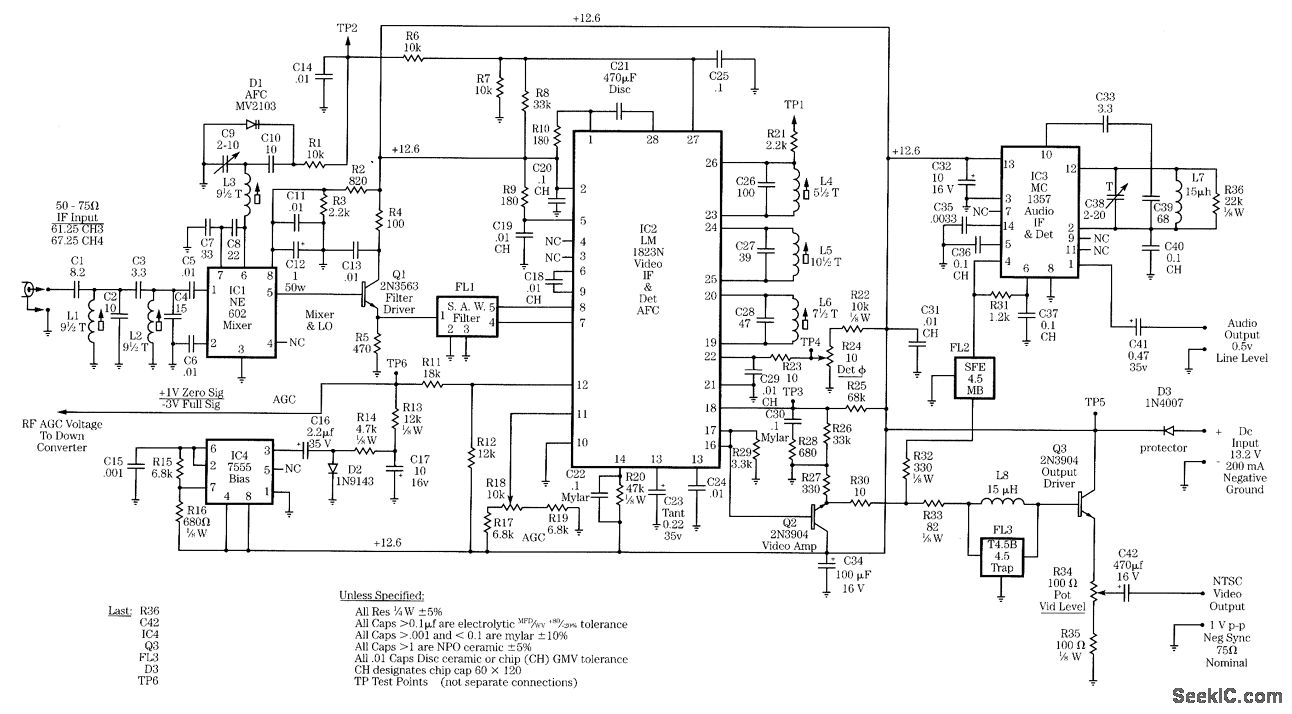
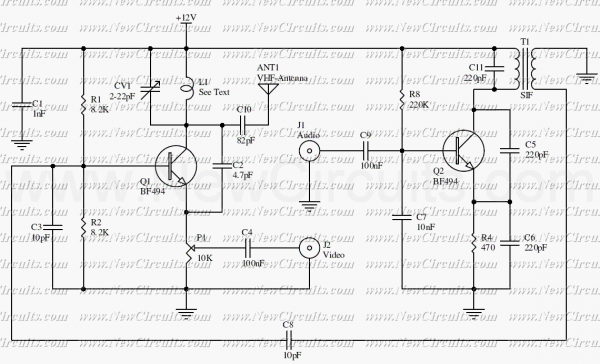
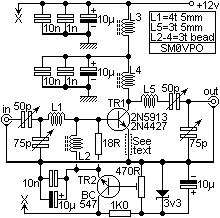
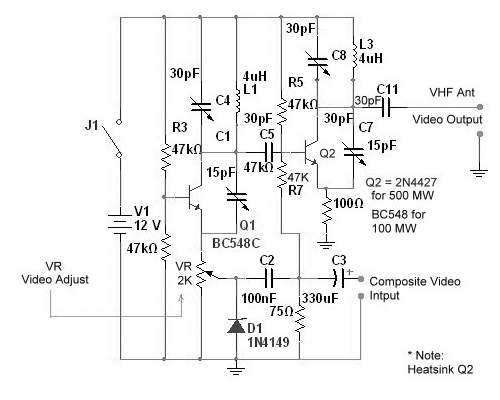
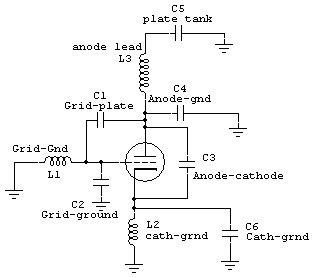
VHF Beacon
The 555 timer oscillator section can be removed and replaced with a preferred microphone modulating circuit to transmit audio to a television set, requiring minimal tuning. The schematics available on Schematics Depot were sourced from the internet and are presumed to be in the public domain. The webmaster should be contacted if the copyright holder requests their removal.
The circuit modification involves taking out the 555 timer oscillator, which is typically used for generating pulse-width modulation signals, and integrating a microphone modulating circuit instead. This modification allows for the transmission of audio signals, such as voice, directly to a television set.
To implement this, a suitable microphone circuit must be selected that can effectively convert sound waves into an electrical signal. Common choices include electret condenser microphones or dynamic microphones, which can be configured to work with a preamplifier to boost the signal strength before modulation.
The microphone output needs to be modulated to ensure compatibility with the transmission requirements of the television set, which may involve amplitude modulation (AM) or frequency modulation (FM) techniques. The choice of modulation will depend on the specific characteristics of the television's audio input.
Once the microphone circuit is integrated, the overall circuit will require tuning. This tuning process may involve adjusting the gain of the microphone preamp, selecting appropriate filter components to eliminate noise, and ensuring the modulation frequency aligns with the television's audio input specifications.
In conclusion, by replacing the 555 timer oscillator with a microphone modulating circuit, it is possible to create a system that facilitates audio transmission to a television set. Careful selection of components and tuning will enhance the performance and clarity of the transmitted audio.You can cut away the 555 timer oscillator part and add your favorite microphone modulating circuit to transmit voice over to your tv set with a little tuning. Schematics in Schematics Depot were found on the internet and assumed to be in public domain. Contact webmaster if the copyright holder wants them pulled for any reason. 🔗 External reference
