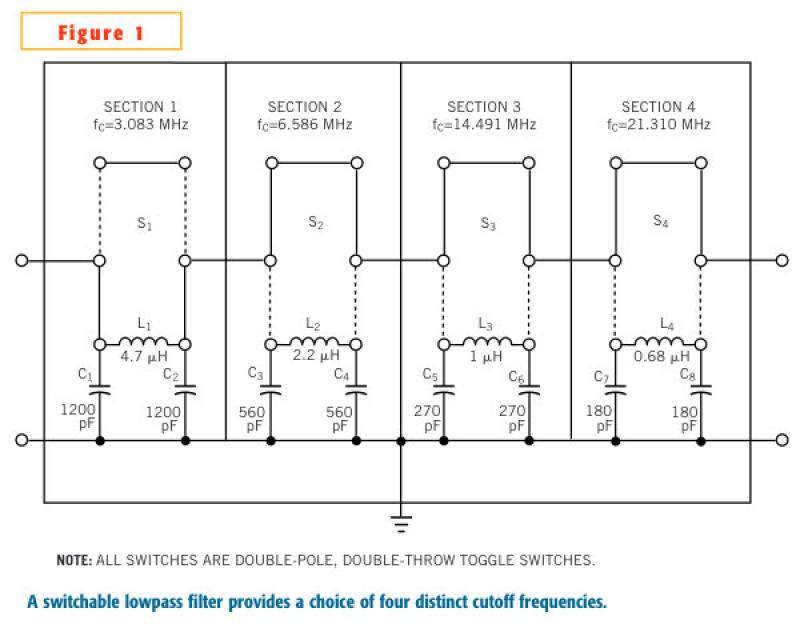
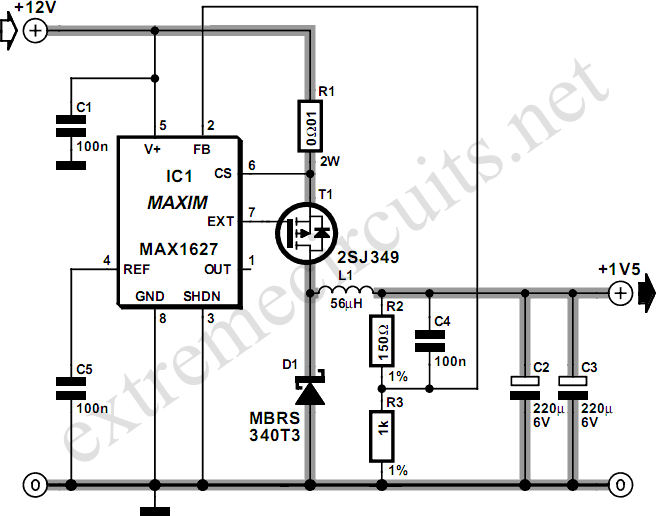
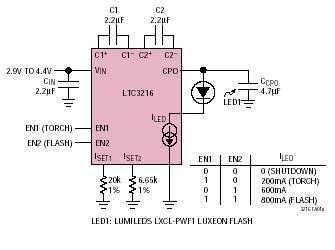
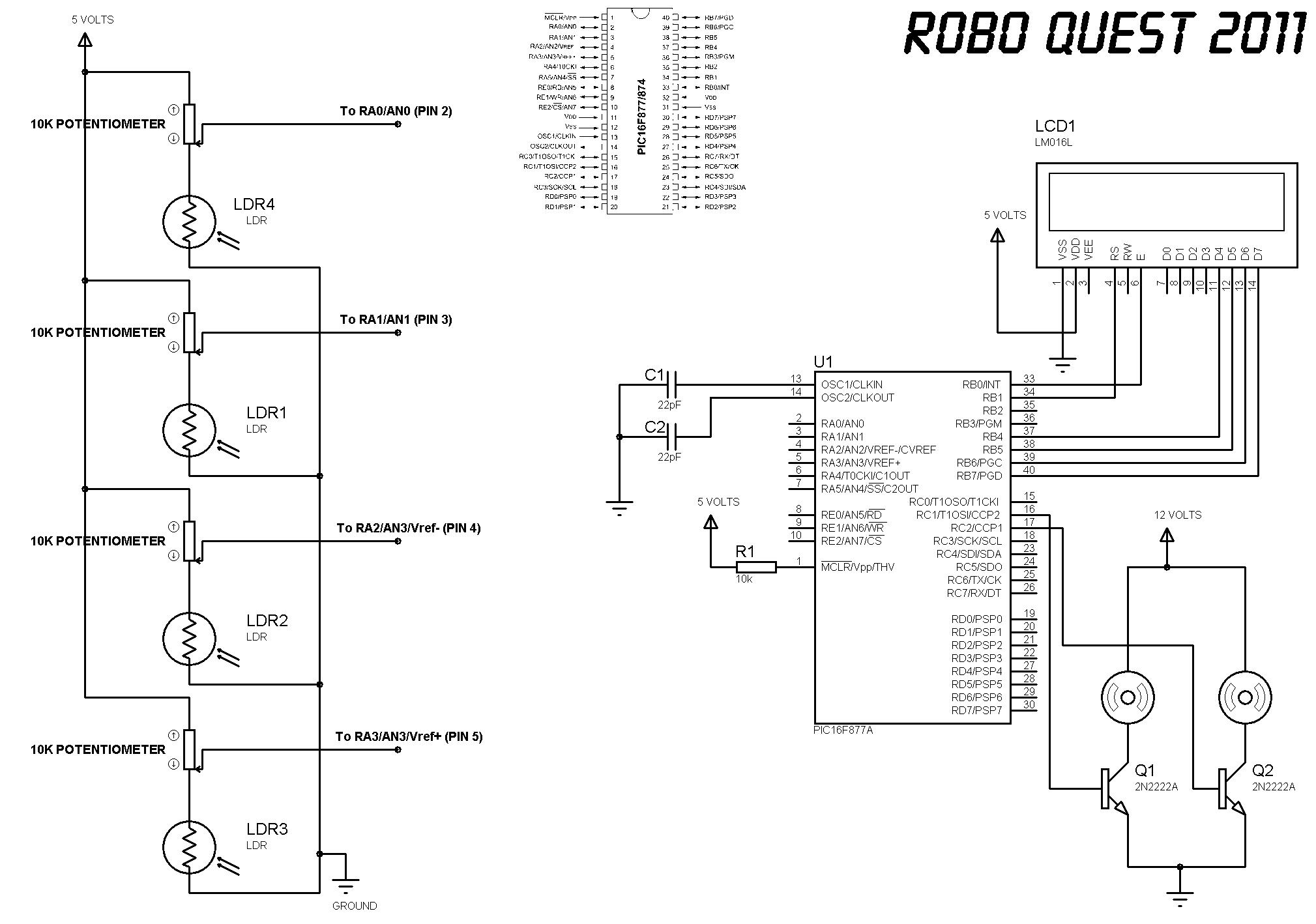
Ultra Low Current Oscillator

The circuit operates as a unijunction transistor relaxation oscillator. The base of the lower PNP transistor is biased at approximately half of the supply voltage. As the 100pF capacitor charges through the 1GΩ resistor, the base of the upper NPN transistor attains a critical voltage, leading to the forward biasing of the base-emitter junction.
The unijunction transistor (UJT) relaxation oscillator circuit typically consists of two transistors: one PNP and one NPN. The PNP transistor is configured to provide a stable reference voltage, while the NPN transistor acts as the switching element. The circuit relies on the charging and discharging of the capacitor, which is key to generating oscillations.
In this configuration, the 100pF capacitor is charged through the 1GΩ resistor, creating a time constant that determines the frequency of oscillation. The charging process continues until the voltage across the capacitor reaches a threshold level sufficient to forward bias the base-emitter junction of the NPN transistor. This forward biasing leads to a rapid increase in collector current, which subsequently discharges the capacitor quickly, causing the voltage to drop.
Once the capacitor discharges below a certain level, the NPN transistor turns off, and the cycle repeats. The frequency of oscillation can be adjusted by varying the capacitance or resistance values in the circuit. This type of oscillator is often used in applications requiring low-frequency square wave signals, such as in timing circuits, tone generation, and clock pulses for digital circuits.
The overall behavior of the circuit can be analyzed using the time constant formula τ = R × C, where τ is the time constant, R is the resistance, and C is the capacitance. The resulting oscillation frequency can be approximated by the formula f = 1 / (2πτ), allowing for precise control over the output frequency by selecting appropriate component values.The circuit functions like a unijunction transistor relaxation oscillator. The base of the lower PNP transistor is biased at roughly half supply. As the 100pF capacitor is charged up through the 1G resistor, the base of the upper NPN transistor reaches a critical voltage, which begins to forward bias the base-emitter junction . 🔗 External reference
