Triac Optimization Circuits Schematic Diagram
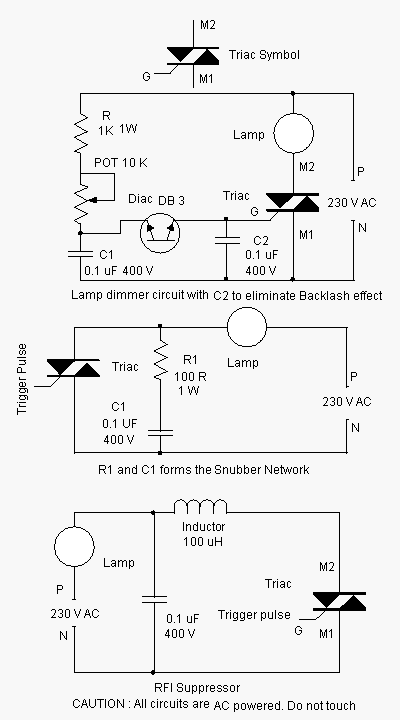
Advanced power control systems utilize electronic components such as thyristors for power switching, motor control, and other applications. These systems are involved in inverter design, lamp dimming, and speed control of motors. Triacs are the most commonly used semiconductor devices in power control and switching applications. Electronic power control circuits are designed to manage the distribution of AC or DC power levels. Such circuits can be used to manually switch power to electrical devices or automatically adjust power based on parameters like temperature or light intensity. A Triac, or Triode for Alternating Current, is an electronic device that consists of two silicon-controlled rectifiers (SCRs) connected in reverse, with their gates linked together. This configuration results in a bi-directional electronic switch that can conduct current in either direction when triggered. Like SCRs, Triacs are three-terminal devices. The MT1 and MT2 terminals are used to conduct current, while the gate terminal (G) is used for triggering. A Triac can be triggered by either a positive or negative voltage applied to its gate. When the voltage on the MT2 terminal is positive with respect to MT1 and a positive voltage is applied to the gate, the Triac conducts. Conversely, if the voltage is reversed and a negative voltage is applied to the gate, the other SCR conducts. A minimum holding current (Ih) must be maintained to keep the Triac conducting. Triacs have some inherent drawbacks, including rate effect, RF interference, and backlash effect. Proper design of Triac-based circuits can enhance their performance. The rate effect occurs due to the inherent capacitance between the MT1 terminal and the gate. When a rapidly increasing voltage is applied to the MT1 terminal, it can generate sufficient gate voltage to trigger the Triac. This is particularly problematic in inductive loads, where high inrush currents can occur. An R-C snubber circuit can mitigate the rate effect and facilitate smoother switching. The R-C snubber is connected between the MT2 and MT1 terminals of the Triac. RF interference is another significant issue with Triac switching. When the Triac is gated on, the load current changes rapidly, generating RF pulses, especially at zero-crossing points. This RF generation is problematic in circuits like lamp dimmers and can be reduced using an L-C-RFI suppression network. Control hysteresis or backlash can develop in Triac-controlled lamp dimmers when the gate current is regulated by a variable potentiometer. As the resistance of the potentiometer increases, the lamp brightness decreases, and it may not turn on until the resistance drops to a few ohms. This behavior is due to the capacitor discharging through the Diac when the Triac fires, resulting in the backlash effect. This issue can be mitigated by adding a resistor in series with the Diac or by including a capacitor connected to the Triac gate, which helps to dampen the backlash effect.
Advanced power control systems leverage electronic components like thyristors for efficient power management in various applications, including inverter design, motor speed control, and lamp dimming. Triacs, which are semiconductor devices that act as bi-directional switches, play a crucial role in these systems. Their ability to conduct current in both directions upon triggering makes them ideal for AC power control. The configuration of two SCRs connected in reverse, with a common gate, allows for versatile operation.
In practical applications, electronic power control circuits are designed to handle both AC and DC power sources, enabling manual or automatic control of electrical devices based on specific parameters such as temperature or light intensity. The Triac’s three-terminal design includes two main terminals (MT1 and MT2) for current conduction and a gate terminal for triggering. The triggering mechanism allows for flexibility, as the device can be activated by either a positive or negative voltage at the gate.
However, the operation of Triacs is not without challenges. The rate effect, caused by the inherent capacitance between the MT1 terminal and the gate, can lead to unintended triggering due to rapid voltage changes. This effect is particularly problematic in inductive loads, where high inrush currents can cause significant transients. To address this, an R-C snubber circuit is often employed to smooth out the voltage transitions and prevent false triggering.
Additionally, RF interference is a concern in Triac switching applications. The rapid changes in load current during switching can generate RF pulses, especially at critical points in the AC cycle. This interference can disrupt the performance of sensitive devices, such as lamp dimmers. Implementing an L-C-RFI suppression network can effectively reduce these unwanted emissions.
