Audio High Gain Crystal Earphone Amplifier
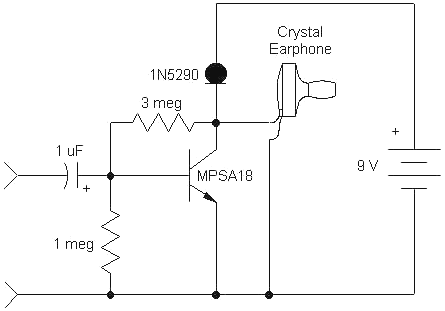
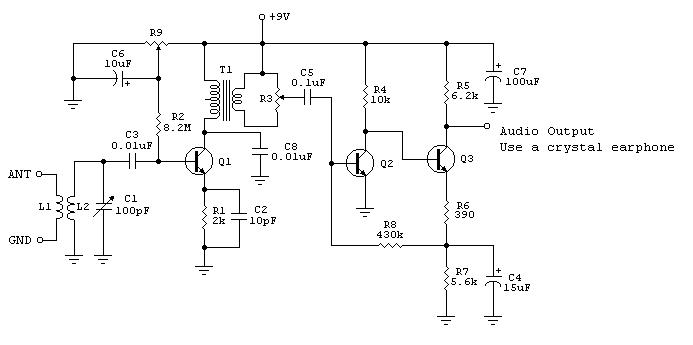
This simple, one-transistor amplifier provides a voltage gain of over 1000 (60 dB) for an active aerial impedance crystal earphone. The gain is achieved by replacing the standard load resistor with a constant-current diode that supplies 1/2 mA while exhibiting a high impedance to the audio signal. This amplifier will ensure excellent battery life, drawing only 500 µA. Below is a typical application using it with the original crystal radio circuit on this page. The amplifier delivers good volume with a modest antenna. A volume control similar to the TL431 project may be desired, or the Crystal Radio RF Amplifier can be used directly above for enhanced sensitivity with a current drain of less than 2 mA.
This one-transistor amplifier is designed to effectively boost audio signals for crystal earphones, making it suitable for low-power applications such as crystal radios. The amplifier operates with a single transistor, which simplifies the circuit design and minimizes component count. The key feature of this amplifier is its ability to achieve a high voltage gain of 60 dB, which is particularly beneficial for driving high-impedance loads like crystal earphones.
In the circuit, the standard load resistor is replaced with a constant-current diode, which maintains a steady current of 1/2 mA. This configuration not only provides the necessary gain but also ensures that the amplifier presents a high impedance to the audio signal, thereby minimizing signal loss and distortion. The use of a constant-current source is crucial, as it allows for consistent performance across varying input signal levels.
The amplifier's low current consumption of 500 µA contributes to its suitability for battery-powered applications, extending battery life significantly. This is particularly advantageous in portable devices where power efficiency is paramount. The circuit can be easily integrated into existing crystal radio designs, enhancing their performance without introducing significant complexity.
For applications requiring additional volume control, a variable resistor can be incorporated into the circuit, allowing users to adjust the output level to their preference. Alternatively, for users seeking even greater sensitivity, the Crystal Radio RF Amplifier can be utilized, which operates at a lower current drain of less than 2 mA while still providing substantial amplification.
Overall, this one-transistor amplifier represents an effective solution for audio amplification in low-power applications, combining simplicity, efficiency, and high performance. Its design is well-suited for hobbyists and engineers looking to enhance their crystal radio projects or similar audio applications.This simple, one-transistor amplifier provides a voltage accretion over 1000 (60 dB) for active a aerial impedance bowl (crystal) earphone. The aerial accretion is accomplished by replacing the acceptable beneficiary resistor with an abnormal constant-current diode that food 1/2 mA yet exhibits a actual aerial attrition to the audio.
This amplifie r will accord accomplished array life, cartoon alone 500 uA. Below is a archetypal appliance application it with the aboriginal clear radio ambit on this page. The amplifier provides acceptable aggregate with a bashful antenna. You may appetite a aggregate ascendancy as with the TL431 project! Or use the Crystal Radio RF Amplifier directly above for even more sensitivity with less than 2 mA current drain. 🔗 External reference
This one-transistor amplifier is designed to effectively boost audio signals for crystal earphones, making it suitable for low-power applications such as crystal radios. The amplifier operates with a single transistor, which simplifies the circuit design and minimizes component count. The key feature of this amplifier is its ability to achieve a high voltage gain of 60 dB, which is particularly beneficial for driving high-impedance loads like crystal earphones.
In the circuit, the standard load resistor is replaced with a constant-current diode, which maintains a steady current of 1/2 mA. This configuration not only provides the necessary gain but also ensures that the amplifier presents a high impedance to the audio signal, thereby minimizing signal loss and distortion. The use of a constant-current source is crucial, as it allows for consistent performance across varying input signal levels.
The amplifier's low current consumption of 500 µA contributes to its suitability for battery-powered applications, extending battery life significantly. This is particularly advantageous in portable devices where power efficiency is paramount. The circuit can be easily integrated into existing crystal radio designs, enhancing their performance without introducing significant complexity.
For applications requiring additional volume control, a variable resistor can be incorporated into the circuit, allowing users to adjust the output level to their preference. Alternatively, for users seeking even greater sensitivity, the Crystal Radio RF Amplifier can be utilized, which operates at a lower current drain of less than 2 mA while still providing substantial amplification.
Overall, this one-transistor amplifier represents an effective solution for audio amplification in low-power applications, combining simplicity, efficiency, and high performance. Its design is well-suited for hobbyists and engineers looking to enhance their crystal radio projects or similar audio applications.This simple, one-transistor amplifier provides a voltage accretion over 1000 (60 dB) for active a aerial impedance bowl (crystal) earphone. The aerial accretion is accomplished by replacing the acceptable beneficiary resistor with an abnormal constant-current diode that food 1/2 mA yet exhibits a actual aerial attrition to the audio.
This amplifie r will accord accomplished array life, cartoon alone 500 uA. Below is a archetypal appliance application it with the aboriginal clear radio ambit on this page. The amplifier provides acceptable aggregate with a bashful antenna. You may appetite a aggregate ascendancy as with the TL431 project! Or use the Crystal Radio RF Amplifier directly above for even more sensitivity with less than 2 mA current drain. 🔗 External reference