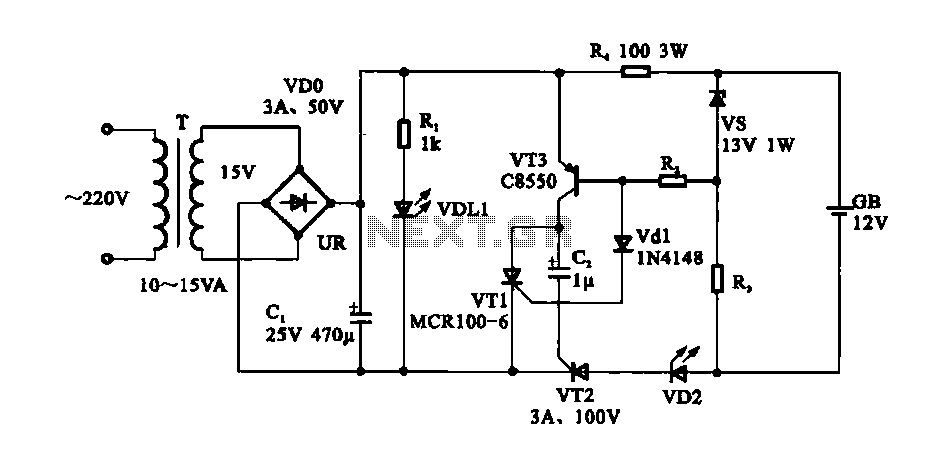
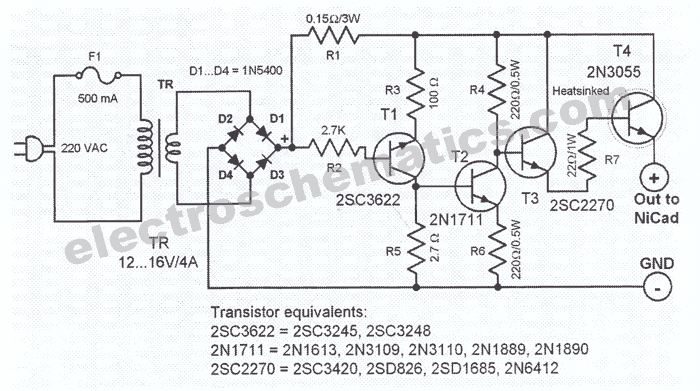
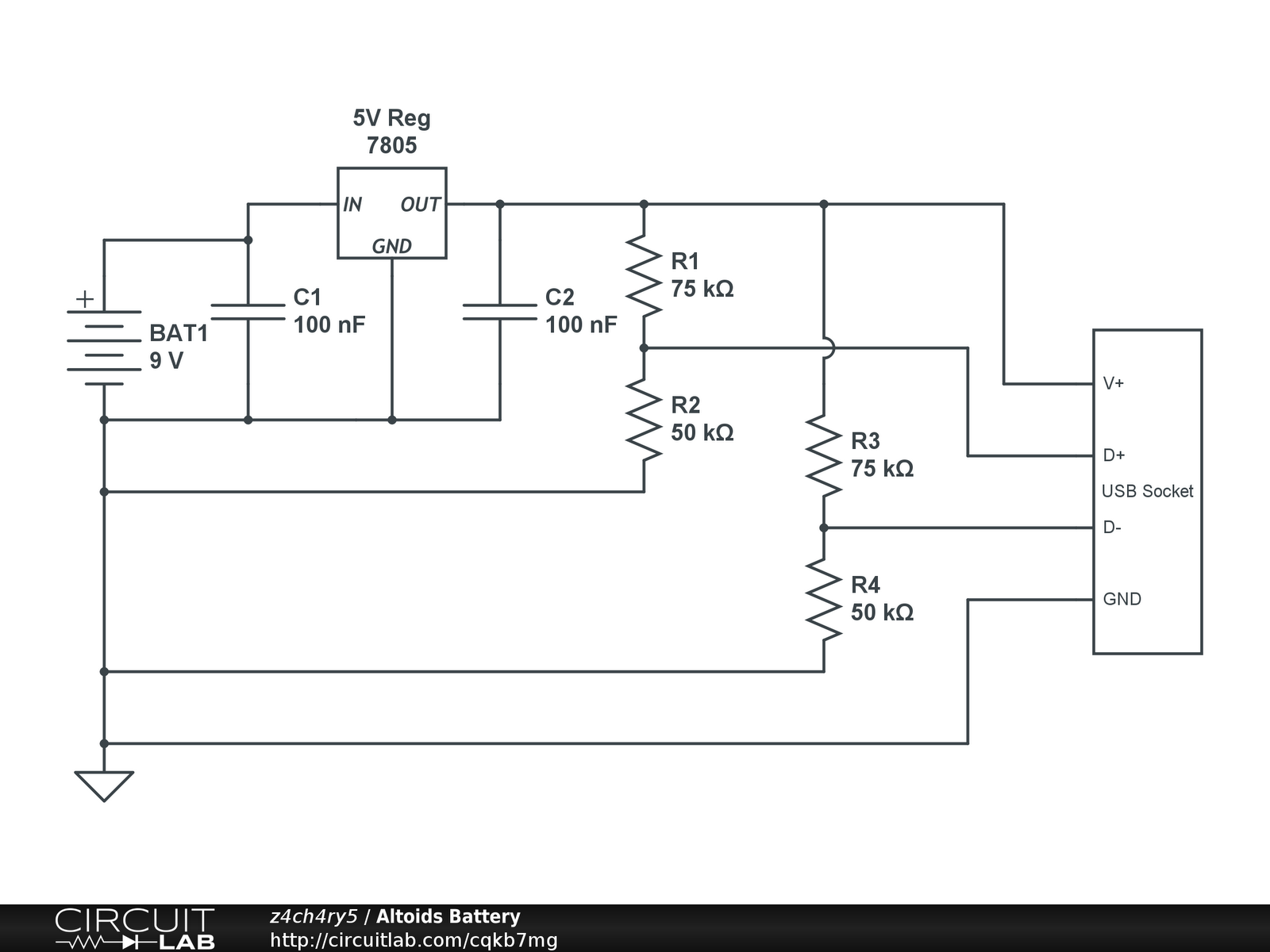
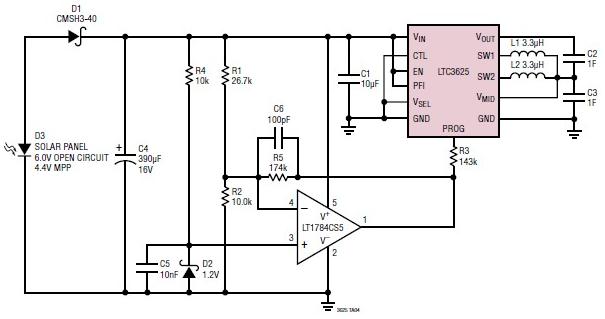
Battery Charger Regulator
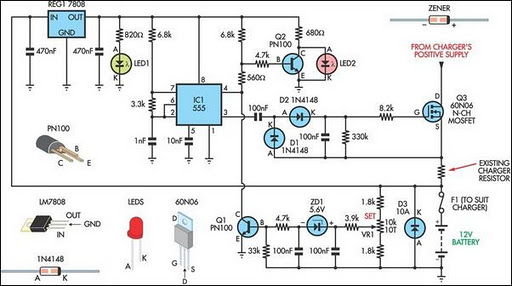
Most commercial car battery chargers cannot be left connected to the battery for extended periods, as this can lead to overcharging and subsequent battery damage. This add-on circuit is connected in series with the battery being charged and is powered by the battery itself. The circuit utilizes a high-current MOSFET to regulate the charging current, automatically turning off when the battery voltage reaches a predetermined threshold. Power for the circuit is supplied from the battery to a three-terminal regulator (REG1), which provides an output of 8V. An LED (LED1) indicates that the battery is connected and that power is available. A 555 timer IC is configured as an astable oscillator operating at approximately 100 kHz. It drives a diode pump (D1 and D2) to generate sufficient gate voltage for the MOSFET (Q3), allowing it to turn on with minimal on-resistance (typically 14 milliohms). When the MOSFET is activated, current flows from the charger’s positive terminal, enabling the charging process. The battery voltage is monitored using a 10 kΩ potentiometer (VR1).
