Chevrolet Malibu 1997 Electrical Wiring Diagram

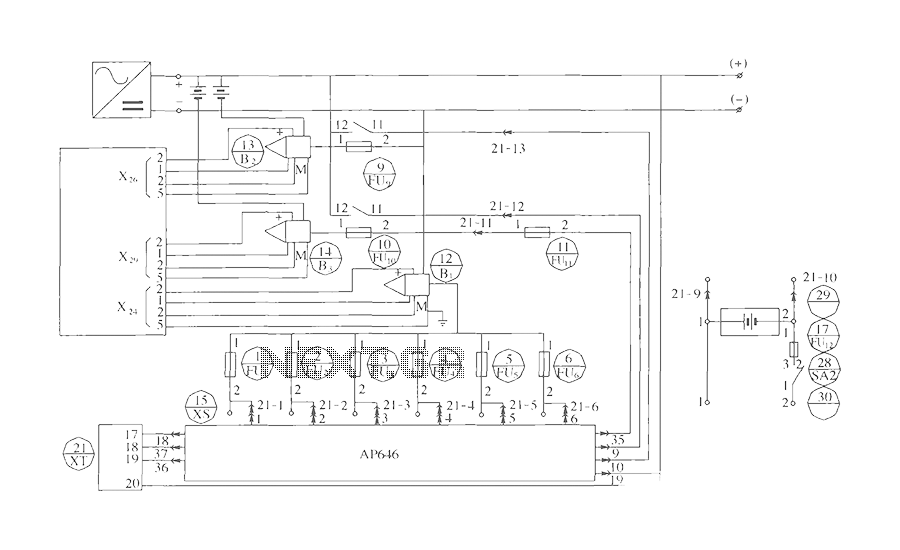
The following circuit illustrates the electrical wiring diagram for the 1997 Chevrolet Malibu. It includes performance circuits for the 2.4L (VIN T) engine and various components.
The electrical wiring diagram for the 1997 Chevrolet Malibu is a crucial resource for understanding the vehicle's electrical system. This diagram provides a detailed representation of the wiring layout, illustrating connections between various electrical components and systems within the vehicle.
Key features of the diagram include the performance circuits associated with the 2.4L engine (VIN T), which encompass critical elements such as the ignition system, fuel injection, and various sensors. Each component is represented with clear labels and symbols, allowing for easy identification and troubleshooting.
The wiring diagram typically includes information on wire colors, gauge sizes, and connection points, which are essential for any repair or modification work. It also highlights the relationship between the engine management system and other systems like the battery, alternator, and starter motor, providing insights into how electrical signals are transmitted throughout the vehicle.
In addition to the engine performance circuits, the diagram may cover other essential systems such as lighting, climate control, and audio, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of the vehicle's electrical architecture. This information is invaluable for automotive technicians and DIY enthusiasts alike, facilitating effective diagnostics and repairs.
In summary, the electrical wiring diagram for the 1997 Chevrolet Malibu serves as a vital tool for maintaining and troubleshooting the vehicle's electrical systems, ensuring optimal performance and reliability.The following circuit shows about Chevrolet Malibu 1997 Electrical Wiring Diagram. Features: 2.4L (VIN T) Engine Performance Circuits,. Component: .. 🔗 External reference
The electrical wiring diagram for the 1997 Chevrolet Malibu is a crucial resource for understanding the vehicle's electrical system. This diagram provides a detailed representation of the wiring layout, illustrating connections between various electrical components and systems within the vehicle.
Key features of the diagram include the performance circuits associated with the 2.4L engine (VIN T), which encompass critical elements such as the ignition system, fuel injection, and various sensors. Each component is represented with clear labels and symbols, allowing for easy identification and troubleshooting.
The wiring diagram typically includes information on wire colors, gauge sizes, and connection points, which are essential for any repair or modification work. It also highlights the relationship between the engine management system and other systems like the battery, alternator, and starter motor, providing insights into how electrical signals are transmitted throughout the vehicle.
In addition to the engine performance circuits, the diagram may cover other essential systems such as lighting, climate control, and audio, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of the vehicle's electrical architecture. This information is invaluable for automotive technicians and DIY enthusiasts alike, facilitating effective diagnostics and repairs.
In summary, the electrical wiring diagram for the 1997 Chevrolet Malibu serves as a vital tool for maintaining and troubleshooting the vehicle's electrical systems, ensuring optimal performance and reliability.The following circuit shows about Chevrolet Malibu 1997 Electrical Wiring Diagram. Features: 2.4L (VIN T) Engine Performance Circuits,. Component: .. 🔗 External reference