Control hysteresis, or backlash, is another issue that can arise in Triac-controlled circuits, particularly in lamp dimmers. This phenomenon occurs when the resistance of a variable potentiometer affects the gate current, leading to inconsistent lamp brightness. To mitigate this, design modifications such as adding a resistor in series with the Diac or incorporating a capacitor to the Triac gate can stabilize operation and improve performance.
Overall, careful design and implementation of Triac-based circuits can enhance their reliability and effectiveness in power control applications, ensuring smooth operation and minimizing undesired effects.Advanced power control systems make use of electronic plans like Thyristors pro power switching, part control, grinder and so forth. These diplomacy and realize applications participating in inverter design, ability control in lamps, quickness control of motors and so on.
Triacs are the largely general semiconductor procedure used in power control and switching applications. The electronic power control circuits are designed to control the distribution before levels of AC or DC power sources. Such power control circuits can exist used to manually switch power to electrical strategy otherwise to switch power inevitably after parameters such while heat before light intensities try away from fixed level Triac or else Triode intended for alternating current is an electronic device equivalent to two silicon controlled rectifiers together hip inverse like (but with polarity reversed) with their gates connected as one.
This results in a bi-directional electronic switch`, which can conduct current in either direction after triggered. Like SCR, Triac is besides a three terminal device. The MT1 and MT2 (key Terminals 1 and 2) terminals are used to pass current inside either direction while the third terminal G ( gate ) is used to fire trigger pulse to the device.
Triac can live triggered by either a sure before unconstructive voltage functional to its gate electrode. as soon as the voltage on the MT2 terminal is positive with respect to MT2 and a positive voltage is functional to the gate, the missing SCR` appearing in the triac conducts.
If the voltage is reversed and a unconstructive voltage is useful to the gate, the` authentic SCR` conducts. tiniest holding current Ih` have to befall maintained to keep the triac conducting. Triacs are borne with a few inherent drawbacks, which wish chew on featuring in their working. conscientious crafty of triac based circuits impart better performance in their working. The central drawbacks of Triacs are Rate effect, RF interference Backlash effect and so forth. Involving the MT1 terminal and gate of a triac, an` home capacitance` exists. If the MT1 terminal is supplied with a sharply increasing voltage, it causes as much as necessary gate voltage break through to trigger the triac.
This condition is referred to equally Rate Effect`, an surplus effect caused generally by the lofty transients during the AC line. Rate effect furthermore occurs as soon as the load is switched on due to high inrush voltage`. Rate effect is awful particularly in driving inductive heaps such as motor since the load current and voltage are old hat of point`.
An R-C Snubber arrangement desire curtail the rate effect and makes the switching clean. The R-C Snubber network is connected connecting the MT2 and MT1 terminals of triac to the same extent exposed happening the assume. Unwelcome RF generation is an extra chief crisis encountered in triac switching. both stretch the triac is gated on its load, the load current switches sharply from nothing to a from top to bottom price depending on the load resistance and supply voltage.
This switching clash (now a hardly any microseconds) generates a pulse of RF1. It is slightest as the triac is triggered close to 00 and 1800 nil crossing points but most in 90 0 wave form. This is as by the side of 00 and 1800 nought crossing points, switch on current` is lowest possible. Switch on current is most on 900 producing very high RFI. The strength of RFI is proportional to the chunk of the wire between the load with the triac. The RFI is irritating particularly arrived lamp dimmer circuits and can be situated eliminated using a austere L-C- RFI suppression group.
A serious Control Hysteresis` otherwise Backlash` develops in triac controlled lamp dimmer circuits, what time the gate current is controlled by a adjustable potentiometer. while the resistance of pot measuring device increases to utmost, the brightness of the lamp reduces to lowest amount.
similar to this, the lamp in no way turns on turn over the resistance of the pot measuring device is on sale to a not many ohms, say 50 to 70 ohms. This occurs due to the discharging of capacitor connected to the Diac. Whilst the triac fires, capacitor discharges by the Diac and generate the backlash effect`. This crisis can be situated clearly rectified by involving a 47 to 100 ohms resistor fashionable cycle with the Diac otherwise count a capacitor (C2) to the gate of the triac.
This capacitor (C2) preference stupid down the backlash effect and the packed excursion effect can be located obtained. The connection of capacitor is exposed in map. You are reading the Circuits of Triac Optimization Circuits And this circuit permalink url it is 🔗 External reference
Advanced power control systems leverage electronic components like thyristors for efficient power management in various applications, including inverter design, motor speed control, and lamp dimming. Triacs, which are semiconductor devices that act as bi-directional switches, play a crucial role in these systems. Their ability to conduct current in both directions upon triggering makes them ideal for AC power control. The configuration of two SCRs connected in reverse, with a common gate, allows for versatile operation.
In practical applications, electronic power control circuits are designed to handle both AC and DC power sources, enabling manual or automatic control of electrical devices based on specific parameters such as temperature or light intensity. The Triac’s three-terminal design includes two main terminals (MT1 and MT2) for current conduction and a gate terminal for triggering. The triggering mechanism allows for flexibility, as the device can be activated by either a positive or negative voltage at the gate.
