dtmf cell phone controlled home appliances automation project
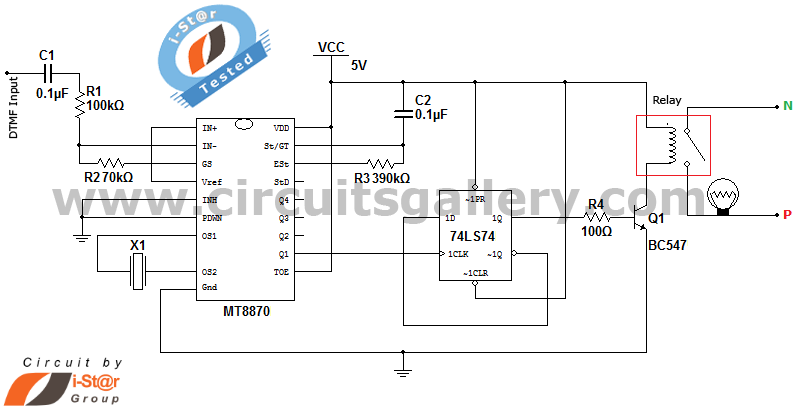
It is possible to control home and office electrical appliances using a mobile phone. This document presents a simple home automation electronic mini project circuit diagram designed for engineering students, allowing the control of electrical appliances without the use of a microcontroller. The circuit utilizes the DTMF (Dual Tone Multi Frequency) technique. Previously, information was shared regarding DTMF and a DTMF decoder circuit using the M8870 decoder IC. This home automation project incorporates the DTMF decoder circuit with minor modifications to manage various electrical devices. By connecting a mobile phone headset jack to the phone, users can control electrical appliances through the DTMF keypad. For demonstration purposes, the project controls an electrical bulb, but the circuit can be adapted to manage multiple devices using a 4-to-16 decoder IC. When a key is pressed on the mobile phone during a call, the other party hears tones corresponding to the pressed keys, which are based on DTMF technology. Data is transmitted as pairs of tones, and the receiver identifies the valid frequency pair, producing the appropriate BCD code as output from the DTMF decoder IC. The microphone wire is cut to reveal four wires, of which only the Ground and Right wires are necessary. The signals from the microphone wire are processed by the DTMF decoder IC, generating a corresponding binary sequence output at Q1, Q2, Q3, and Q4. The IC7474 is configured in toggle mode, meaning that upon receiving a clock pulse, its output (Pin 5) goes high, and subsequent clock pulses reset the IC. Outputs toggle each time a key is pressed. When keys 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, or * are pressed and released, the DTMF decoder IC produces a high pulse, acting as a clock for the flip-flop and setting its output high. This output connects to a relay driver circuit through a 100-ohm resistor, energizing the relay coil via a BC547 transistor and turning on the bulb connected to the normally open terminal of the relay circuit.
The circuit operates by utilizing the DTMF technology, which encodes the pressed keys into specific frequency pairs. The DTMF decoder IC, such as the M8870, decodes these frequencies into a binary-coded decimal (BCD) output. The configuration of the IC7474 as a toggle flip-flop allows for the detection of key presses, enabling the control of the relay circuit that ultimately operates the electrical appliance.
To implement this circuit, the following components are required: a mobile phone with DTMF capability, a headset jack, a DTMF decoder IC (M8870), a flip-flop IC (7474), a transistor (BC547), a relay, and an electrical bulb. The circuit's design ensures that it can be expanded to control additional appliances by integrating a 4-to-16 decoder IC, which facilitates the management of multiple devices from a single mobile phone interface.
The practical aspect of this project lies in its simplicity and effectiveness, making it an excellent choice for engineering students to understand the principles of home automation and remote control systems. The circuit can be further enhanced by incorporating safety features, such as overcurrent protection and isolation, to ensure reliable operation in various home and office environments.Do you think that you can control your home and office electrical appliances using your cell phone Yes. !you can Here is a simple home controls home automation electronic mini project circuit diagram for engineering students, to control any electrical appliances using mobile phone without using a microcontroller.
This circuit makes use of DTMF (Dual Tone Multi Frequency) technique. We have already posted on What is DTMF and DTMF decoder circuit using M8870 decoder IC. This home appliances control or home automation project also uses the same DTMF decoder circuit section with little modifications to control home and office electrical appliances. Just connect your cell phone headset (headphone) jack to the mobile phone and then mobile will control electrical appliances and electricalequipment through theDTMF key pad of your cell phone.
