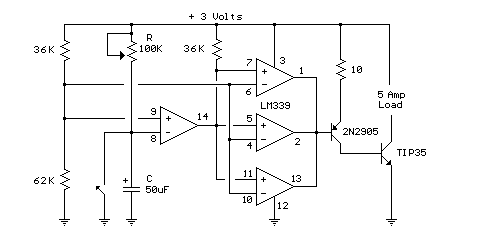
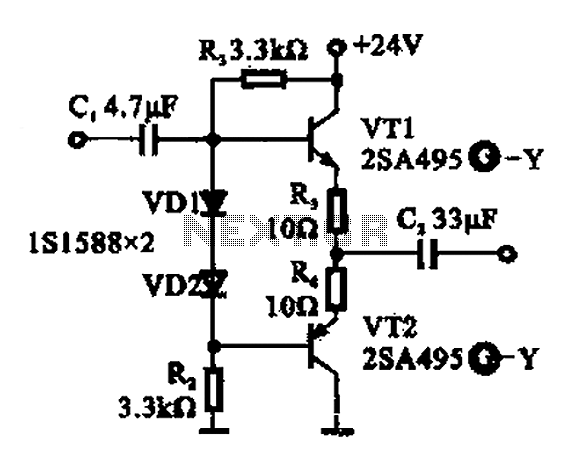
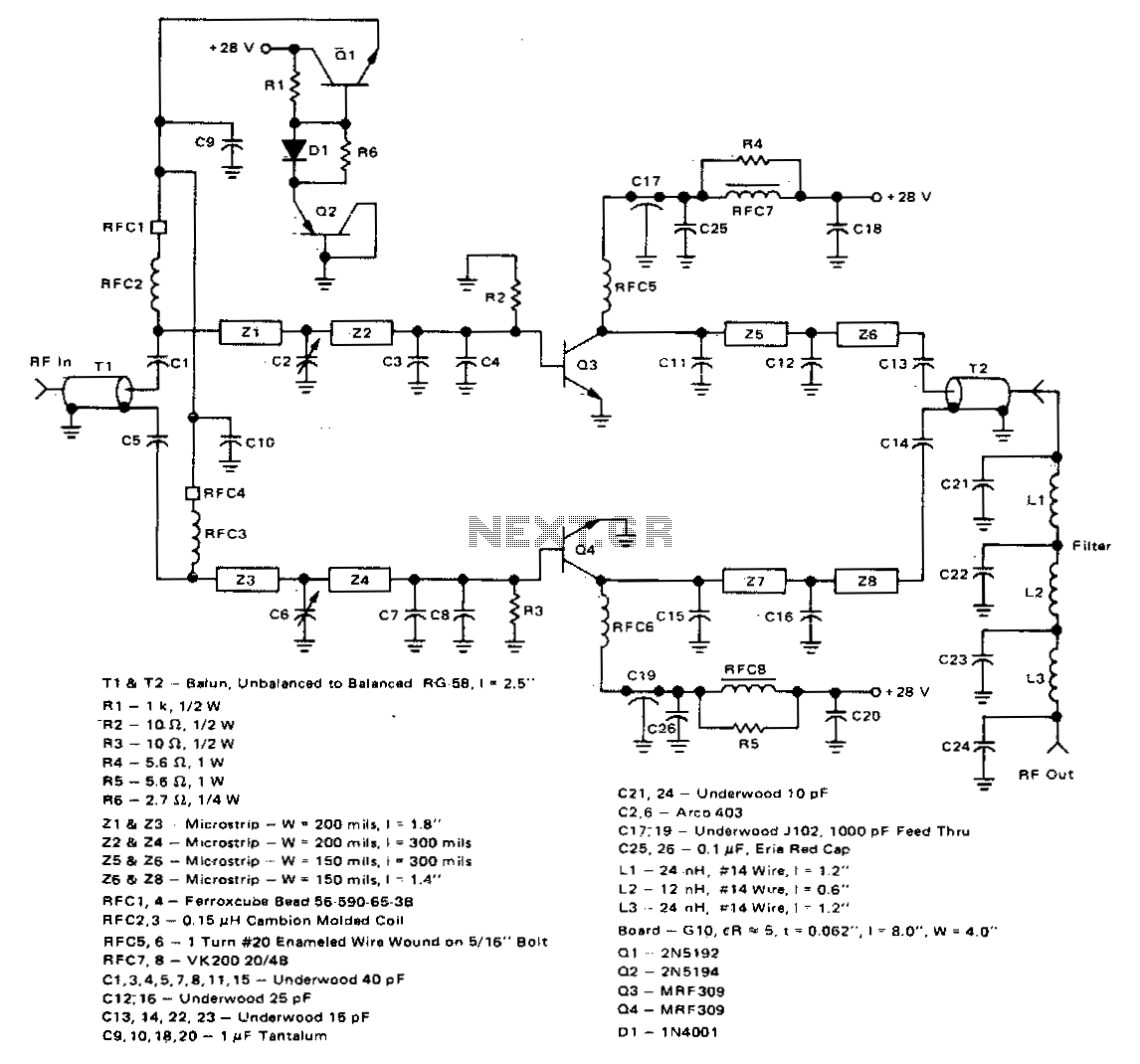
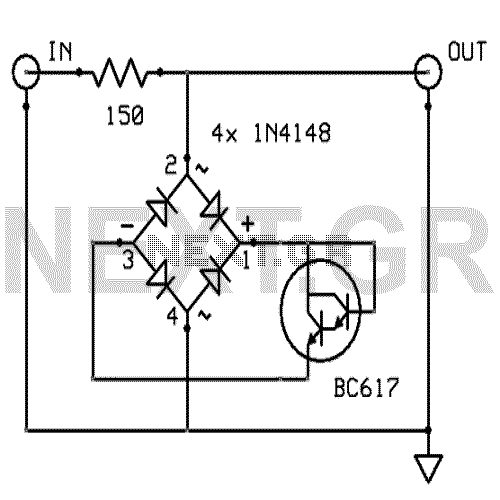
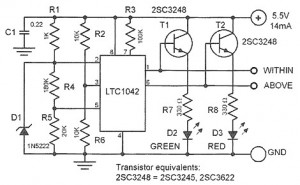
Tube amplifier input voltage input
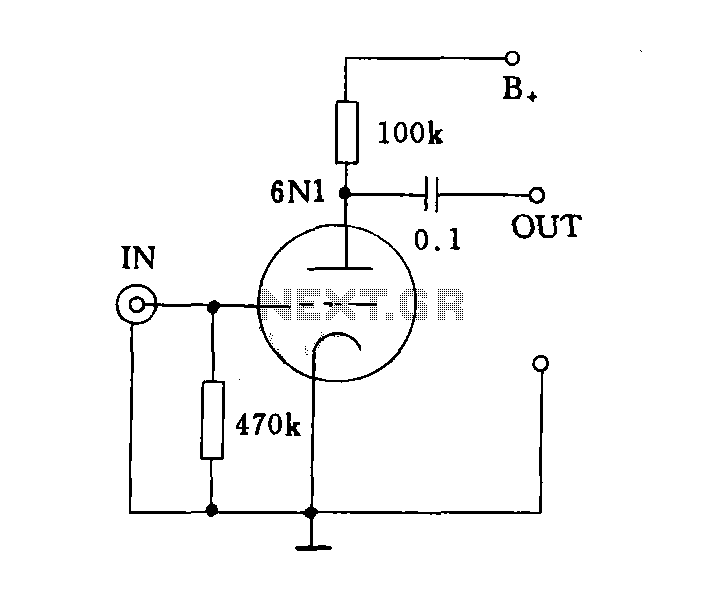
The input impedance can be classified into high-impedance and low-impedance inputs based on the requirements of various audio equipment and the load impedance. High-impedance input mode is typically utilized in general audio devices such as CD players, VCD players, DVD players, recording decks, and tuner input voltage amplifiers.
In audio systems, the input impedance plays a critical role in determining the compatibility between different components. High-impedance inputs are designed to connect with sources that have a high output impedance, ensuring minimal loading on the source device. This is especially important in audio applications, where maintaining signal integrity is crucial for optimal performance.
For instance, devices like CD players and tuners often utilize high-impedance inputs to interface with microphones or other audio sources, which may have varying output impedances. The high input impedance allows these devices to receive signals without significantly affecting the source's performance, preserving audio quality and dynamic range.
Conversely, low-impedance inputs are typically used in applications where the input device can drive the load effectively, such as in professional audio equipment or mixing consoles. These inputs are designed to handle lower output impedances, ensuring that the audio signal is transmitted efficiently without distortion.
In summary, understanding the distinction between high-impedance and low-impedance inputs is essential for designing audio systems that meet the specific requirements of various devices, ensuring optimal performance and sound quality across the entire audio chain.Depending on the input impedance can be divided into a high-impedance input and low impedance input in two ways. Its major input in various audio equipment to the requirements of the load impedance to decide.High impedance input mode: As a general audio equipment such as CD, VCD, DVD, recording deck, tuner input voltage amplifier.
In audio systems, the input impedance plays a critical role in determining the compatibility between different components. High-impedance inputs are designed to connect with sources that have a high output impedance, ensuring minimal loading on the source device. This is especially important in audio applications, where maintaining signal integrity is crucial for optimal performance.
For instance, devices like CD players and tuners often utilize high-impedance inputs to interface with microphones or other audio sources, which may have varying output impedances. The high input impedance allows these devices to receive signals without significantly affecting the source's performance, preserving audio quality and dynamic range.
Conversely, low-impedance inputs are typically used in applications where the input device can drive the load effectively, such as in professional audio equipment or mixing consoles. These inputs are designed to handle lower output impedances, ensuring that the audio signal is transmitted efficiently without distortion.
In summary, understanding the distinction between high-impedance and low-impedance inputs is essential for designing audio systems that meet the specific requirements of various devices, ensuring optimal performance and sound quality across the entire audio chain.Depending on the input impedance can be divided into a high-impedance input and low impedance input in two ways. Its major input in various audio equipment to the requirements of the load impedance to decide.High impedance input mode: As a general audio equipment such as CD, VCD, DVD, recording deck, tuner input voltage amplifier.
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713