Hearing Aids Circuit
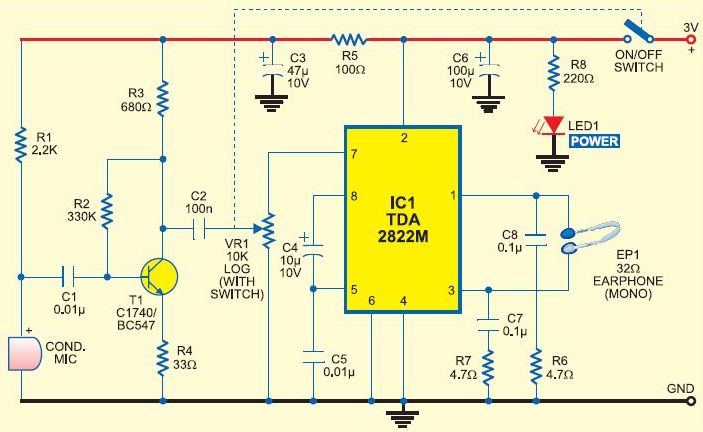
This is a cost-effective DIY option for a hearing aid. It should not be considered a replacement for a genuine hearing aid prescribed by an audiologist. Amplifying all sounds and frequencies, or using it continuously in loud environments, may lead to further hearing loss. This circuit may be beneficial for certain types of hearing loss and for occasional use, especially during the average waiting period of seven years to obtain a hearing aid. This low-cost, general-purpose electronic circuit operates on 3V DC, utilizing two 1.5V batteries. Transistor T1 and its associated components form the audio signal preamplifier, which captures acoustic signals through the condenser microphone and converts them into corresponding electrical signals. Medical-grade hearing aids are often prohibitively expensive; therefore, this circuit may serve as an alternative for individuals who need auditory assistance without incurring the full cost and capabilities of a prescribed hearing aid. The medium-power amplifier section is built around the TDA2822M audio amplifier IC (not TDA2822). This IC, designed specifically for portable low-power applications, is available in an 8-pin mini DIP package. In this configuration, the IC is arranged in a bridge setup to drive a 32-ohm general-purpose monophonic earphone. The audio output of this circuit ranges from 10 to 15 mW, with a quiescent current drain of less than 1 mA. The circuit can be easily assembled on a veroboard, and for convenience in assembly and maintenance, it is recommended to use an 8-pin DIP IC socket for the TDA2822M.
This hearing aid circuit provides a practical solution for individuals experiencing mild to moderate hearing loss. The design includes a condenser microphone that captures sound waves and converts them into electrical signals. These signals are amplified by the transistor T1, which serves as the preamplifier, enhancing the acoustic signals before they are sent to the main amplifier section.
The TDA2822M IC functions as a medium-power amplifier capable of driving low-impedance earphones, making it ideal for portable applications. The bridge configuration allows for increased output power, ensuring that the user experiences sufficient sound levels.
The circuit's low power consumption is a significant advantage, as it operates on a minimal quiescent current, allowing for prolonged usage without frequent battery replacement. This feature is particularly beneficial for users who may rely on the device for extended periods.
Assembly on a veroboard is straightforward, and the use of an IC socket for the TDA2822M not only simplifies the initial construction but also facilitates any future repairs or replacements. Overall, this DIY hearing aid circuit represents an accessible and effective alternative for those in need of auditory assistance while awaiting more advanced solutions.This is a less expensive, and DIY option for a hearing aid. It is not a substitute for a real hearing aid that an audiologist would prescribe. Amplification of all sounds and frequencies, or constant use in loud environments can cause additional hearing loss. This circuit could be helpful for some types of hearing loss and occasional use, as well as fill in during the average amount of time people wait to get a hearing aid (7 years). This low-cost, general-purpose electronic circuit works off 3V DC (2G—1. 5V battery). Transistor T1 and associated components form the audio signal preamplifier for the acoustic signals picked up by the condenser microphone and converted into corresponding electrical signals. Medical grade hearing aids are very expensive, if a person needs help hearing but not necessarily the full cost and capability of a prescribed hearing aid, this might be an option.
The medium-power amplifier section is wired around popular audio amplifier IC TDA2822M (not TDA2822). This IC, specially designed for portable low-power applications, is readily available in 8-pin mini DIP package.
Here the IC is wired in bridge configuration to drive the 32-ohm general-purpose monophonic earphone. The audio output of this aid circuit is 10 to 15 mW and the quiescent current drain is below 1 mA. The circuit can be easily assembled on a veroboard. For easy assembling and maintenance, use an 8-pin DIP IC socket for TDA2822M. 🔗 External reference
This hearing aid circuit provides a practical solution for individuals experiencing mild to moderate hearing loss. The design includes a condenser microphone that captures sound waves and converts them into electrical signals. These signals are amplified by the transistor T1, which serves as the preamplifier, enhancing the acoustic signals before they are sent to the main amplifier section.
The TDA2822M IC functions as a medium-power amplifier capable of driving low-impedance earphones, making it ideal for portable applications. The bridge configuration allows for increased output power, ensuring that the user experiences sufficient sound levels.
The circuit's low power consumption is a significant advantage, as it operates on a minimal quiescent current, allowing for prolonged usage without frequent battery replacement. This feature is particularly beneficial for users who may rely on the device for extended periods.
Assembly on a veroboard is straightforward, and the use of an IC socket for the TDA2822M not only simplifies the initial construction but also facilitates any future repairs or replacements. Overall, this DIY hearing aid circuit represents an accessible and effective alternative for those in need of auditory assistance while awaiting more advanced solutions.This is a less expensive, and DIY option for a hearing aid. It is not a substitute for a real hearing aid that an audiologist would prescribe. Amplification of all sounds and frequencies, or constant use in loud environments can cause additional hearing loss. This circuit could be helpful for some types of hearing loss and occasional use, as well as fill in during the average amount of time people wait to get a hearing aid (7 years). This low-cost, general-purpose electronic circuit works off 3V DC (2G—1. 5V battery). Transistor T1 and associated components form the audio signal preamplifier for the acoustic signals picked up by the condenser microphone and converted into corresponding electrical signals. Medical grade hearing aids are very expensive, if a person needs help hearing but not necessarily the full cost and capability of a prescribed hearing aid, this might be an option.
The medium-power amplifier section is wired around popular audio amplifier IC TDA2822M (not TDA2822). This IC, specially designed for portable low-power applications, is readily available in 8-pin mini DIP package.
Here the IC is wired in bridge configuration to drive the 32-ohm general-purpose monophonic earphone. The audio output of this aid circuit is 10 to 15 mW and the quiescent current drain is below 1 mA. The circuit can be easily assembled on a veroboard. For easy assembling and maintenance, use an 8-pin DIP IC socket for TDA2822M. 🔗 External reference