However, the operation of Triacs is not without challenges. The rate effect, caused by the inherent capacitance between the MT1 terminal and the gate, can lead to unintended triggering due to rapid voltage changes. This effect is particularly problematic in inductive loads, where high inrush currents can cause significant transients. To address this, an R-C snubber circuit is often employed to smooth out the voltage transitions and prevent false triggering.
Additionally, RF interference is a concern in Triac switching applications. The rapid changes in load current during switching can generate RF pulses, especially at critical points in the AC cycle. This interference can disrupt the performance of sensitive devices, such as lamp dimmers. Implementing an L-C-RFI suppression network can effectively reduce these unwanted emissions.
Control hysteresis, or backlash, is another issue that can arise in Triac-controlled circuits, particularly in lamp dimmers. This phenomenon occurs when the resistance of a variable potentiometer affects the gate current, leading to inconsistent lamp brightness. To mitigate this, design modifications such as adding a resistor in series with the Diac or incorporating a capacitor to the Triac gate can stabilize operation and improve performance.
Overall, careful design and implementation of Triac-based circuits can enhance their reliability and effectiveness in power control applications, ensuring smooth operation and minimizing undesired effects.Advanced power control systems make use of electronic plans like Thyristors pro power switching, part control, grinder and so forth. These diplomacy and realize applications participating in inverter design, ability control in lamps, quickness control of motors and so on.
Triacs are the largely general semiconductor procedure used in power control and switching applications. The electronic power control circuits are designed to control the distribution before levels of AC or DC power sources. Such power control circuits can exist used to manually switch power to electrical strategy otherwise to switch power inevitably after parameters such while heat before light intensities try away from fixed level Triac or else Triode intended for alternating current is an electronic device equivalent to two silicon controlled rectifiers together hip inverse like (but with polarity reversed) with their gates connected as one.
This results in a bi-directional electronic switch`, which can conduct current in either direction after triggered. Like SCR, Triac is besides a three terminal device. The MT1 and MT2 (key Terminals 1 and 2) terminals are used to pass current inside either direction while the third terminal G ( gate ) is used to fire trigger pulse to the device.
Triac can live triggered by either a sure before unconstructive voltage functional to its gate electrode. as soon as the voltage on the MT2 terminal is positive with respect to MT2 and a positive voltage is functional to the gate, the missing SCR` appearing in the triac conducts.
If the voltage is reversed and a unconstructive voltage is useful to the gate, the` authentic SCR` conducts. tiniest holding current Ih` have to befall maintained to keep the triac conducting. Triacs are borne with a few inherent drawbacks, which wish chew on featuring in their working. conscientious crafty of triac based circuits impart better performance in their working. The central drawbacks of Triacs are Rate effect, RF interference Backlash effect and so forth. Involving the MT1 terminal and gate of a triac, an` home capacitance` exists. If the MT1 terminal is supplied with a sharply increasing voltage, it causes as much as necessary gate voltage break through to trigger the triac.
This condition is referred to equally Rate Effect`, an surplus effect caused generally by the lofty transients during the AC line. Rate effect furthermore occurs as soon as the load is switched on due to high inrush voltage`. Rate effect is awful particularly in driving inductive heaps such as motor since the load current and voltage are old hat of point`.
An R-C Snubber arrangement desire curtail the rate effect and makes the switching clean. The R-C Snubber network is connected connecting the MT2 and MT1 terminals of triac to the same extent exposed happening the assume. Unwelcome RF generation is an extra chief crisis encountered in triac switching. both stretch the triac is gated on its load, the load current switches sharply from nothing to a from top to bottom price depending on the load resistance and supply voltage.
This switching clash (now a hardly any microseconds) generates a pulse of RF1. It is slightest as the triac is triggered close to 00 and 1800 nil crossing points but most in 90 0 wave form. This is as by the side of 00 and 1800 nought crossing points, switch on current` is lowest possible. Switch on current is most on 900 producing very high RFI. The strength of RFI is proportional to the chunk of the wire between the load with the triac. The RFI is irritating particularly arrived lamp dimmer circuits and can be situated eliminated using a austere L-C- RFI suppression group.
A serious Control Hysteresis` otherwise Backlash` develops in triac controlled lamp dimmer circuits, what time the gate current is controlled by a adjustable potentiometer. while the resistance of pot measuring device increases to utmost, the brightness of the lamp reduces to lowest amount.
similar to this, the lamp in no way turns on turn over the resistance of the pot measuring device is on sale to a not many ohms, say 50 to 70 ohms. This occurs due to the discharging of capacitor connected to the Diac. Whilst the triac fires, capacitor discharges by the Diac and generate the backlash effect`. This crisis can be situated clearly rectified by involving a 47 to 100 ohms resistor fashionable cycle with the Diac otherwise count a capacitor (C2) to the gate of the triac.
This capacitor (C2) preference stupid down the backlash effect and the packed excursion effect can be located obtained. The connection of capacitor is exposed in map. You are reading the Circuits of Triac Optimization Circuits And this circuit permalink url it is 🔗 External reference