Autoranging Circuit
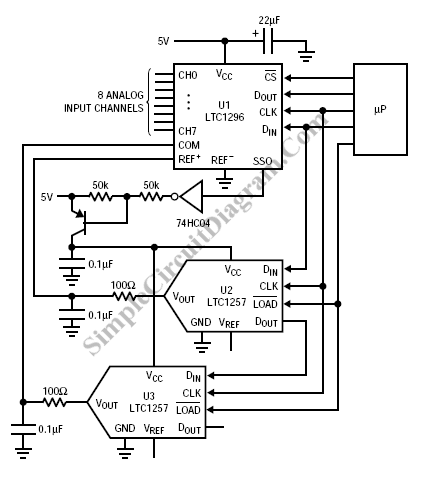
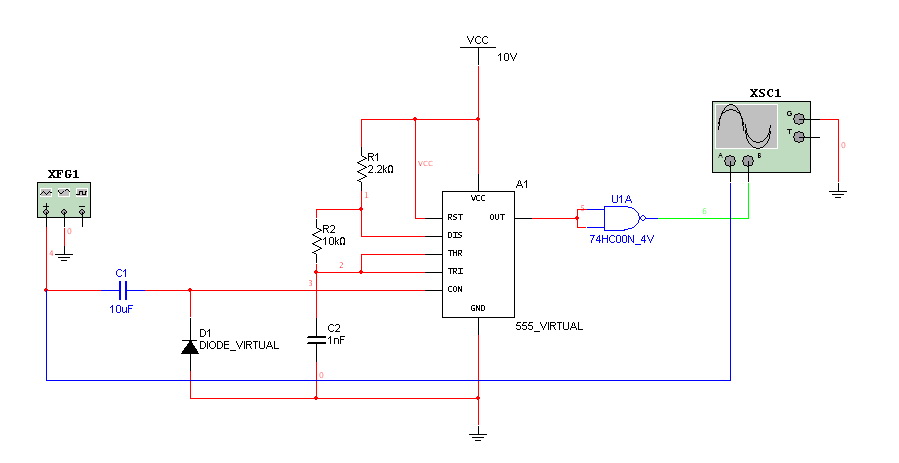
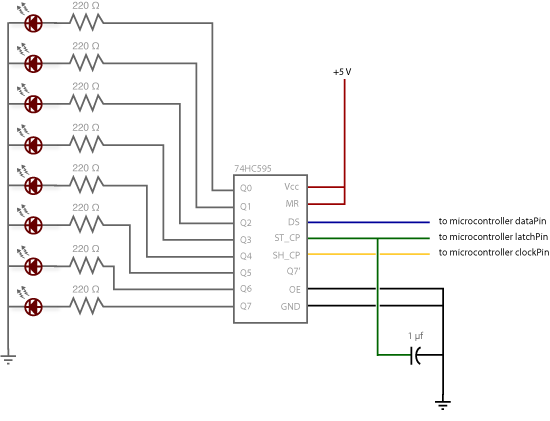
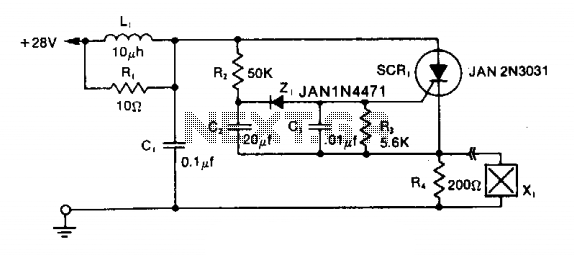
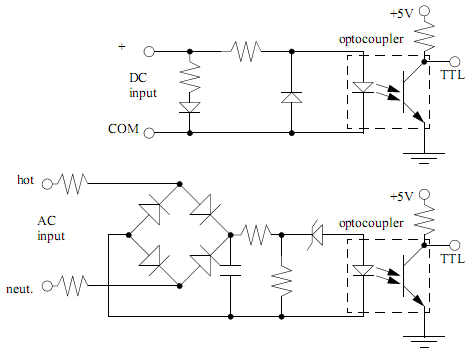
To extend the measurement range of an available ADC (analog to digital converter), autoranging can be utilized. If implemented on multiplexed input, this...
Autoranging is a technique employed in electronic measurement systems to automatically adjust the range of an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) based on the input signal level. This method enhances the ADC's ability to accurately measure a wider range of input voltages without requiring manual range adjustments. In a typical autoranging setup, the ADC is connected to a multiplexed input system that can switch between different resistor divider configurations or gain settings.
The circuit generally consists of an ADC, a multiplexer, and a set of resistors or operational amplifiers (op-amps) configured to provide various gain levels. The multiplexer selects the appropriate gain setting based on the detected input voltage. A feedback mechanism is often included, which continuously monitors the ADC output and adjusts the gain accordingly to ensure optimal measurement accuracy.
For example, if the input voltage exceeds a predefined threshold, the system can switch to a lower gain setting or a higher resistor divider ratio to bring the input voltage within the ADC's operational range. Conversely, if the input voltage is low, the system can switch to a higher gain setting to maximize resolution.
The implementation of autoranging in a multiplexed input system allows for efficient use of ADC resources, enabling the measurement of signals that vary significantly in amplitude without sacrificing precision or requiring user intervention. This capability is particularly beneficial in applications such as data acquisition systems, sensor interfaces, and instrumentation where signal levels can fluctuate widely.To extend the measurement range of an available ADC(analog to digital conveter) we can use this autoranging. If it implemented on multiplexed input, this.. 🔗 External reference
Autoranging is a technique employed in electronic measurement systems to automatically adjust the range of an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) based on the input signal level. This method enhances the ADC's ability to accurately measure a wider range of input voltages without requiring manual range adjustments. In a typical autoranging setup, the ADC is connected to a multiplexed input system that can switch between different resistor divider configurations or gain settings.
The circuit generally consists of an ADC, a multiplexer, and a set of resistors or operational amplifiers (op-amps) configured to provide various gain levels. The multiplexer selects the appropriate gain setting based on the detected input voltage. A feedback mechanism is often included, which continuously monitors the ADC output and adjusts the gain accordingly to ensure optimal measurement accuracy.
For example, if the input voltage exceeds a predefined threshold, the system can switch to a lower gain setting or a higher resistor divider ratio to bring the input voltage within the ADC's operational range. Conversely, if the input voltage is low, the system can switch to a higher gain setting to maximize resolution.
The implementation of autoranging in a multiplexed input system allows for efficient use of ADC resources, enabling the measurement of signals that vary significantly in amplitude without sacrificing precision or requiring user intervention. This capability is particularly beneficial in applications such as data acquisition systems, sensor interfaces, and instrumentation where signal levels can fluctuate widely.To extend the measurement range of an available ADC(analog to digital conveter) we can use this autoranging. If it implemented on multiplexed input, this.. 🔗 External reference