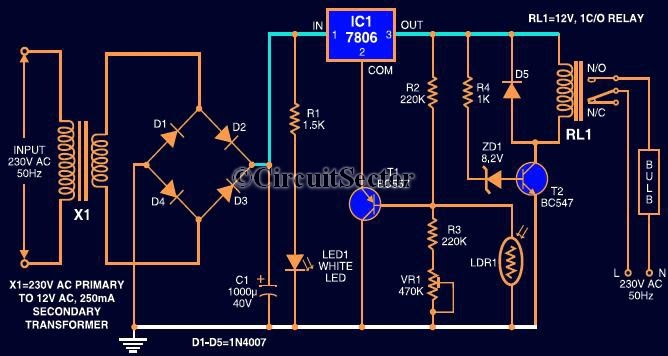
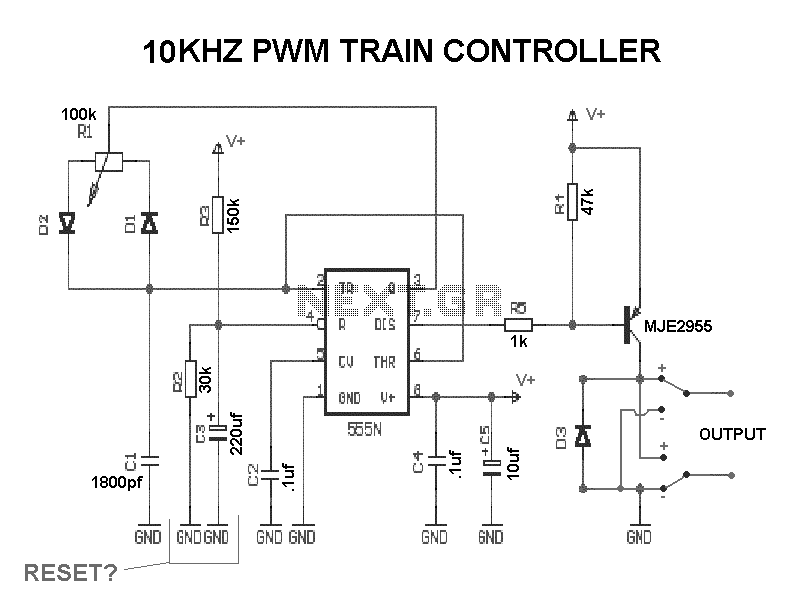
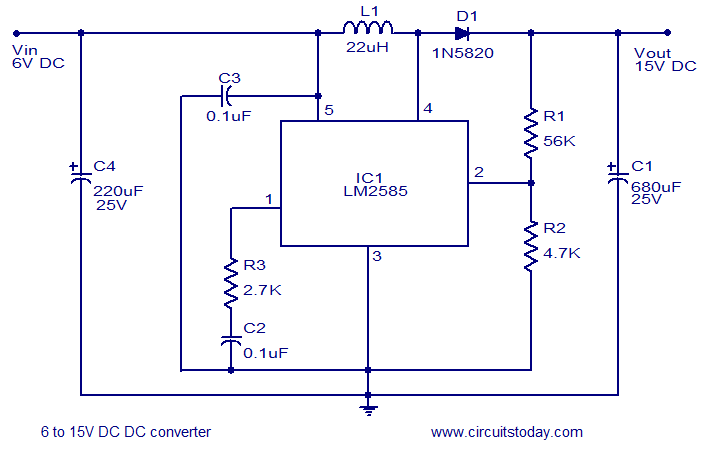
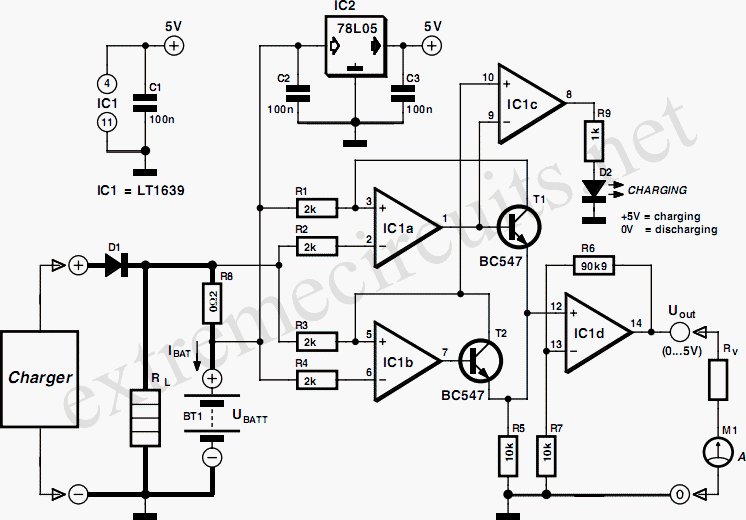
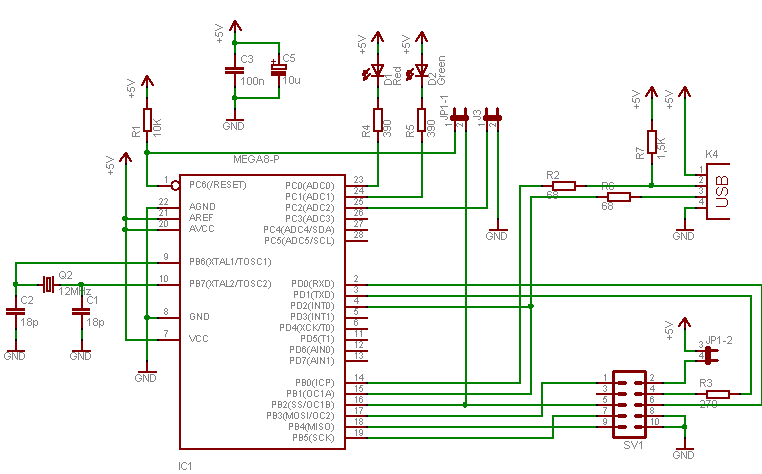
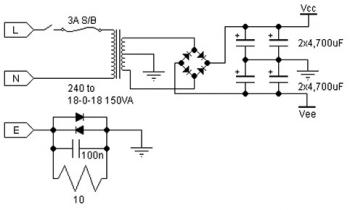
The simple joule thief using AVR microcontroller
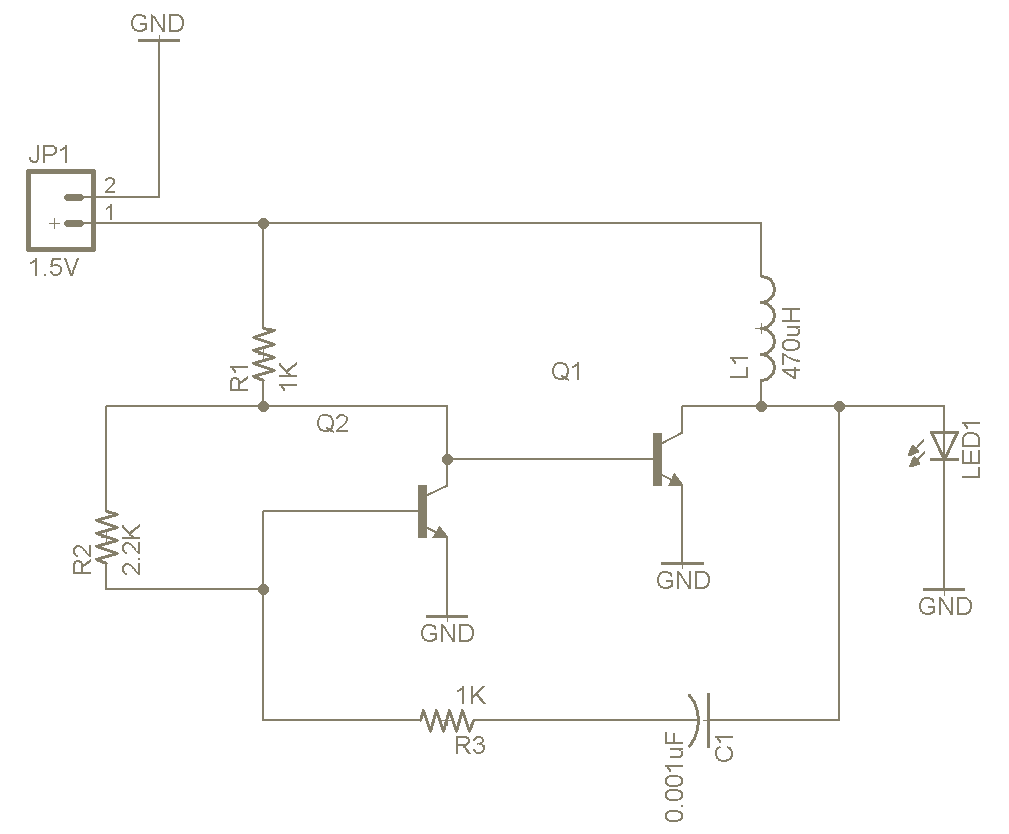
The Joule Thief is a straightforward and uncomplicated device, yet its functionality is remarkable. It can utilize a battery that is otherwise deemed unusable in any other electronic device, and it is very easy to construct on a breadboard due to its minimal parts count. Refer to the schematic for details.
