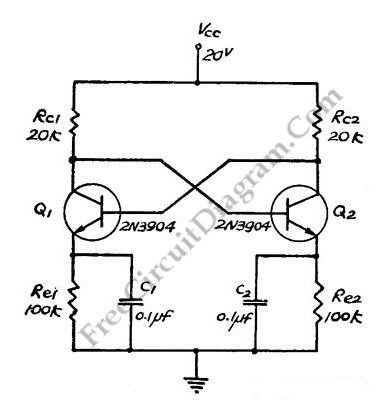
Crystal Controlled Oscillator Circuit
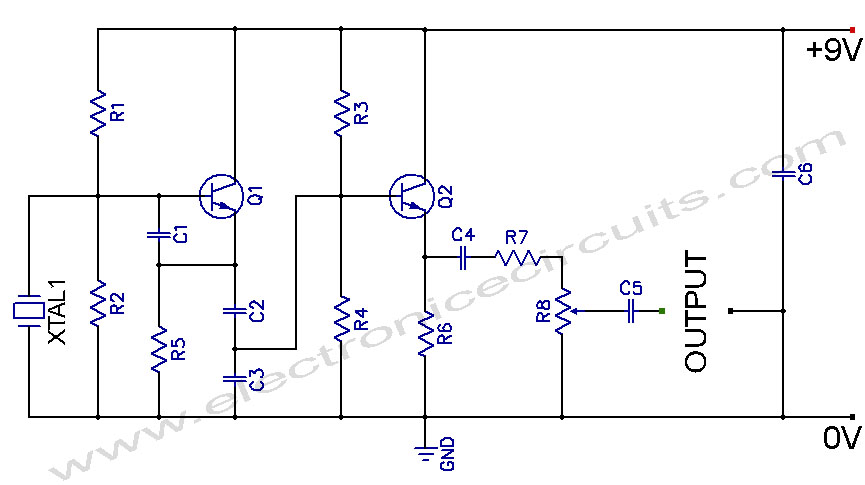
Crystal Controlled Oscillator Circuit. This general-purpose signal source is highly effective in signal-tracing applications. The output level is adjustable.
The crystal-controlled oscillator circuit is designed to provide a stable and precise frequency output, which is essential for various electronic applications, particularly in signal tracing and testing. The core component of this circuit is a quartz crystal, which serves as a frequency-determining element. When the crystal is excited by an alternating current, it vibrates at its fundamental frequency, producing a consistent waveform.
The oscillator typically includes an amplifier, which is used to boost the signal generated by the crystal. This amplifier can be configured in various ways, such as a Colpitts or Clapp oscillator configuration, depending on the desired frequency range and output characteristics. The output level can be adjusted using a variable resistor or potentiometer, allowing for flexibility in signal strength to suit different applications.
Power supply considerations are also crucial for the performance of the oscillator. A stable DC power source is required to ensure the oscillator operates efficiently and consistently. The circuit may include bypass capacitors to filter out any noise, ensuring a clean output signal.
In addition to signal tracing, crystal-controlled oscillators are widely used in communication systems, frequency synthesizers, and clock generation circuits. Their high stability and accuracy make them suitable for applications requiring precise timing and frequency control. Overall, the crystal-controlled oscillator circuit is a fundamental building block in modern electronics, providing reliable signal generation for a variety of uses.Crystal Controlled Oscillator Circuit This general purpose signal source serves very well in signal-tracing applications. The output level is.. 🔗 External reference
The crystal-controlled oscillator circuit is designed to provide a stable and precise frequency output, which is essential for various electronic applications, particularly in signal tracing and testing. The core component of this circuit is a quartz crystal, which serves as a frequency-determining element. When the crystal is excited by an alternating current, it vibrates at its fundamental frequency, producing a consistent waveform.
The oscillator typically includes an amplifier, which is used to boost the signal generated by the crystal. This amplifier can be configured in various ways, such as a Colpitts or Clapp oscillator configuration, depending on the desired frequency range and output characteristics. The output level can be adjusted using a variable resistor or potentiometer, allowing for flexibility in signal strength to suit different applications.
Power supply considerations are also crucial for the performance of the oscillator. A stable DC power source is required to ensure the oscillator operates efficiently and consistently. The circuit may include bypass capacitors to filter out any noise, ensuring a clean output signal.
In addition to signal tracing, crystal-controlled oscillators are widely used in communication systems, frequency synthesizers, and clock generation circuits. Their high stability and accuracy make them suitable for applications requiring precise timing and frequency control. Overall, the crystal-controlled oscillator circuit is a fundamental building block in modern electronics, providing reliable signal generation for a variety of uses.Crystal Controlled Oscillator Circuit This general purpose signal source serves very well in signal-tracing applications. The output level is.. 🔗 External reference