
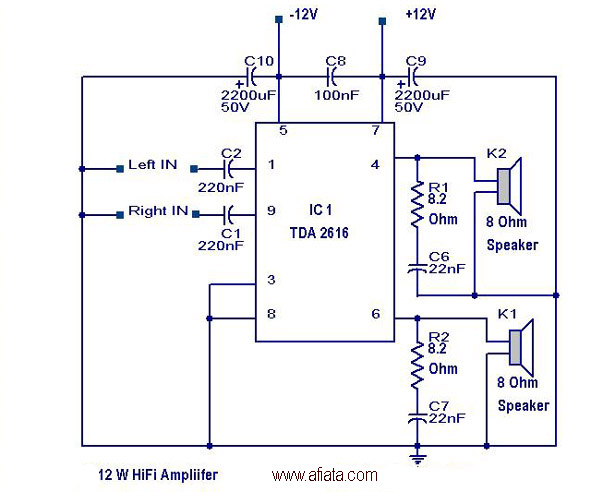
qsc power amplifiers tda2616 circuit diagram
No description available.
Related Circuits

This application note provides a concise overview of power amplifier theory and presents simulation results that offer insights into the operation of the power amplifier across all of MAXIM's LFRF transmitters and transceivers. Power amplifiers are critical components in communication...
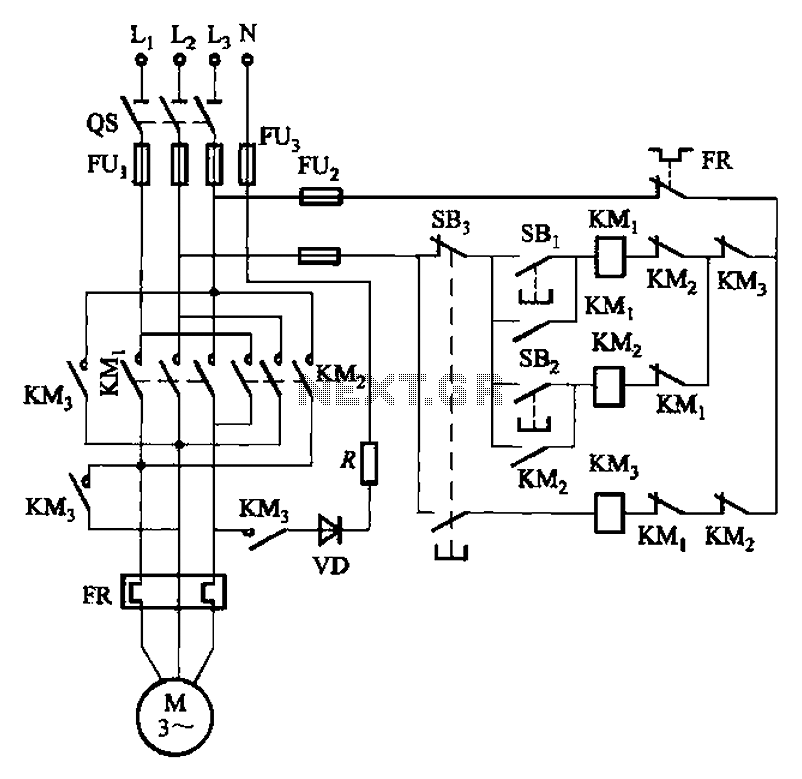
The circuit illustrated in Figure 3-145 employs a rectifier diode brake for neutral grounding in a three-phase, four-wire power supply system. This circuit design incorporates a rectifier diode brake, which plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety and reliability of...
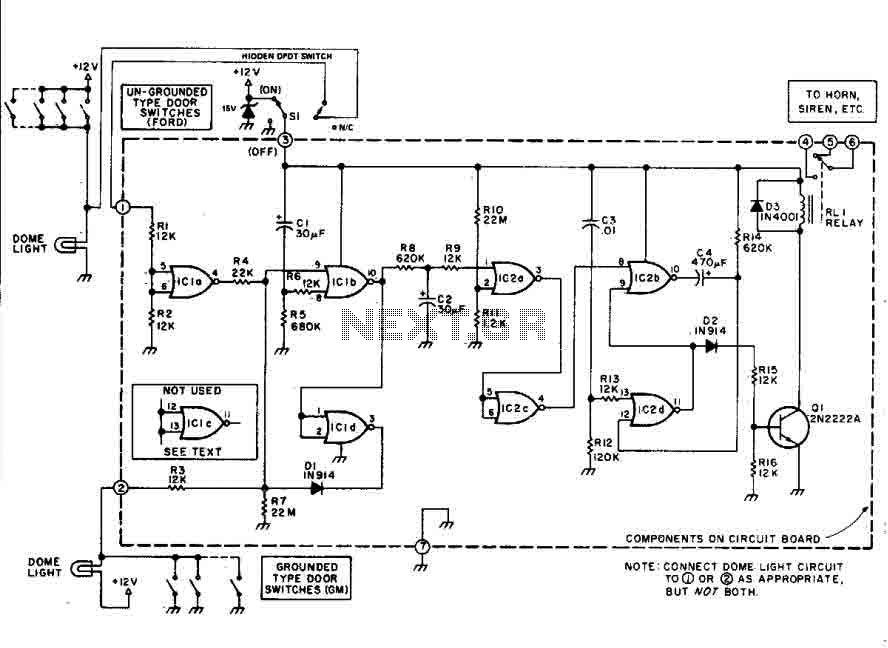
This car alarm circuit features an 18-second delay for both entrance and exit. It sounds continuously for 6 minutes before automatically turning off the horn and preparing for the next triggering event. The alarm remains activated even if the...
