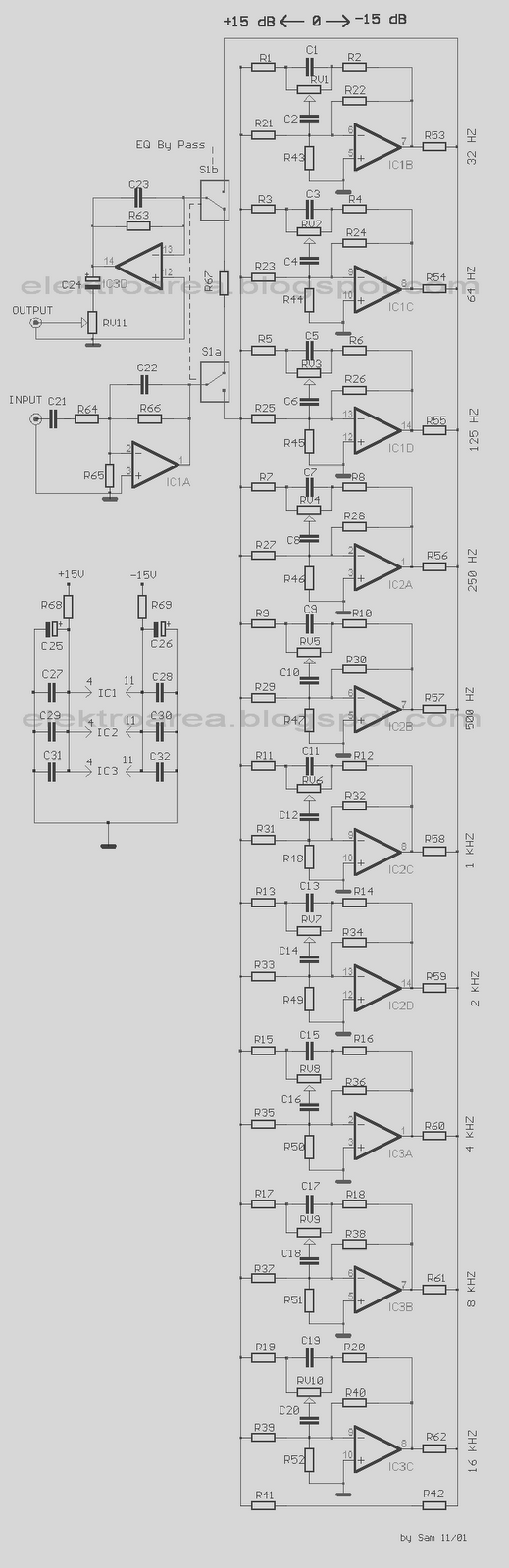
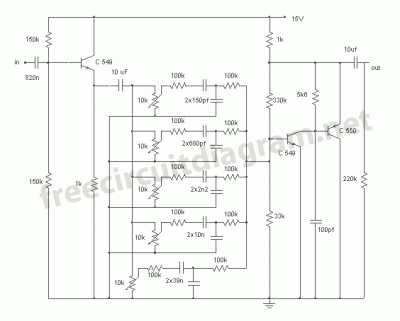
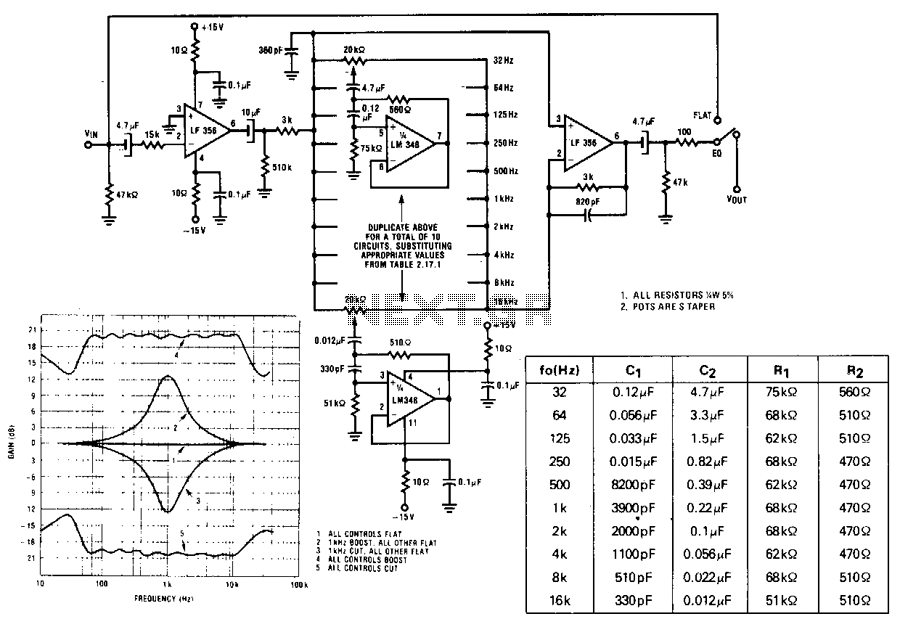
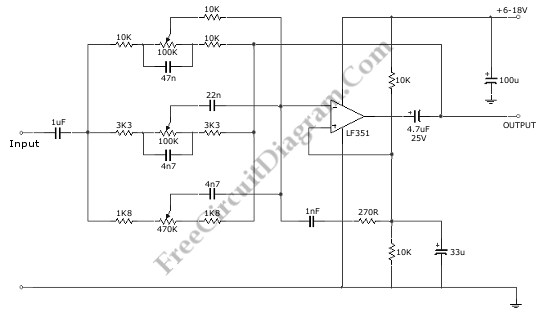
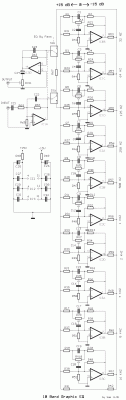
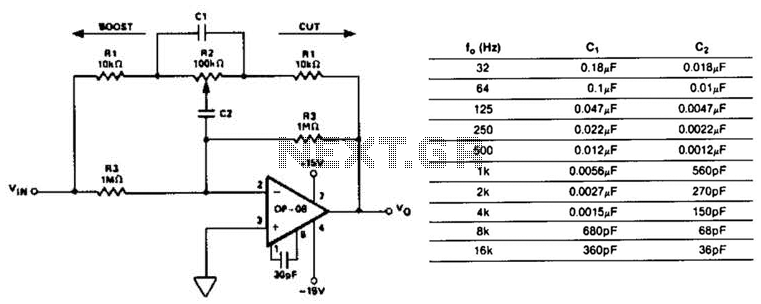
Ten-Band Equalizer

The equalizer discussed in this article is appropriate for use with high-fidelity installations, public address systems, mixers, and electronic musical instruments.
The equalizer is an essential audio processing device that allows for the adjustment of specific frequency bands within an audio signal. This capability is crucial in various applications, including high-fidelity audio systems, where sound quality is paramount, and public address systems, where clarity and intelligibility of speech are critical.
In a typical hi-fi installation, an equalizer can enhance the listening experience by compensating for acoustic deficiencies in the environment or the inherent characteristics of the audio equipment. Users can tailor the frequency response to their preferences, ensuring that vocals, instruments, and other audio elements are balanced and clear.
For public address systems, equalizers help to mitigate feedback issues and enhance speech intelligibility. By adjusting the gain of specific frequency ranges, the equalizer can reduce unwanted resonances and boost frequencies that are crucial for clear communication, such as mid-range frequencies where human speech typically resides.
In mixers, equalizers are often integrated to provide sound engineers with the tools necessary to shape the audio signal from multiple sources. This allows for the blending of different audio tracks in a way that maintains clarity and prevents muddiness in the mix.
In the context of electronic musical instruments, equalizers can be used to sculpt the sound of synthesized tones or sampled audio. Musicians and producers can manipulate the tonal characteristics of their instruments, creating unique sounds that fit well within a musical composition.
