4 Watts FM Transmitter
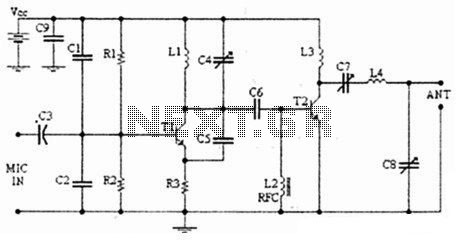
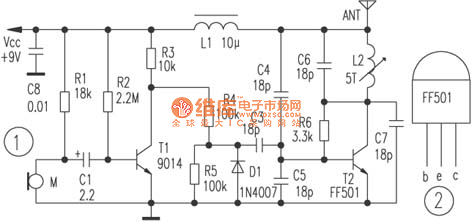
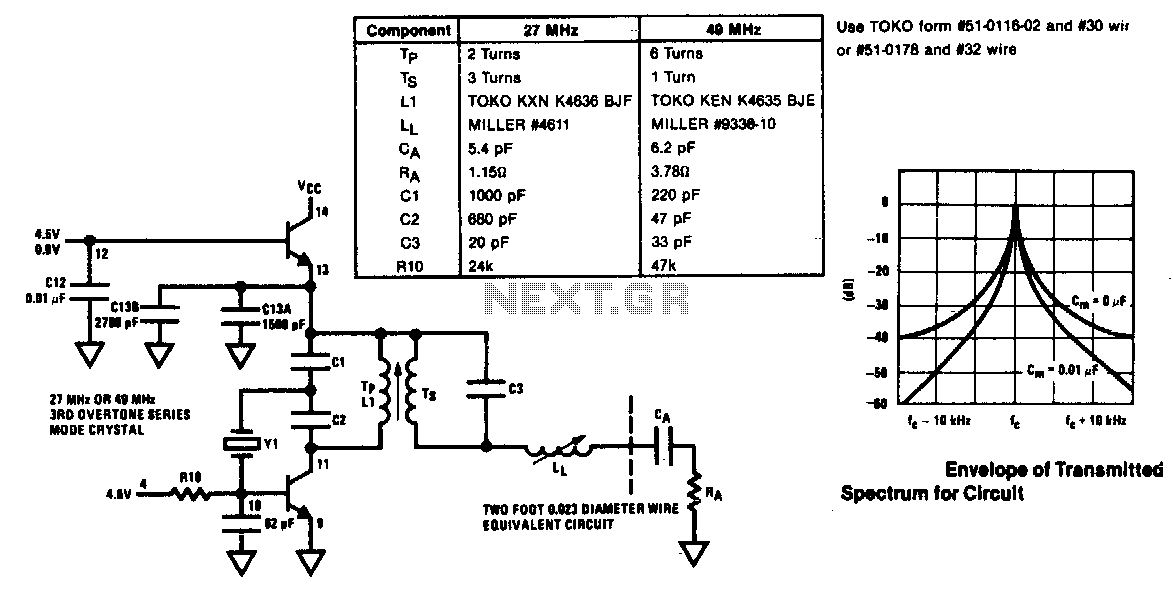
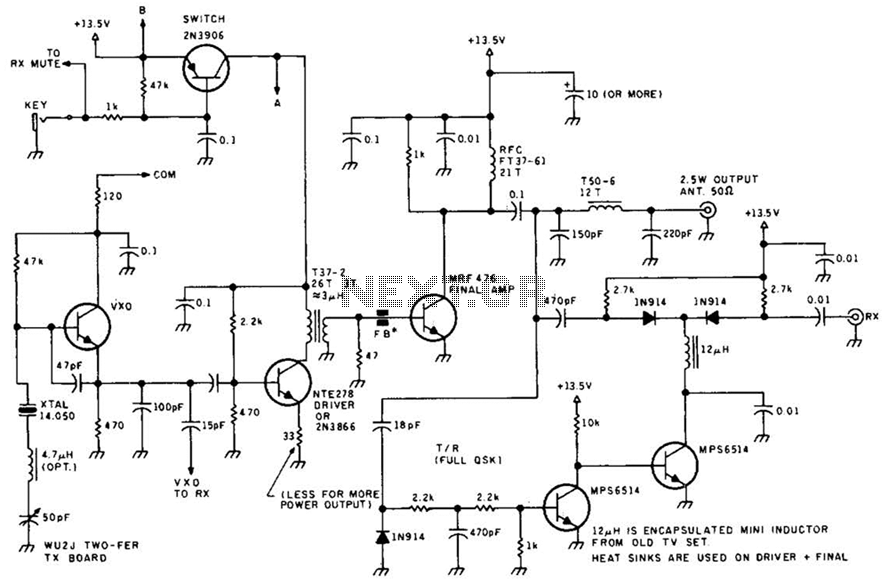
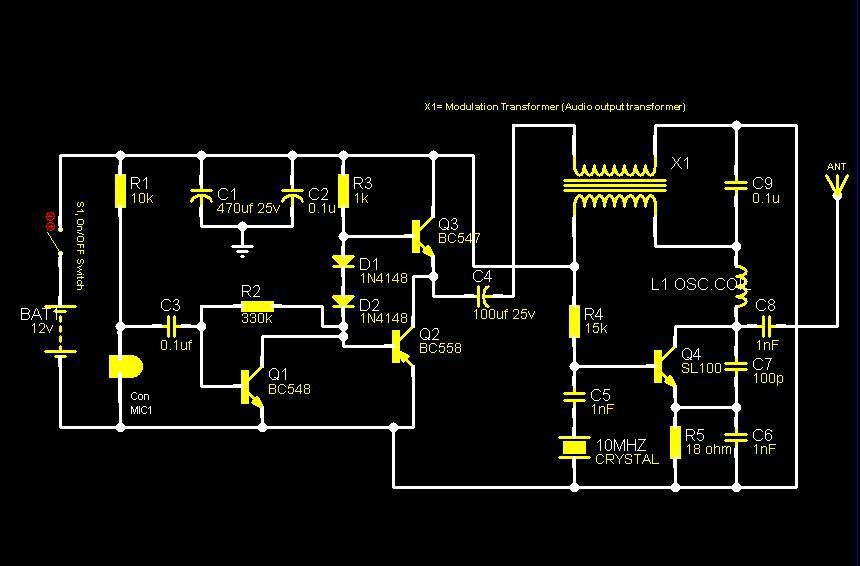
The following diagram illustrates an FM transmitter circuit capable of FM transmission up to 4W. The voltage supply for this circuit ranges from 12V to 16V, with a current consumption between 100mA and 400mA. This circuit operates within an emission frequency range of 88MHz to 108MHz. Components...
The FM transmitter circuit is designed to provide reliable transmission of frequency-modulated signals within the VHF band, specifically between 88MHz and 108MHz, which is the standard FM radio band. The circuit typically includes several key components such as a voltage regulator, oscillator, modulator, amplifier, and antenna.
The voltage supply of 12V to 16V is essential for the operation of the circuit, ensuring that all components receive adequate power for optimal performance. The current consumption of 100mA to 400mA indicates that the circuit is efficient, allowing for prolonged use without excessive power draw.
The oscillator is responsible for generating the carrier frequency, which is modulated by the audio signal to create the FM signal. This modulation process typically involves a varactor diode or a similar component that varies the capacitance in response to the audio input, thus changing the frequency of the oscillator slightly to encode the audio information onto the carrier wave.
The amplifier stage boosts the power of the modulated signal, allowing it to achieve the desired output of up to 4W. This output power is sufficient for local broadcasting, ensuring that the signal can be received clearly by standard FM receivers within a reasonable range.
Finally, the antenna plays a critical role in radiating the FM signal into the environment. The design of the antenna should be matched to the operating frequency to maximize efficiency and range.
Overall, this FM transmitter circuit is a valuable tool for various applications, including hobbyist projects, educational demonstrations, and small-scale broadcasting. Proper assembly and tuning of the components will ensure effective operation and compliance with relevant transmission regulations.The following diagram is the FM transmitter circuit with FM transmision up to 4W. Voltage supply for this circuit is 12-16V with current consumption of 100-400mA. This circuit works with frequency of emission range of 88-108MHz. Components.. 🔗 External reference