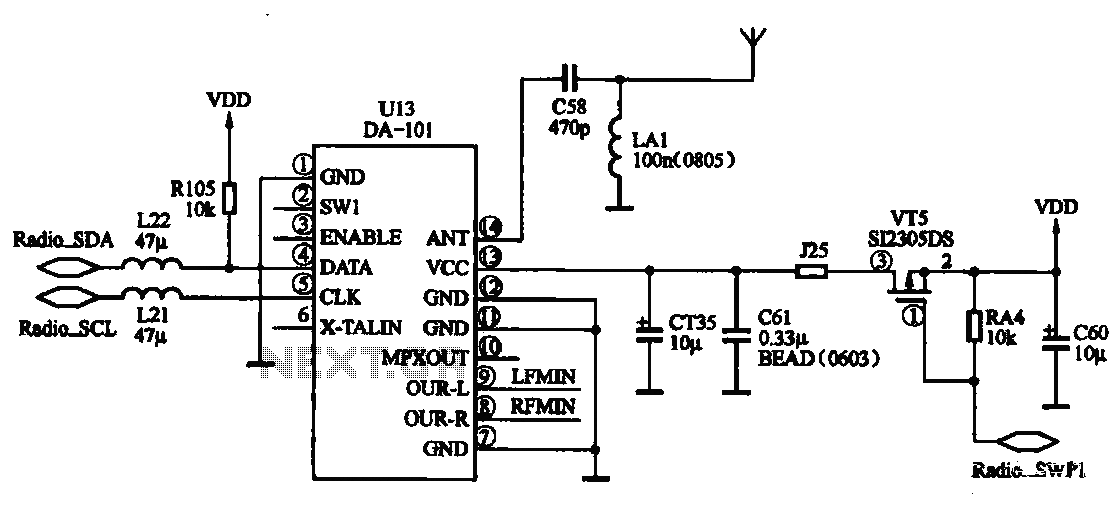
FM radio chip circuits operate differently, as illustrated by the DA-101 chip FM radio circuit. In this configuration, the FM radio broadcast program is received through the headset jack, which functions as an antenna. The signal captured by the...
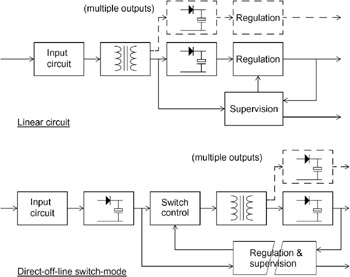
The power supply is a crucial yet often overlooked component of any electronic device. It serves as the interface between the noisy, variable, and poorly defined power sources from the external environment and the precise voltage and current requirements...
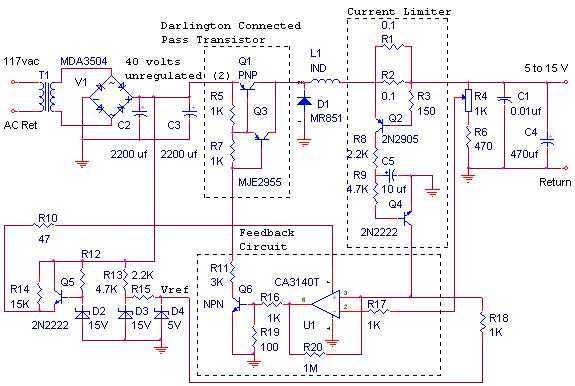
The switching power supply, shown in the schematic, provides 12 volts, at 10 amps, maximum, using a discrete transistor regulator with an op-amp functioning as a comparator in the feedback circuit. The supply was constructed in 1984 and is...
We use cookies to enhance your experience, analyze traffic, and serve personalized ads. By clicking "Accept", you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more