DC Voltage Doubler Circuit with 555
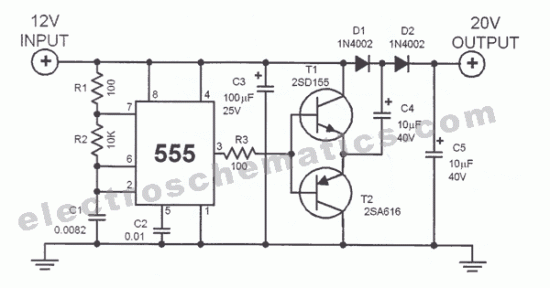
This DC voltage doubler circuit generates a voltage that is double its supply voltage. It is beneficial when a higher voltage level is required from a single power source.
The DC voltage doubler circuit typically employs a combination of capacitors and diodes to achieve its voltage multiplication effect. The circuit operates by charging capacitors to the supply voltage and then utilizing the diodes to transfer this charge in a manner that effectively doubles the output voltage.
In a basic configuration, the circuit consists of two diodes (D1 and D2) and two capacitors (C1 and C2). The input voltage is applied across C1, which charges to the supply voltage (Vs). During the first half of the AC cycle, D1 conducts, allowing C1 to charge. When the voltage reaches its peak, D1 becomes reverse-biased, and C2 begins to charge through D2. The voltage across C2 then rises to Vs + Vs, effectively doubling the output voltage.
The output can be taken from the junction between C2 and D2, providing a DC voltage that is twice the input voltage. This configuration is particularly useful in applications where higher voltage levels are necessary, such as in powering operational amplifiers, sensors, or other electronic components that require a voltage greater than what is available from the single supply.
It is important to consider the load that the circuit will drive, as the output voltage may sag under heavy load conditions. Additionally, the choice of diodes and capacitors will influence the efficiency and performance of the circuit. Schottky diodes are often preferred for their low forward voltage drop, which contributes to higher efficiency, while capacitors should be selected based on their voltage rating and capacitance value to ensure stable operation.
Overall, the DC voltage doubler circuit is a practical and effective solution for applications requiring higher voltage outputs from a lower voltage supply.This dc voltage doubler circuit produces a voltage that is twice its voltage supply. This is useful when a higher voltage level is needed out of a single l. 🔗 External reference
The DC voltage doubler circuit typically employs a combination of capacitors and diodes to achieve its voltage multiplication effect. The circuit operates by charging capacitors to the supply voltage and then utilizing the diodes to transfer this charge in a manner that effectively doubles the output voltage.
In a basic configuration, the circuit consists of two diodes (D1 and D2) and two capacitors (C1 and C2). The input voltage is applied across C1, which charges to the supply voltage (Vs). During the first half of the AC cycle, D1 conducts, allowing C1 to charge. When the voltage reaches its peak, D1 becomes reverse-biased, and C2 begins to charge through D2. The voltage across C2 then rises to Vs + Vs, effectively doubling the output voltage.
The output can be taken from the junction between C2 and D2, providing a DC voltage that is twice the input voltage. This configuration is particularly useful in applications where higher voltage levels are necessary, such as in powering operational amplifiers, sensors, or other electronic components that require a voltage greater than what is available from the single supply.
It is important to consider the load that the circuit will drive, as the output voltage may sag under heavy load conditions. Additionally, the choice of diodes and capacitors will influence the efficiency and performance of the circuit. Schottky diodes are often preferred for their low forward voltage drop, which contributes to higher efficiency, while capacitors should be selected based on their voltage rating and capacitance value to ensure stable operation.
Overall, the DC voltage doubler circuit is a practical and effective solution for applications requiring higher voltage outputs from a lower voltage supply.This dc voltage doubler circuit produces a voltage that is twice its voltage supply. This is useful when a higher voltage level is needed out of a single l. 🔗 External reference