The unijunction transistor (UJT) relaxation oscillator circuit typically consists of two transistors: one PNP and one NPN. The PNP transistor is configured to provide a stable reference voltage, while the NPN transistor acts as the switching element. The circuit relies on the charging and discharging of the capacitor, which is key to generating oscillations.
In this configuration, the 100pF capacitor is charged through the 1GΩ resistor, creating a time constant that determines the frequency of oscillation. The charging process continues until the voltage across the capacitor reaches a threshold level sufficient to forward bias the base-emitter junction of the NPN transistor. This forward biasing leads to a rapid increase in collector current, which subsequently discharges the capacitor quickly, causing the voltage to drop.
Once the capacitor discharges below a certain level, the NPN transistor turns off, and the cycle repeats. The frequency of oscillation can be adjusted by varying the capacitance or resistance values in the circuit. This type of oscillator is often used in applications requiring low-frequency square wave signals, such as in timing circuits, tone generation, and clock pulses for digital circuits.
The overall behavior of the circuit can be analyzed using the time constant formula τ = R × C, where τ is the time constant, R is the resistance, and C is the capacitance. The resulting oscillation frequency can be approximated by the formula f = 1 / (2πτ), allowing for precise control over the output frequency by selecting appropriate component values.The circuit functions like a unijunction transistor relaxation oscillator. The base of the lower PNP transistor is biased at roughly half supply. As the 100pF capacitor is charged up through the 1G resistor, the base of the upper NPN transistor reaches a critical voltage, which begins to forward bias the base-emitter junction . 🔗 External reference