This circuit design addresses the common issue of overcharging in traditional car battery chargers by incorporating a smart control mechanism. The high-current MOSFET serves as the primary switching device, efficiently managing the flow of current to the battery. The use of a 555 timer configured as an astable oscillator allows for precise timing control, ensuring that the MOSFET operates at the optimal frequency for gate voltage generation. The diode pump configuration (D1 and D2) is essential for boosting the gate voltage of the MOSFET, which is crucial for achieving low on-resistance and thereby minimizing power loss during operation.
The three-terminal regulator (REG1) plays a vital role in providing a stable voltage supply for the circuit's operation, ensuring that the components function reliably regardless of variations in the battery voltage. The inclusion of LED1 serves a dual purpose: it provides a visual indication of the charger’s operational status and confirms that the battery connection is secure.
The monitoring of the battery voltage through the 10 kΩ potentiometer (VR1) allows for user adjustments and fine-tuning of the voltage threshold at which the charging process will cease. This feature enhances the circuit's adaptability to different battery types and conditions, making it suitable for a variety of applications.
Overall, this add-on circuit effectively mitigates the risks associated with prolonged charging, ensuring that the battery is charged safely and efficiently, thereby prolonging its lifespan and enhancing performance.Most off-the-shelf car battery chargers cannot not be left connected to the battery for long periods of time as over-charging and consequent battery damage will occur. This add-on circuit is placed in series with the battery being charged and is powered by the battery itself.
In effect, the circuit uses a high-current Mosfet to control the chargin g current and it turns off when the battery voltage reaches a preset threshold. Power for the circuit is fed from the battery to 3-terminal regulator REG1 which provides 8V. LED1 indicates that the battery is connected and that power is available. The 555 timer IC is configured as an astable oscillator running at approximately 100kHz. It feeds a diode pump (D1 & D2) to generate adequate gate voltage for Mosfet Q3, enabling it to turn on with very little on resistance (typically 14 milliohms). With the Mosfet turned on, current flows from the charger`s positive terminal so that charging can proceed.
The battery voltage is monitored by 10kO pot VR1. 🔗 External reference
This circuit design addresses the common issue of overcharging in traditional car battery chargers by incorporating a smart control mechanism. The high-current MOSFET serves as the primary switching device, efficiently managing the flow of current to the battery. The use of a 555 timer configured as an astable oscillator allows for precise timing control, ensuring that the MOSFET operates at the optimal frequency for gate voltage generation. The diode pump configuration (D1 and D2) is essential for boosting the gate voltage of the MOSFET, which is crucial for achieving low on-resistance and thereby minimizing power loss during operation.
The three-terminal regulator (REG1) plays a vital role in providing a stable voltage supply for the circuit's operation, ensuring that the components function reliably regardless of variations in the battery voltage. The inclusion of LED1 serves a dual purpose: it provides a visual indication of the charger’s operational status and confirms that the battery connection is secure.
The monitoring of the battery voltage through the 10 kΩ potentiometer (VR1) allows for user adjustments and fine-tuning of the voltage threshold at which the charging process will cease. This feature enhances the circuit's adaptability to different battery types and conditions, making it suitable for a variety of applications.
Overall, this add-on circuit effectively mitigates the risks associated with prolonged charging, ensuring that the battery is charged safely and efficiently, thereby prolonging its lifespan and enhancing performance.Most off-the-shelf car battery chargers cannot not be left connected to the battery for long periods of time as over-charging and consequent battery damage will occur. This add-on circuit is placed in series with the battery being charged and is powered by the battery itself.
In effect, the circuit uses a high-current Mosfet to control the chargin g current and it turns off when the battery voltage reaches a preset threshold. Power for the circuit is fed from the battery to 3-terminal regulator REG1 which provides 8V. LED1 indicates that the battery is connected and that power is available. The 555 timer IC is configured as an astable oscillator running at approximately 100kHz. It feeds a diode pump (D1 & D2) to generate adequate gate voltage for Mosfet Q3, enabling it to turn on with very little on resistance (typically 14 milliohms). With the Mosfet turned on, current flows from the charger`s positive terminal so that charging can proceed.
The battery voltage is monitored by 10kO pot VR1. 🔗 External reference