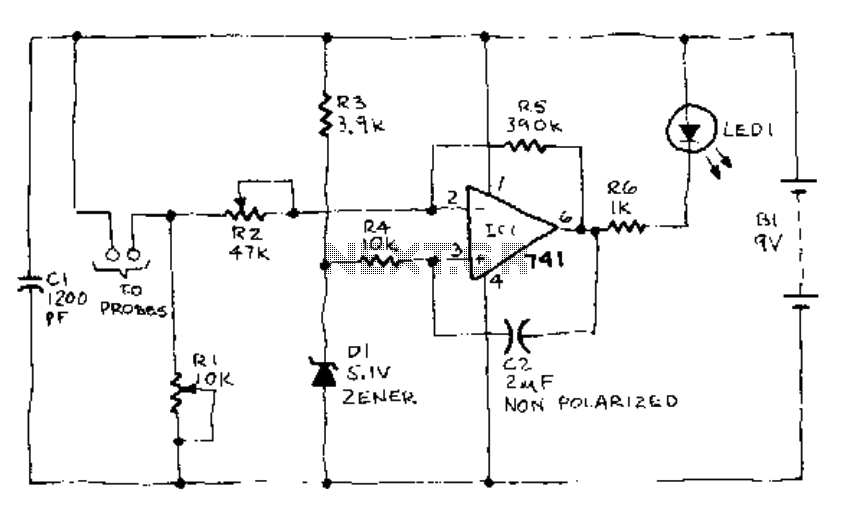
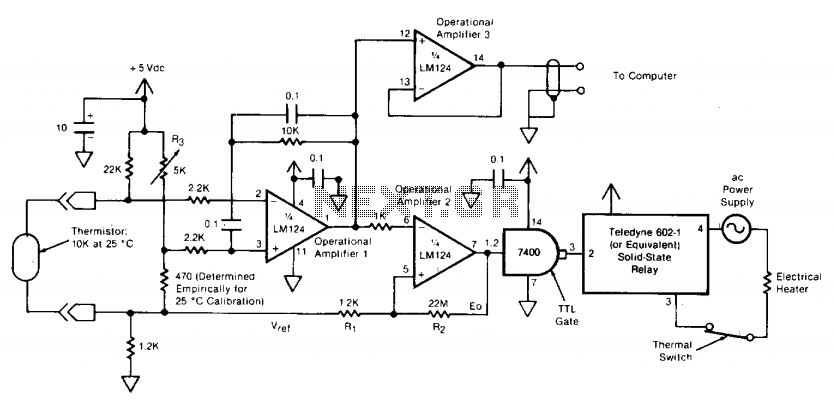
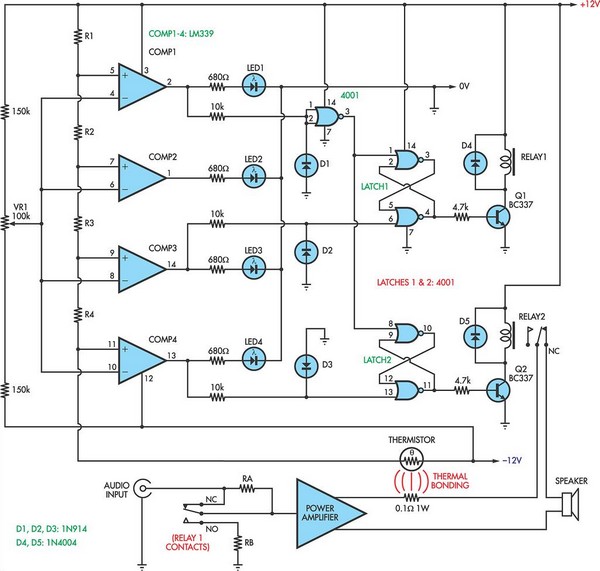
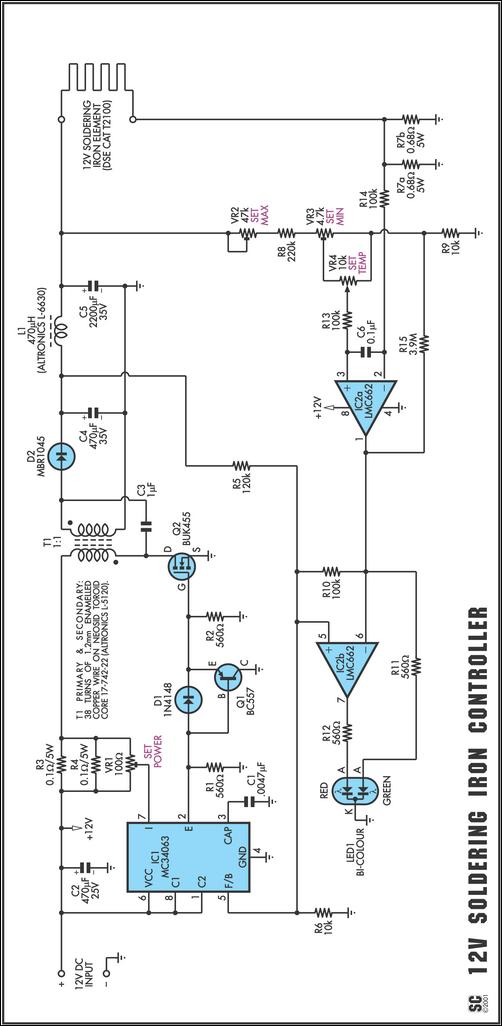
Temperature Monitor
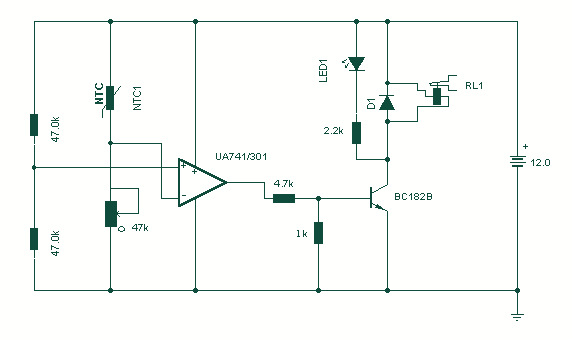
Using a thermistor in the position shown makes a heat activated sensor. A change in temperature will alter the output of the opamp and energize the relay and light the LED. Swapping the position of the thermistor and 47k resistor makes a cold or frost alarm.
The described circuit utilizes a thermistor as a temperature-sensitive element within a thermal sensing application. The thermistor, which is a type of resistor whose resistance varies significantly with temperature, is strategically placed to detect temperature changes. When the temperature rises, the resistance of the thermistor decreases, leading to a change in voltage at the input of the operational amplifier (op-amp). This voltage change is processed by the op-amp, which is configured as a comparator.
The output of the op-amp is connected to a relay, which acts as a switch to control a higher power circuit. When the op-amp detects a temperature increase beyond a predetermined threshold, it energizes the relay, allowing current to flow through the load, which could be an LED or another device. The LED serves as a visual indicator that the temperature has crossed the set point.
In an alternative configuration, swapping the positions of the thermistor and a 47kΩ resistor allows the circuit to function as a cold or frost alarm. In this setup, the thermistor is positioned such that it responds to lower temperatures, increasing its resistance as the temperature drops. This change in resistance will again alter the voltage input to the op-amp, but in this case, it will trigger the relay when the temperature falls below a specific threshold, indicating a frost condition.
The circuit may also include additional components such as diodes for flyback protection across the relay coil, capacitors for filtering, and potentially adjustable resistors to calibrate the sensitivity of the temperature detection. The design's simplicity and effectiveness make it suitable for various applications, including home automation systems, HVAC controls, and environmental monitoring systems.Using a thermistor in the position shown makes a heat activated sensor. A change in temperature will alter the output of the opamp and energize the relay and light the LED. Swapping the position of the< thermistor and 47k resistor makes a cold or frost alarm. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit utilizes a thermistor as a temperature-sensitive element within a thermal sensing application. The thermistor, which is a type of resistor whose resistance varies significantly with temperature, is strategically placed to detect temperature changes. When the temperature rises, the resistance of the thermistor decreases, leading to a change in voltage at the input of the operational amplifier (op-amp). This voltage change is processed by the op-amp, which is configured as a comparator.
The output of the op-amp is connected to a relay, which acts as a switch to control a higher power circuit. When the op-amp detects a temperature increase beyond a predetermined threshold, it energizes the relay, allowing current to flow through the load, which could be an LED or another device. The LED serves as a visual indicator that the temperature has crossed the set point.
In an alternative configuration, swapping the positions of the thermistor and a 47kΩ resistor allows the circuit to function as a cold or frost alarm. In this setup, the thermistor is positioned such that it responds to lower temperatures, increasing its resistance as the temperature drops. This change in resistance will again alter the voltage input to the op-amp, but in this case, it will trigger the relay when the temperature falls below a specific threshold, indicating a frost condition.
The circuit may also include additional components such as diodes for flyback protection across the relay coil, capacitors for filtering, and potentially adjustable resistors to calibrate the sensitivity of the temperature detection. The design's simplicity and effectiveness make it suitable for various applications, including home automation systems, HVAC controls, and environmental monitoring systems.Using a thermistor in the position shown makes a heat activated sensor. A change in temperature will alter the output of the opamp and energize the relay and light the LED. Swapping the position of the< thermistor and 47k resistor makes a cold or frost alarm. 🔗 External reference