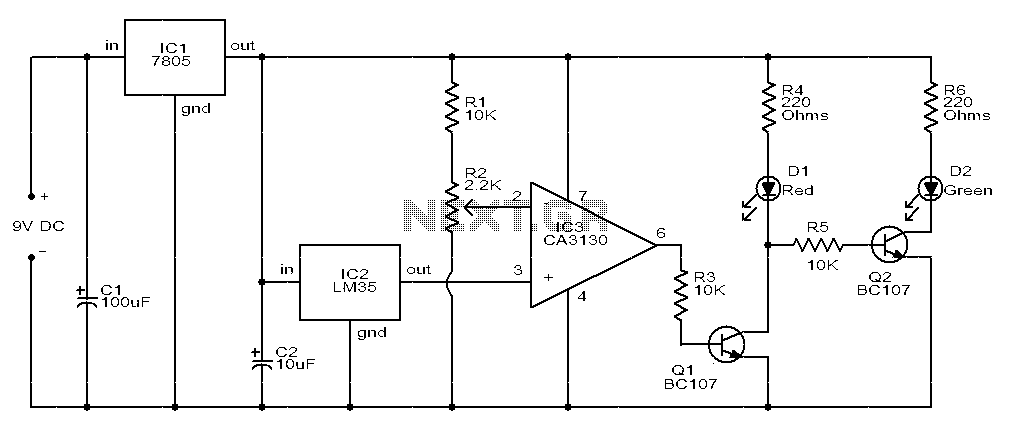
DC servo motor circuit design using A3952S motor driver
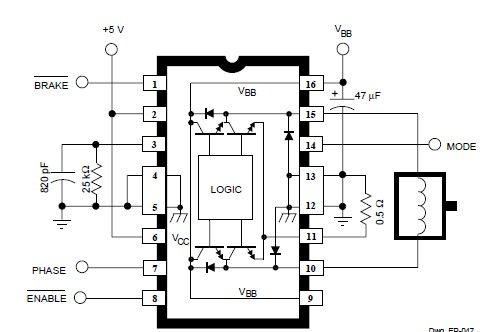
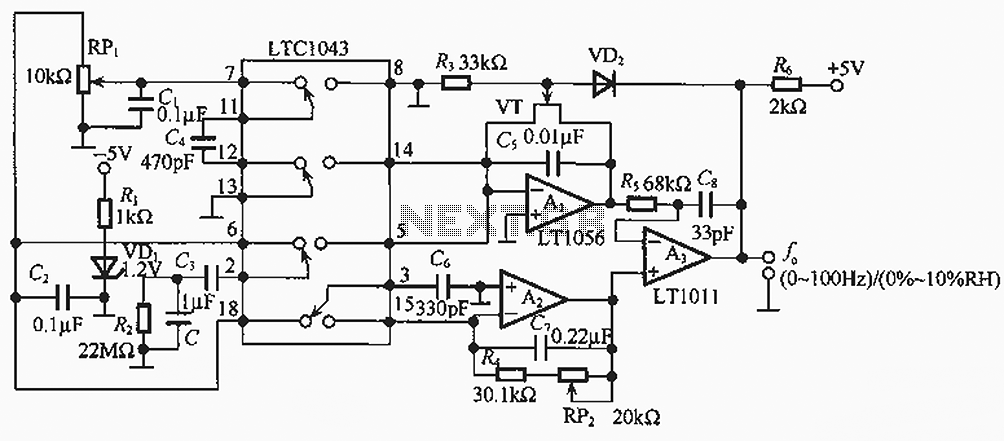
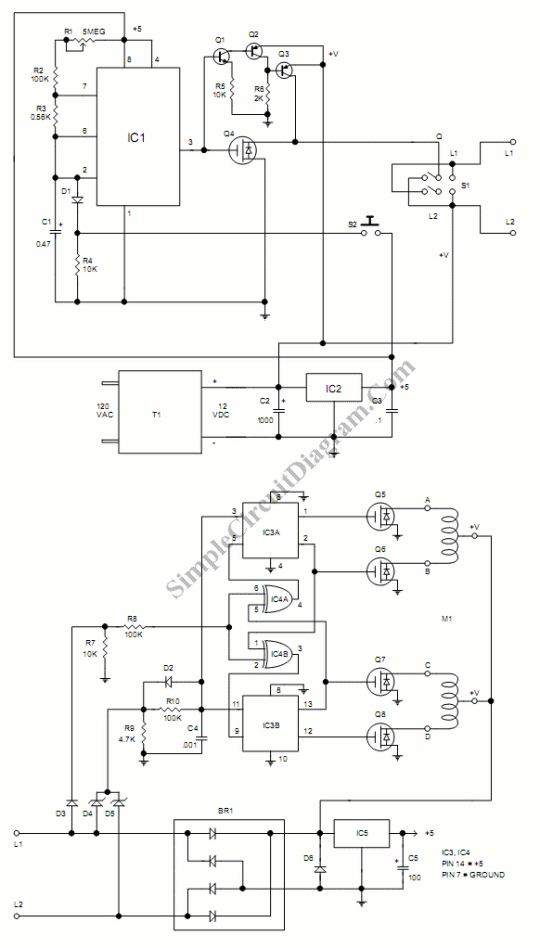
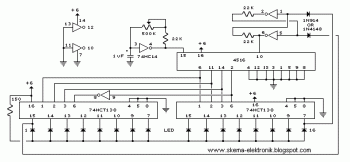
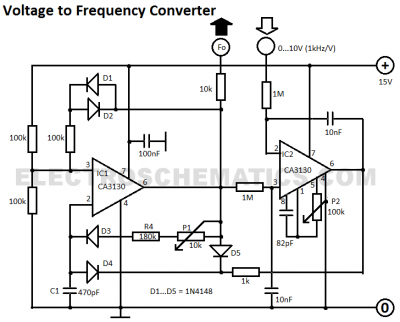
This simple DC servo motor circuit design can be utilized in various electronic projects. The circuit schematic illustrates that this DC servo motor driver employs a single integrated circuit along with a few external electronic components. For bidirectional DC servo motors, the PHASE terminal can be utilized for mechanical direction control. Similar to dynamic braking of the motor, abrupt changes in the direction of a rotating motor generate a current due to back EMF. The amount of current generated will depend on the mode of operation.
The described DC servo motor circuit is designed to control the motion of a servo motor efficiently. The core of the design is a single integrated circuit (IC), which simplifies the control mechanism while maintaining functionality. The IC typically serves as a driver, regulating the power supplied to the motor based on input signals.
In the schematic, the connections to the PHASE terminal are crucial for enabling bidirectional control of the motor. By adjusting the signal at this terminal, the direction of the motor's rotation can be reversed. This feature is particularly useful in applications requiring precise control over rotational direction, such as robotics or automated systems.
The circuit also incorporates several passive components, including resistors and capacitors, which serve to filter signals and stabilize the operation of the IC. These components help mitigate noise and ensure smooth transitions between different operational states of the motor.
When the motor experiences abrupt directional changes, it generates back EMF, which can lead to sudden spikes in current. The design must account for this phenomenon to protect the circuit and ensure reliable operation. The current generated by back EMF is influenced by the speed and load conditions of the motor, necessitating careful consideration during the design phase to avoid potential damage to the components.