The circuit modification involves taking out the 555 timer oscillator, which is typically used for generating pulse-width modulation signals, and integrating a microphone modulating circuit instead. This modification allows for the transmission of audio signals, such as voice, directly to a television set.
To implement this, a suitable microphone circuit must be selected that can effectively convert sound waves into an electrical signal. Common choices include electret condenser microphones or dynamic microphones, which can be configured to work with a preamplifier to boost the signal strength before modulation.
The microphone output needs to be modulated to ensure compatibility with the transmission requirements of the television set, which may involve amplitude modulation (AM) or frequency modulation (FM) techniques. The choice of modulation will depend on the specific characteristics of the television's audio input.
Once the microphone circuit is integrated, the overall circuit will require tuning. This tuning process may involve adjusting the gain of the microphone preamp, selecting appropriate filter components to eliminate noise, and ensuring the modulation frequency aligns with the television's audio input specifications.
In conclusion, by replacing the 555 timer oscillator with a microphone modulating circuit, it is possible to create a system that facilitates audio transmission to a television set. Careful selection of components and tuning will enhance the performance and clarity of the transmitted audio.You can cut away the 555 timer oscillator part and add your favorite microphone modulating circuit to transmit voice over to your tv set with a little tuning. Schematics in Schematics Depot were found on the internet and assumed to be in public domain. Contact webmaster if the copyright holder wants them pulled for any reason. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713