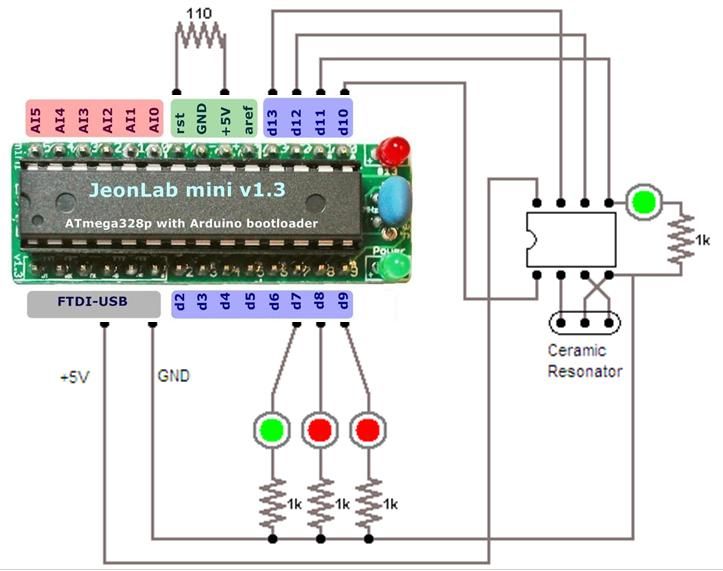
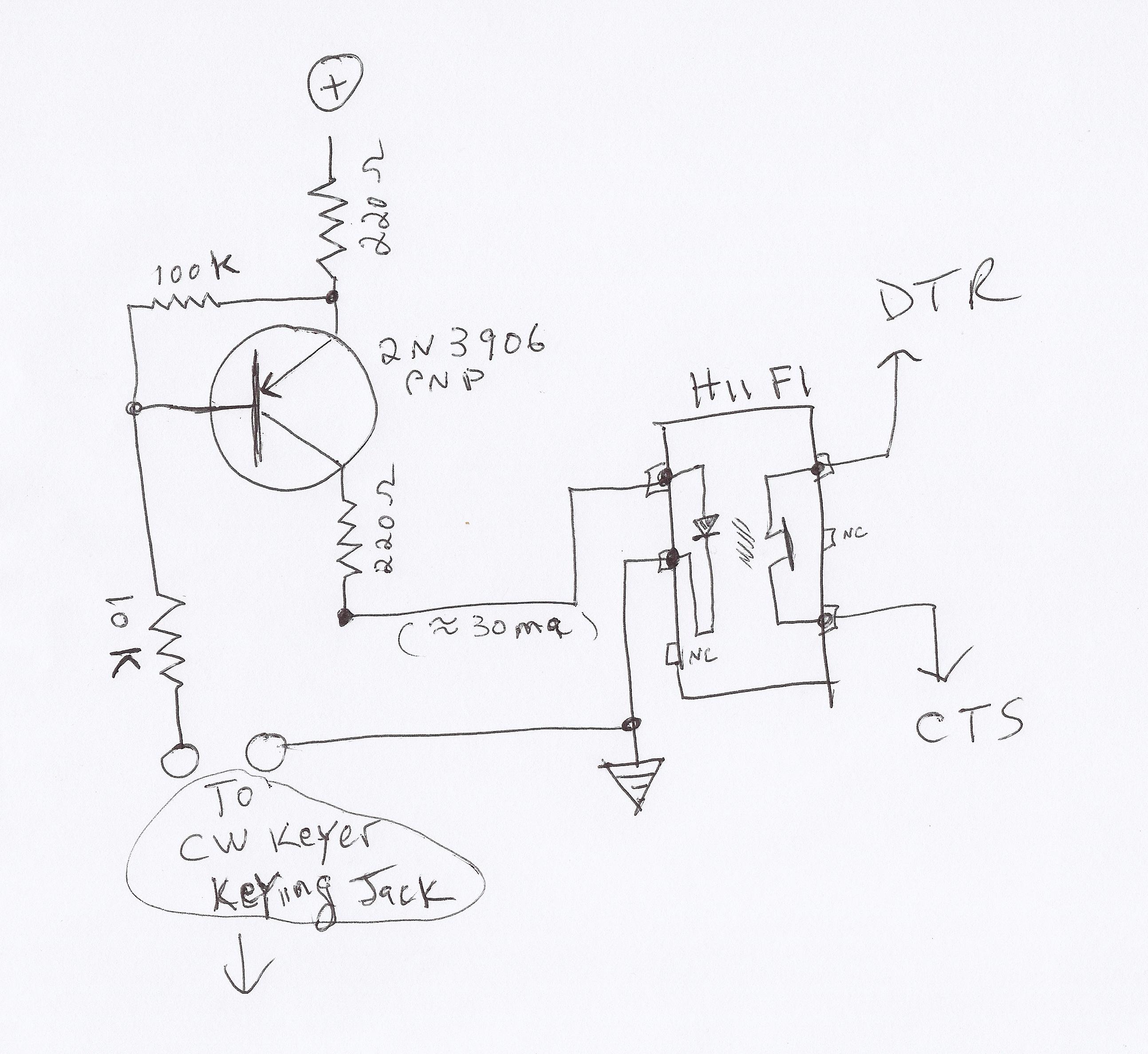
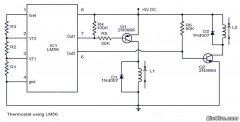
What should I take in account when using a more powerful triac
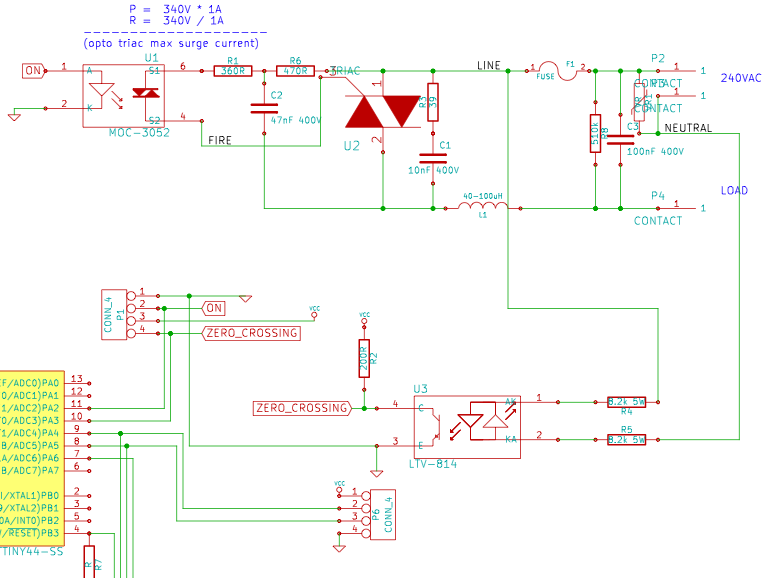
The resistance of the heater is constructed using 9 Ω nichrome wire with a diameter of 3 mm. When supplied with 240V (rms) voltage, this configuration results in a current of 25A (rms). Access to a mains line that can deliver 30A suggests that, theoretically, the heater can operate at full load. However, practical limitations may prevent this from being achieved, yet the intention is to design a unit capable of such operation in theory if required.
The heater's design incorporates a nichrome wire element, renowned for its high resistivity and ability to withstand high temperatures, making it suitable for heating applications. The 9 Ω resistance value indicates that the wire is optimized for efficient heat generation when subjected to the specified voltage. The diameter of 3 mm contributes to the wire's mechanical robustness while ensuring adequate surface area for heat dissipation.
To calculate the power output of the heater, the formula P = V × I can be applied, where P is the power in watts, V is the voltage in volts, and I is the current in amperes. In this case, with V at 240V and I at 25A, the power output can be calculated as follows:
P = 240V × 25A = 6000W
This indicates that the heater is capable of generating up to 6000 watts of thermal energy under ideal conditions. However, it is important to consider the efficiency of the system, as factors such as heat losses and the thermal resistance of the surrounding environment may reduce the actual output.
For safety and performance, the circuit design should include appropriate overcurrent protection, such as circuit breakers or fuses rated slightly above the expected load. Additionally, thermal management should be considered, including the use of heat sinks or insulative materials to prevent overheating of surrounding components.
In terms of circuit configuration, a simple series circuit can be employed, connecting the heater directly to the mains supply. However, the incorporation of a control mechanism, such as a relay or a solid-state switch, can enhance functionality by allowing for temperature regulation and automated operation. A thermostat can be integrated to monitor the temperature and adjust the power supplied to the heater accordingly, ensuring optimal performance while preventing overheating.