Overall, the equalizer serves as a versatile tool in audio processing, enabling users to enhance sound quality across various applications, ensuring that the final output meets the desired acoustic standards.The equalizer presented in this article is suitable for use with hi-fi installations, public-address systems. mixers and electronic musical instruments. T.. 🔗 External reference
The equalizer is an essential audio processing device that allows for the adjustment of specific frequency bands within an audio signal. This capability is crucial in various applications, including high-fidelity audio systems, where sound quality is paramount, and public address systems, where clarity and intelligibility of speech are critical.
In a typical hi-fi installation, an equalizer can enhance the listening experience by compensating for acoustic deficiencies in the environment or the inherent characteristics of the audio equipment. Users can tailor the frequency response to their preferences, ensuring that vocals, instruments, and other audio elements are balanced and clear.
For public address systems, equalizers help to mitigate feedback issues and enhance speech intelligibility. By adjusting the gain of specific frequency ranges, the equalizer can reduce unwanted resonances and boost frequencies that are crucial for clear communication, such as mid-range frequencies where human speech typically resides.
In mixers, equalizers are often integrated to provide sound engineers with the tools necessary to shape the audio signal from multiple sources. This allows for the blending of different audio tracks in a way that maintains clarity and prevents muddiness in the mix.
In the context of electronic musical instruments, equalizers can be used to sculpt the sound of synthesized tones or sampled audio. Musicians and producers can manipulate the tonal characteristics of their instruments, creating unique sounds that fit well within a musical composition.
Overall, the equalizer serves as a versatile tool in audio processing, enabling users to enhance sound quality across various applications, ensuring that the final output meets the desired acoustic standards.The equalizer presented in this article is suitable for use with hi-fi installations, public-address systems. mixers and electronic musical instruments. T.. 🔗 External reference