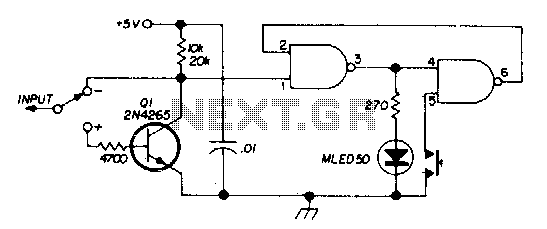
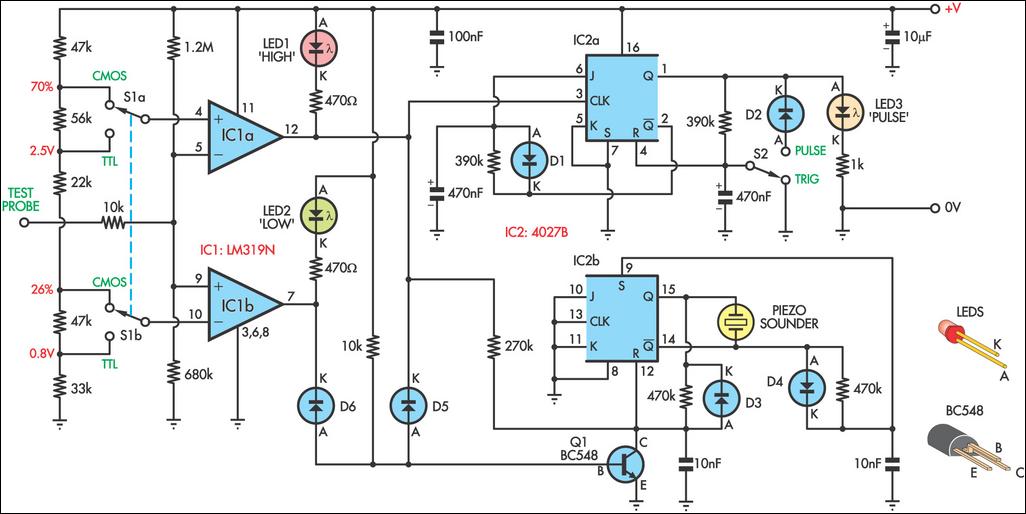
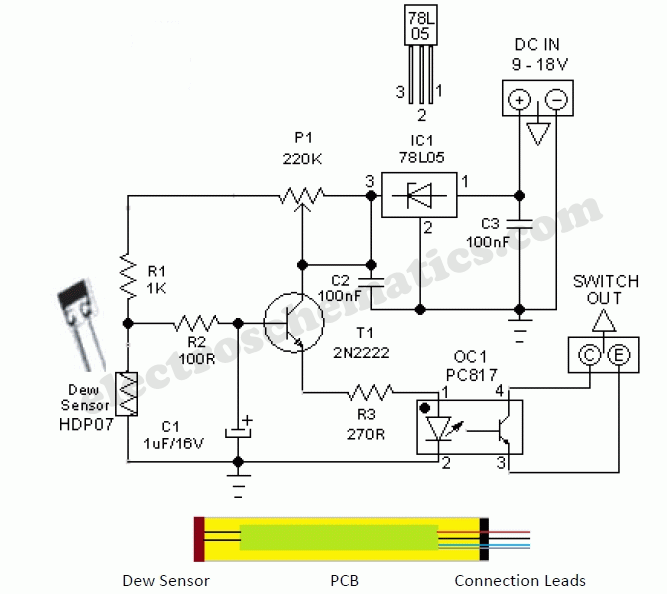
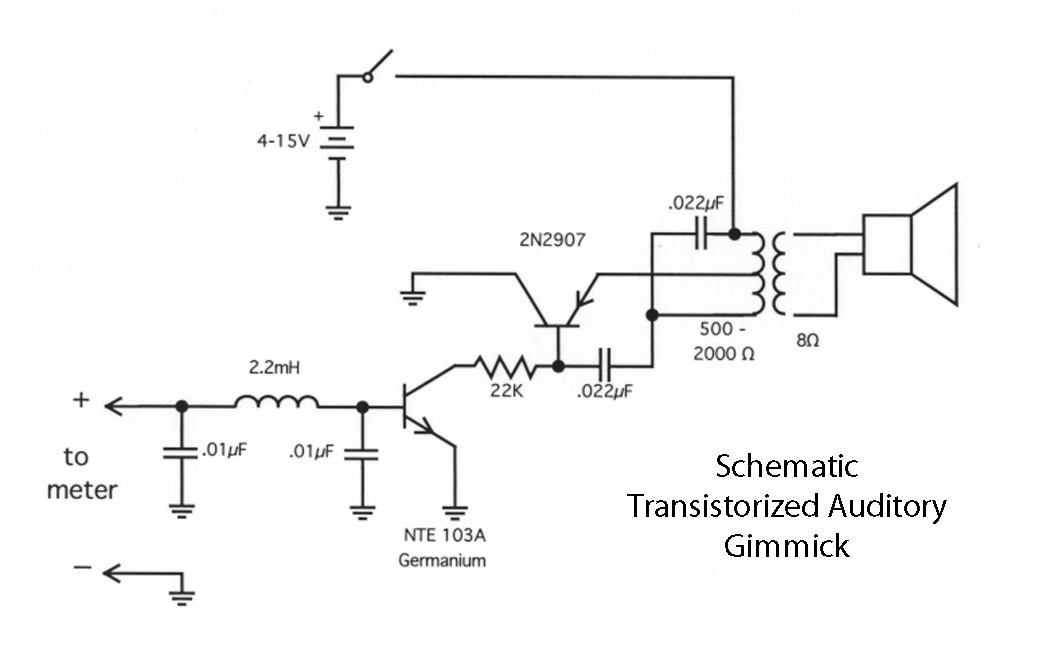
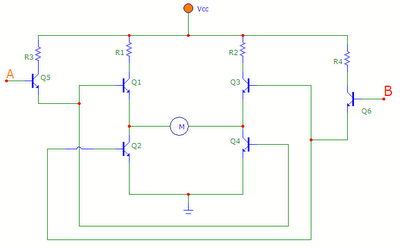
Darlington Transistor Pair Logic Probe
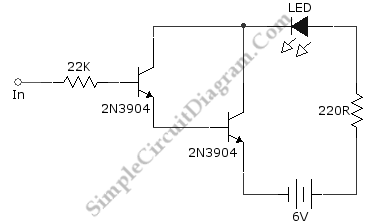
Ideally, any testing equipment will not draw any current from the device under test. This ideal condition can be approximated by designing a testing device.
To achieve the ideal condition where testing equipment does not draw current from the device under test (DUT), it is essential to design the testing device with high input impedance. This can be accomplished by utilizing operational amplifiers (op-amps) in a voltage follower configuration, which presents a very high impedance to the DUT.
The circuit can be composed of an op-amp connected in a non-inverting configuration. The output of the op-amp will follow the input voltage while ensuring minimal loading on the DUT. The input terminals of the op-amp should be connected to the DUT, while the output can be routed to a measurement instrument, such as a digital multimeter or an oscilloscope, for voltage readings.
Additionally, the power supply for the op-amp should be carefully selected to match the expected voltage levels of the DUT, ensuring that the op-amp operates within its linear range. Bypass capacitors may be added near the power supply pins of the op-amp to filter out any noise and provide stable operation.
To further minimize the current drawn from the DUT, the testing device can incorporate a high-value resistor in series with the input. This resistor should be large enough to ensure that the current drawn is negligible compared to the operational characteristics of the DUT.