Overall, the design should be robust, with careful attention to the wire gauge, insulation materials, and thermal management strategies to ensure safe and efficient operation of the heater in practical applications.The resistance of my heater is made of 9$Omega$ 3mm diameter nichrome wire. On 240V(rms) voltage this makes 25A(rms) current. I have an access to a mains line capable of delivering 30A, so in theory I will be able to drive heater at full load. In reality I probably won`t, but nevertheless, I want to build a unit that could do that in theory if
needed. 🔗 External reference
The heater's design incorporates a nichrome wire element, renowned for its high resistivity and ability to withstand high temperatures, making it suitable for heating applications. The 9 Ω resistance value indicates that the wire is optimized for efficient heat generation when subjected to the specified voltage. The diameter of 3 mm contributes to the wire's mechanical robustness while ensuring adequate surface area for heat dissipation.
To calculate the power output of the heater, the formula P = V × I can be applied, where P is the power in watts, V is the voltage in volts, and I is the current in amperes. In this case, with V at 240V and I at 25A, the power output can be calculated as follows:
P = 240V × 25A = 6000W
This indicates that the heater is capable of generating up to 6000 watts of thermal energy under ideal conditions. However, it is important to consider the efficiency of the system, as factors such as heat losses and the thermal resistance of the surrounding environment may reduce the actual output.
For safety and performance, the circuit design should include appropriate overcurrent protection, such as circuit breakers or fuses rated slightly above the expected load. Additionally, thermal management should be considered, including the use of heat sinks or insulative materials to prevent overheating of surrounding components.
In terms of circuit configuration, a simple series circuit can be employed, connecting the heater directly to the mains supply. However, the incorporation of a control mechanism, such as a relay or a solid-state switch, can enhance functionality by allowing for temperature regulation and automated operation. A thermostat can be integrated to monitor the temperature and adjust the power supplied to the heater accordingly, ensuring optimal performance while preventing overheating.
Overall, the design should be robust, with careful attention to the wire gauge, insulation materials, and thermal management strategies to ensure safe and efficient operation of the heater in practical applications.The resistance of my heater is made of 9$Omega$ 3mm diameter nichrome wire. On 240V(rms) voltage this makes 25A(rms) current. I have an access to a mains line capable of delivering 30A, so in theory I will be able to drive heater at full load. In reality I probably won`t, but nevertheless, I want to build a unit that could do that in theory if
needed. 🔗 External reference