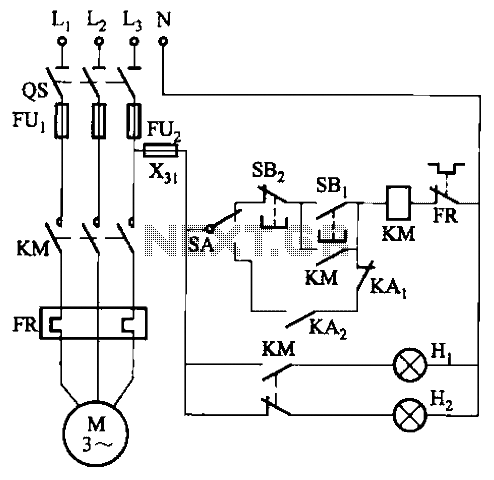
Ultrasonic Remote Control Circuit
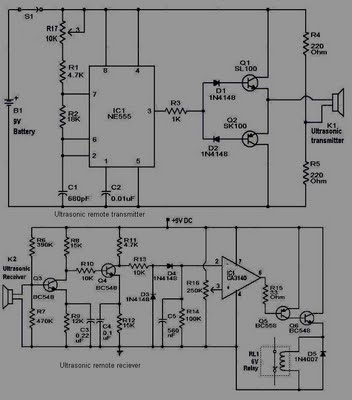
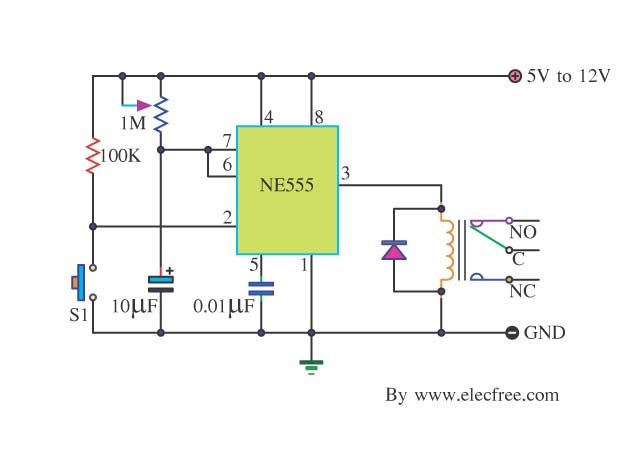
This circuit is straightforward and well-defined. The transmitter operates at 9 volts, while the receiver circuit functions at 5 volts. The transmitter utilizes a 555 timer and two SL100 transistors to perform its function. The receiver incorporates a small relay to manage the intended operation.
The circuit design features a transmitter and receiver system that operates at different voltage levels, specifically 9 volts for the transmitter and 5 volts for the receiver. The transmitter employs a 555 timer integrated circuit, which is widely utilized for generating precise timing pulses and oscillations. This timer is configured in astable mode to produce a square wave output, which is essential for modulating the signal.
To amplify the output from the 555 timer, two SL100 transistors are used in a push-pull configuration. This setup enhances the current driving capability of the transmitter, allowing it to effectively transmit signals over a distance. The choice of SL100 transistors, known for their high gain and frequency response, ensures robust performance and reliability in signal transmission.
On the receiving end, a small relay is implemented to control the desired application or load. The relay acts as an electrically operated switch, which is triggered by the incoming signal from the transmitter. When the relay is activated, it can control higher power devices or circuits, making it versatile for various applications, such as turning on lights, motors, or other electronic devices.
Overall, this circuit design demonstrates a practical application of basic electronic components to achieve wireless communication and control, showcasing the effectiveness of the 555 timer, transistors, and relays in circuit design.This circuit is as shown, simple and clear. The transmitter needs 9 volts and the receiver circuit needs 5 volts. The transmitter uses the 555 timer and two SL100 transistors to make the job. The receiver needs a small relay to control the desired job. 🔗 External reference
The circuit design features a transmitter and receiver system that operates at different voltage levels, specifically 9 volts for the transmitter and 5 volts for the receiver. The transmitter employs a 555 timer integrated circuit, which is widely utilized for generating precise timing pulses and oscillations. This timer is configured in astable mode to produce a square wave output, which is essential for modulating the signal.
To amplify the output from the 555 timer, two SL100 transistors are used in a push-pull configuration. This setup enhances the current driving capability of the transmitter, allowing it to effectively transmit signals over a distance. The choice of SL100 transistors, known for their high gain and frequency response, ensures robust performance and reliability in signal transmission.
On the receiving end, a small relay is implemented to control the desired application or load. The relay acts as an electrically operated switch, which is triggered by the incoming signal from the transmitter. When the relay is activated, it can control higher power devices or circuits, making it versatile for various applications, such as turning on lights, motors, or other electronic devices.
Overall, this circuit design demonstrates a practical application of basic electronic components to achieve wireless communication and control, showcasing the effectiveness of the 555 timer, transistors, and relays in circuit design.This circuit is as shown, simple and clear. The transmitter needs 9 volts and the receiver circuit needs 5 volts. The transmitter uses the 555 timer and two SL100 transistors to make the job. The receiver needs a small relay to control the desired job. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713