Overall, this DC servo motor circuit is a versatile solution, suitable for a range of applications in electronic projects, providing effective control and reliability in motor operation.This simple DC servo motor circuit design that can be used in various electronic projects. As you can see in the circuit schematic this Dc servo motor driver schematic circuit use just one integrated circuit and other few external electronic components. With bidirectional dc servo motors, the PHASE terminal can be used for mechanical direction c ontrol. Similar to when braking the motor dynamically, abrupt changes in the direction of a rotating motor produce a current generated by the back EMF. The current generated will depend on the mode of operation. 🔗 External reference
The described DC servo motor circuit is designed to control the motion of a servo motor efficiently. The core of the design is a single integrated circuit (IC), which simplifies the control mechanism while maintaining functionality. The IC typically serves as a driver, regulating the power supplied to the motor based on input signals.
In the schematic, the connections to the PHASE terminal are crucial for enabling bidirectional control of the motor. By adjusting the signal at this terminal, the direction of the motor's rotation can be reversed. This feature is particularly useful in applications requiring precise control over rotational direction, such as robotics or automated systems.
The circuit also incorporates several passive components, including resistors and capacitors, which serve to filter signals and stabilize the operation of the IC. These components help mitigate noise and ensure smooth transitions between different operational states of the motor.
When the motor experiences abrupt directional changes, it generates back EMF, which can lead to sudden spikes in current. The design must account for this phenomenon to protect the circuit and ensure reliable operation. The current generated by back EMF is influenced by the speed and load conditions of the motor, necessitating careful consideration during the design phase to avoid potential damage to the components.
Overall, this DC servo motor circuit is a versatile solution, suitable for a range of applications in electronic projects, providing effective control and reliability in motor operation.This simple DC servo motor circuit design that can be used in various electronic projects. As you can see in the circuit schematic this Dc servo motor driver schematic circuit use just one integrated circuit and other few external electronic components. With bidirectional dc servo motors, the PHASE terminal can be used for mechanical direction c ontrol. Similar to when braking the motor dynamically, abrupt changes in the direction of a rotating motor produce a current generated by the back EMF. The current generated will depend on the mode of operation. 🔗 External reference