Arms single-phase rectifier bridge rectifier circuit
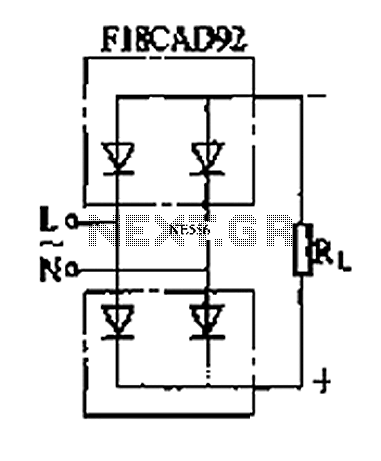
The circuit depicted is a single-phase bridge rectifier. It consists of arms with a cathode (negative electrode) and parallel anodes (positive electrodes) arranged in a configuration that connects multiple rectifier modules to form a bridge, commonly referred to as a bridge rectifier circuit.
The single-phase bridge rectifier circuit is a fundamental electronic configuration that converts alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC). The circuit typically consists of four diodes arranged in a bridge topology. This arrangement allows both halves of the AC waveform to be utilized, providing a more efficient conversion compared to half-wave rectification.
In this configuration, the AC input is connected to the two opposite corners of the bridge, while the output is taken from the other two corners. During the positive half-cycle of the AC input, two diodes become forward-biased, allowing current to flow through the load in one direction. Conversely, during the negative half-cycle, the other two diodes conduct, maintaining the same direction of current through the load. This results in a pulsating DC output.
The bridge rectifier circuit is commonly employed in power supply applications, where it is essential to convert AC mains voltage to a usable DC voltage for various electronic devices. Additional components, such as filter capacitors, are often included in the design to smooth the pulsating DC output, reducing ripple voltage and providing a more stable DC supply. The selection of diodes is critical, as they must be rated to handle the peak inverse voltage (PIV) of the AC source and the maximum load current.
Overall, the single-phase bridge rectifier circuit is a vital component in power electronics, enabling efficient power conversion and facilitating the operation of numerous electronic devices. As shown for the single-phase bridge rectifier arms rectifier circuit. The circuit consists of arms cathode (negative electrode) and arms parallel anode (positive electrode) in parallel rectifier modules, circuits connected to form a bridge, so called bridge rectifier circuit.
The single-phase bridge rectifier circuit is a fundamental electronic configuration that converts alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC). The circuit typically consists of four diodes arranged in a bridge topology. This arrangement allows both halves of the AC waveform to be utilized, providing a more efficient conversion compared to half-wave rectification.
In this configuration, the AC input is connected to the two opposite corners of the bridge, while the output is taken from the other two corners. During the positive half-cycle of the AC input, two diodes become forward-biased, allowing current to flow through the load in one direction. Conversely, during the negative half-cycle, the other two diodes conduct, maintaining the same direction of current through the load. This results in a pulsating DC output.
The bridge rectifier circuit is commonly employed in power supply applications, where it is essential to convert AC mains voltage to a usable DC voltage for various electronic devices. Additional components, such as filter capacitors, are often included in the design to smooth the pulsating DC output, reducing ripple voltage and providing a more stable DC supply. The selection of diodes is critical, as they must be rated to handle the peak inverse voltage (PIV) of the AC source and the maximum load current.
Overall, the single-phase bridge rectifier circuit is a vital component in power electronics, enabling efficient power conversion and facilitating the operation of numerous electronic devices. As shown for the single-phase bridge rectifier arms rectifier circuit. The circuit consists of arms cathode (negative electrode) and arms parallel anode (positive electrode) in parallel rectifier modules, circuits connected to form a bridge, so called bridge rectifier circuit.