The Joule Thief is a simple DC-DC converter designed to extract usable voltage from a nearly depleted battery, such as a single-cell alkaline battery that has dropped below the nominal operating voltage of many electronic devices. The circuit typically consists of a few key components: a transistor, a resistor, an inductor (or transformer), and a diode.
In operation, the Joule Thief begins with the battery supplying power to the base of the transistor through a resistor. This initiates the switching action of the transistor, allowing current to flow through the inductor. The inductor stores energy in its magnetic field as the current increases. When the transistor turns off, the collapsing magnetic field induces a voltage spike in the opposite direction, which is significantly higher than the original battery voltage. This induced voltage is then rectified by the diode and can be utilized to power a low-voltage LED or other electronic components.
The low parts count makes the Joule Thief an excellent project for beginners in electronics, as it allows for hands-on experience with fundamental concepts such as inductance, switching, and energy conversion. The schematic typically shows the arrangement of components: the transistor is connected to the inductor, which is in turn connected to the battery and the load (often an LED). The simplicity of the design facilitates easy assembly on a breadboard, making it an ideal educational tool for understanding basic electronic principles and energy efficiency.
Overall, the Joule Thief exemplifies innovative circuit design by demonstrating how to harness energy from sources that would otherwise be discarded, thus promoting sustainability in electronic applications.The Joule Thief is such an easy and simple device, but what it does is amazing. It can use a battery that is not usable in any other electronic device and It is super simple to make on a breadboard because it has such a low parts count. Look at the schematic to figure it out. 🔗 External reference
The Joule Thief is a simple DC-DC converter designed to extract usable voltage from a nearly depleted battery, such as a single-cell alkaline battery that has dropped below the nominal operating voltage of many electronic devices. The circuit typically consists of a few key components: a transistor, a resistor, an inductor (or transformer), and a diode.
In operation, the Joule Thief begins with the battery supplying power to the base of the transistor through a resistor. This initiates the switching action of the transistor, allowing current to flow through the inductor. The inductor stores energy in its magnetic field as the current increases. When the transistor turns off, the collapsing magnetic field induces a voltage spike in the opposite direction, which is significantly higher than the original battery voltage. This induced voltage is then rectified by the diode and can be utilized to power a low-voltage LED or other electronic components.
The low parts count makes the Joule Thief an excellent project for beginners in electronics, as it allows for hands-on experience with fundamental concepts such as inductance, switching, and energy conversion. The schematic typically shows the arrangement of components: the transistor is connected to the inductor, which is in turn connected to the battery and the load (often an LED). The simplicity of the design facilitates easy assembly on a breadboard, making it an ideal educational tool for understanding basic electronic principles and energy efficiency.
Overall, the Joule Thief exemplifies innovative circuit design by demonstrating how to harness energy from sources that would otherwise be discarded, thus promoting sustainability in electronic applications.The Joule Thief is such an easy and simple device, but what it does is amazing. It can use a battery that is not usable in any other electronic device and It is super simple to make on a breadboard because it has such a low parts count. Look at the schematic to figure it out. 🔗 External reference