By implementing these design considerations, the testing equipment can effectively approximate the ideal condition of not drawing current from the DUT, allowing for accurate and reliable testing results.Ideally, any testing equipment will not draw any current from the device under test. This ideal condition can be approximated by designing a testing device.. 🔗 External reference
To achieve the ideal condition where testing equipment does not draw current from the device under test (DUT), it is essential to design the testing device with high input impedance. This can be accomplished by utilizing operational amplifiers (op-amps) in a voltage follower configuration, which presents a very high impedance to the DUT.
The circuit can be composed of an op-amp connected in a non-inverting configuration. The output of the op-amp will follow the input voltage while ensuring minimal loading on the DUT. The input terminals of the op-amp should be connected to the DUT, while the output can be routed to a measurement instrument, such as a digital multimeter or an oscilloscope, for voltage readings.
Additionally, the power supply for the op-amp should be carefully selected to match the expected voltage levels of the DUT, ensuring that the op-amp operates within its linear range. Bypass capacitors may be added near the power supply pins of the op-amp to filter out any noise and provide stable operation.
To further minimize the current drawn from the DUT, the testing device can incorporate a high-value resistor in series with the input. This resistor should be large enough to ensure that the current drawn is negligible compared to the operational characteristics of the DUT.
By implementing these design considerations, the testing equipment can effectively approximate the ideal condition of not drawing current from the DUT, allowing for accurate and reliable testing results.Ideally, any testing equipment will not draw any current from the device under test. This ideal condition can be approximated by designing a testing device.. 🔗 External reference