Here for demonstrating, we are controlling an electrical bulb using this circuit project but you can extend this circuit to control many electrical devices with some modifications using 4G—16 decoder IC. When you press any key on your mobile phone while call is in progress, the other person will hear some tones corresponding to the keys pressed.
These tones are based on the DTMF (Dual Tone Multi Frequency) technology. Data is transmitted as pairs of tones. The receiver detects the valid frequency pair and gives the appropriate BCD code as the output of the DTMF decoder IC. See the figure below. Cut the microphone wire and you will be able to see 4 wires. Among these wires you need only 2 wires- Ground and Right as shown in figure. The signals from the microphone wire are processed by the DTMF decoder IC which generates the equivalent binary sequence as a parallel output of Q1, Q2, Q3, and Q4.
IC7474 is configured as Toggling mode, that is if it gets a clock pulse the output of this IC (Pin 5) sets to high and further clock pulse resets back the IC. (The outputs toggle whenever a key is pressed). When we press and release any of the keys among 1, 3, 5, 7, 9 and *, the DTMF decoder IC generates a high pulse which acts as a clock to our flip flop and sets the output flip flop to high.
The output of flip flop is connected to the relay driver circuit via 100 © resistor; this output energizes the relay coil through BC547 transistor and turns ON the bulb that is connected at the normally open terminal of relay circuit. 🔗 External reference
The circuit operates by utilizing the DTMF technology, which encodes the pressed keys into specific frequency pairs. The DTMF decoder IC, such as the M8870, decodes these frequencies into a binary-coded decimal (BCD) output. The configuration of the IC7474 as a toggle flip-flop allows for the detection of key presses, enabling the control of the relay circuit that ultimately operates the electrical appliance.
To implement this circuit, the following components are required: a mobile phone with DTMF capability, a headset jack, a DTMF decoder IC (M8870), a flip-flop IC (7474), a transistor (BC547), a relay, and an electrical bulb. The circuit's design ensures that it can be expanded to control additional appliances by integrating a 4-to-16 decoder IC, which facilitates the management of multiple devices from a single mobile phone interface.
The practical aspect of this project lies in its simplicity and effectiveness, making it an excellent choice for engineering students to understand the principles of home automation and remote control systems. The circuit can be further enhanced by incorporating safety features, such as overcurrent protection and isolation, to ensure reliable operation in various home and office environments.Do you think that you can control your home and office electrical appliances using your cell phone Yes. !you can Here is a simple home controls home automation electronic mini project circuit diagram for engineering students, to control any electrical appliances using mobile phone without using a microcontroller.
This circuit makes use of DTMF (Dual Tone Multi Frequency) technique. We have already posted on What is DTMF and DTMF decoder circuit using M8870 decoder IC. This home appliances control or home automation project also uses the same DTMF decoder circuit section with little modifications to control home and office electrical appliances. Just connect your cell phone headset (headphone) jack to the mobile phone and then mobile will control electrical appliances and electricalequipment through theDTMF key pad of your cell phone.
Here for demonstrating, we are controlling an electrical bulb using this circuit project but you can extend this circuit to control many electrical devices with some modifications using 4G—16 decoder IC. When you press any key on your mobile phone while call is in progress, the other person will hear some tones corresponding to the keys pressed.
These tones are based on the DTMF (Dual Tone Multi Frequency) technology. Data is transmitted as pairs of tones. The receiver detects the valid frequency pair and gives the appropriate BCD code as the output of the DTMF decoder IC. See the figure below. Cut the microphone wire and you will be able to see 4 wires. Among these wires you need only 2 wires- Ground and Right as shown in figure. The signals from the microphone wire are processed by the DTMF decoder IC which generates the equivalent binary sequence as a parallel output of Q1, Q2, Q3, and Q4.
IC7474 is configured as Toggling mode, that is if it gets a clock pulse the output of this IC (Pin 5) sets to high and further clock pulse resets back the IC. (The outputs toggle whenever a key is pressed). When we press and release any of the keys among 1, 3, 5, 7, 9 and *, the DTMF decoder IC generates a high pulse which acts as a clock to our flip flop and sets the output flip flop to high.
The output of flip flop is connected to the relay driver circuit via 100 © resistor; this output energizes the relay coil through BC547 transistor and turns ON the bulb that is connected at the normally open terminal of relay circuit. 🔗 External reference