Ultra Bright LED Lamp
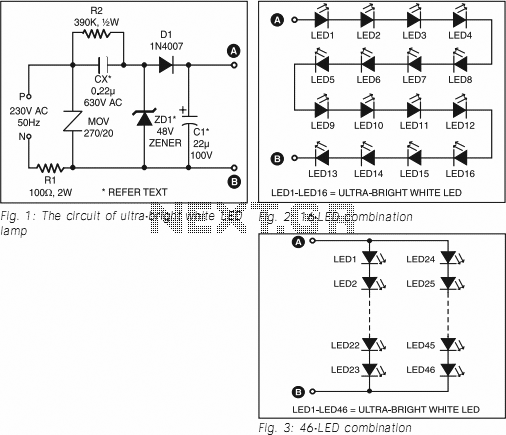
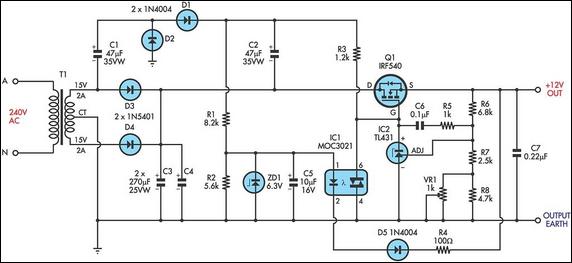
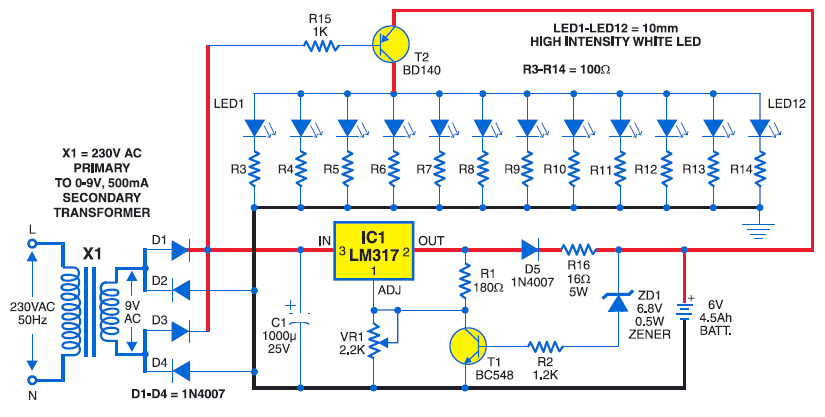
This ultra-bright white LED lamp operates on 230V AC with minimal power consumption. It is suitable for illuminating VU meters, SWR meters, and similar applications. The cost of ultra-bright LEDs available in the market ranges from Rs 8 to 15. These LEDs emit a bright white light with a luminous intensity between 1000 to 6000 mCd, resembling the brightness of a welding arc, and function at 3 volts with a current of 10 mA. The maximum voltage rating is 3.6 volts, and the current can reach up to 25 mA. Anti-static precautions must be observed when handling the LEDs. The LEDs housed in a water-clear plastic package emit a focused spotlight, while diffused type LEDs provide a wider radiation pattern. The circuit utilizes capacitive reactance to limit the current flowing through the LEDs when mains voltage is applied. Using only a series resistor for current limiting in a mains operation would result in the resistor dissipating approximately 2 to 3 watts of power, whereas a capacitor does not dissipate power. The capacitor value is calculated using the relationships involving capacitive reactance (XC), capacitance (C), LED current (I), mains frequency (f), and input mains voltage (Vrms). A 100-ohm, 2W series resistor is included to prevent heavy inrush current during transients. A Metal-Oxide Varistor (MOV) at the input safeguards against surges or spikes, protecting the circuit. A 390-kilo-ohm, ½-watt resistor serves as a bleeder, providing a discharge path for capacitor Cx when the mains supply is disconnected. A zener diode in the output section prevents excessive reverse voltage across the LEDs during negative half cycles, while limiting the voltage across the LEDs to the zener voltage during positive half cycles. AC capacitors should be used for Cx, and a filter capacitor (C1) across the output ensures flicker-free light. The circuit can be enclosed in a CFL round case, allowing direct connection to an AC bulb holder socket. A series configuration of 16 LEDs yields a luminance equivalent to a 12W bulb. Alternatively, two series combinations of 23 LEDs in parallel (totaling 46 LEDs) produce light comparable to a 35W bulb. Fifteen LEDs are appropriate for table-lamp lighting. Diode D1 (1N4007) and capacitor C1 function as rectifying and smoothing elements to supply DC voltage to the LED array. For a 16-LED configuration, a Cx of 0.22 µF, 630V; C1 of 22 µF, 100V; and a zener diode rated at 48V, 1W should be used. For the 23+23 LED combination, a Cx of 0.47 mF, 630V; C1 of 33 µF, 150V; and a zener diode rated at 69V, 1W are recommended. The total cost of this circuit, including the LEDs, is estimated to be between Rs 200 and Rs 400.