The FM transmitter circuit is designed to provide reliable transmission of frequency-modulated signals within the VHF band, specifically between 88MHz and 108MHz, which is the standard FM radio band. The circuit typically includes several key components such as a voltage regulator, oscillator, modulator, amplifier, and antenna.
The voltage supply of 12V to 16V is essential for the operation of the circuit, ensuring that all components receive adequate power for optimal performance. The current consumption of 100mA to 400mA indicates that the circuit is efficient, allowing for prolonged use without excessive power draw.
The oscillator is responsible for generating the carrier frequency, which is modulated by the audio signal to create the FM signal. This modulation process typically involves a varactor diode or a similar component that varies the capacitance in response to the audio input, thus changing the frequency of the oscillator slightly to encode the audio information onto the carrier wave.
The amplifier stage boosts the power of the modulated signal, allowing it to achieve the desired output of up to 4W. This output power is sufficient for local broadcasting, ensuring that the signal can be received clearly by standard FM receivers within a reasonable range.
Finally, the antenna plays a critical role in radiating the FM signal into the environment. The design of the antenna should be matched to the operating frequency to maximize efficiency and range.
Overall, this FM transmitter circuit is a valuable tool for various applications, including hobbyist projects, educational demonstrations, and small-scale broadcasting. Proper assembly and tuning of the components will ensure effective operation and compliance with relevant transmission regulations.The following diagram is the FM transmitter circuit with FM transmision up to 4W. Voltage supply for this circuit is 12-16V with current consumption of 100-400mA. This circuit works with frequency of emission range of 88-108MHz. Components.. 🔗 External reference