The circuit design for the ultra-bright white LED lamp incorporates several key components that ensure efficient operation and protection of the LEDs. The use of capacitive reactance for current limiting is a critical feature, as it minimizes power loss compared to a resistive approach. The choice of a MOV provides an additional layer of protection against voltage spikes that could potentially damage the LEDs.
The series resistor plays a crucial role in managing inrush current, particularly during power-up events, which can otherwise lead to premature failure of the LEDs. The bleeder resistor ensures that the capacitors discharge safely when the circuit is powered down, preventing unexpected voltage levels that could harm the components.
The zener diode's function in clamping the voltage across the LEDs is essential for maintaining their longevity. By limiting the reverse voltage during negative cycles, it protects the LEDs from breakdown. The selection of capacitors, both for Cx and C1, is critical; they must be rated adequately to handle the voltage and provide the necessary filtering to achieve a stable output.
The configuration options for the LED arrays allow for flexibility in application, enabling the designer to choose the appropriate setup based on the desired luminance output. The cost-effectiveness of the circuit, combined with its efficiency and protective features, makes it an attractive solution for various lighting applications.This ultra-bright white LED lamp works on 230V AC with minimal power consumption. It can be used to illuminate VU meters, SWR meters, etc. Ultra-bright LEDs available in the market cost Rs 8 to 15. These LEDs emit a 1000-6000mCd bright white light like welding arc and work on 3 volts, 10 mA. Their maximum voltage is 3. 6 volts and the current is 25 mA. Anti-static precautions should be taken when handling the LEDs. The LEDs in water-clear plastic package emit spotlight, while diffused type LEDs have a wide-angle radiation pattern. This circuit (Fig. 1) employs capacitive reactance for limiting the current flow through the LEDs on application of mains voltage to the circuit.
If we use only a series resistor for limiting the current with mains operation, the limiting resistor itself will dissipate around 2 to 3 watts of power, whereas no power is dissipated in a capacitor. The value of capacitor is calculated by using the following relationships: where XC is capacitive reactance in ohms, C is capacitance in farads, I is the current through the LED in amperes, f is the mains frequency in Hz, and Vrms is the input mains voltage.
The 100-ohm, 2W series resistor avoids heavy inrush` current during transients. MOV at the input prevents surges or spikes, protecting the circuit. The 390-kilo-ohm, ½-watt resistor acts as a bleeder to provide discharge path for capacitor Cx when mains supply is disconnected. The zener diode at the output section prevents excess reverse voltage levels appearing across the LEDs during negative half cycles.
During positive half cycle, the voltage across LEDs is limited to zener voltage. Use AC capacitors for Cx. Filter capacitor C1 across the output provides flicker-free light. The circuit can be enclosed in a CFL round case, and thus it can be connected directly to AC bulb holder socket. A series combination of 16 LEDs (Fig. 2) gives a luminance (lux) equivalent of a 12W bulb. But if you have two series combinations of 23 LEDs in parallel (total 46 LEDs as shown in Fig. 3), it gives light equal to a 35W bulb. 15 LEDs are suitable for a table-lamp light. Diode D1 (1N4007) and capacitor C1 act as rectifying and smoothing elements to provide DC voltage to the row of LEDs.
For a 16-LED row, use Cx of 0. 22 µF, 630V; C1 of 22 µF, 100V; and zener of 48V, 1W. Similarly, for 23+23 LED combination use Cx of 0. 47 mF, 630V; C1 of 33 µF, 150V; and zener of 69V, 1W. This circuit (inclusive of LEDs) costs Rs 200 to Rs 400. 🔗 External reference
The circuit design for the ultra-bright white LED lamp incorporates several key components that ensure efficient operation and protection of the LEDs. The use of capacitive reactance for current limiting is a critical feature, as it minimizes power loss compared to a resistive approach. The choice of a MOV provides an additional layer of protection against voltage spikes that could potentially damage the LEDs.
The series resistor plays a crucial role in managing inrush current, particularly during power-up events, which can otherwise lead to premature failure of the LEDs. The bleeder resistor ensures that the capacitors discharge safely when the circuit is powered down, preventing unexpected voltage levels that could harm the components.
The zener diode's function in clamping the voltage across the LEDs is essential for maintaining their longevity. By limiting the reverse voltage during negative cycles, it protects the LEDs from breakdown. The selection of capacitors, both for Cx and C1, is critical; they must be rated adequately to handle the voltage and provide the necessary filtering to achieve a stable output.
The configuration options for the LED arrays allow for flexibility in application, enabling the designer to choose the appropriate setup based on the desired luminance output. The cost-effectiveness of the circuit, combined with its efficiency and protective features, makes it an attractive solution for various lighting applications.This ultra-bright white LED lamp works on 230V AC with minimal power consumption. It can be used to illuminate VU meters, SWR meters, etc. Ultra-bright LEDs available in the market cost Rs 8 to 15. These LEDs emit a 1000-6000mCd bright white light like welding arc and work on 3 volts, 10 mA. Their maximum voltage is 3. 6 volts and the current is 25 mA. Anti-static precautions should be taken when handling the LEDs. The LEDs in water-clear plastic package emit spotlight, while diffused type LEDs have a wide-angle radiation pattern. This circuit (Fig. 1) employs capacitive reactance for limiting the current flow through the LEDs on application of mains voltage to the circuit.
If we use only a series resistor for limiting the current with mains operation, the limiting resistor itself will dissipate around 2 to 3 watts of power, whereas no power is dissipated in a capacitor. The value of capacitor is calculated by using the following relationships: where XC is capacitive reactance in ohms, C is capacitance in farads, I is the current through the LED in amperes, f is the mains frequency in Hz, and Vrms is the input mains voltage.
The 100-ohm, 2W series resistor avoids heavy inrush` current during transients. MOV at the input prevents surges or spikes, protecting the circuit. The 390-kilo-ohm, ½-watt resistor acts as a bleeder to provide discharge path for capacitor Cx when mains supply is disconnected. The zener diode at the output section prevents excess reverse voltage levels appearing across the LEDs during negative half cycles.
During positive half cycle, the voltage across LEDs is limited to zener voltage. Use AC capacitors for Cx. Filter capacitor C1 across the output provides flicker-free light. The circuit can be enclosed in a CFL round case, and thus it can be connected directly to AC bulb holder socket. A series combination of 16 LEDs (Fig. 2) gives a luminance (lux) equivalent of a 12W bulb. But if you have two series combinations of 23 LEDs in parallel (total 46 LEDs as shown in Fig. 3), it gives light equal to a 35W bulb. 15 LEDs are suitable for a table-lamp light. Diode D1 (1N4007) and capacitor C1 act as rectifying and smoothing elements to provide DC voltage to the row of LEDs.
For a 16-LED row, use Cx of 0. 22 µF, 630V; C1 of 22 µF, 100V; and zener of 48V, 1W. Similarly, for 23+23 LED combination use Cx of 0. 47 mF, 630V; C1 of 33 µF, 150V; and zener of 69V, 1W. This circuit (inclusive of LEDs) costs Rs 200 to Rs 400. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713