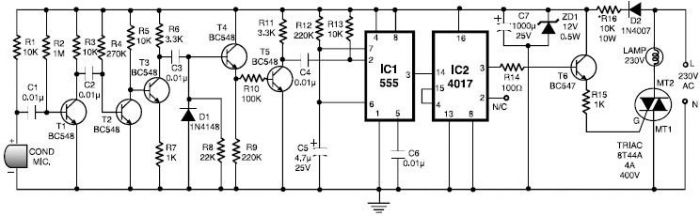
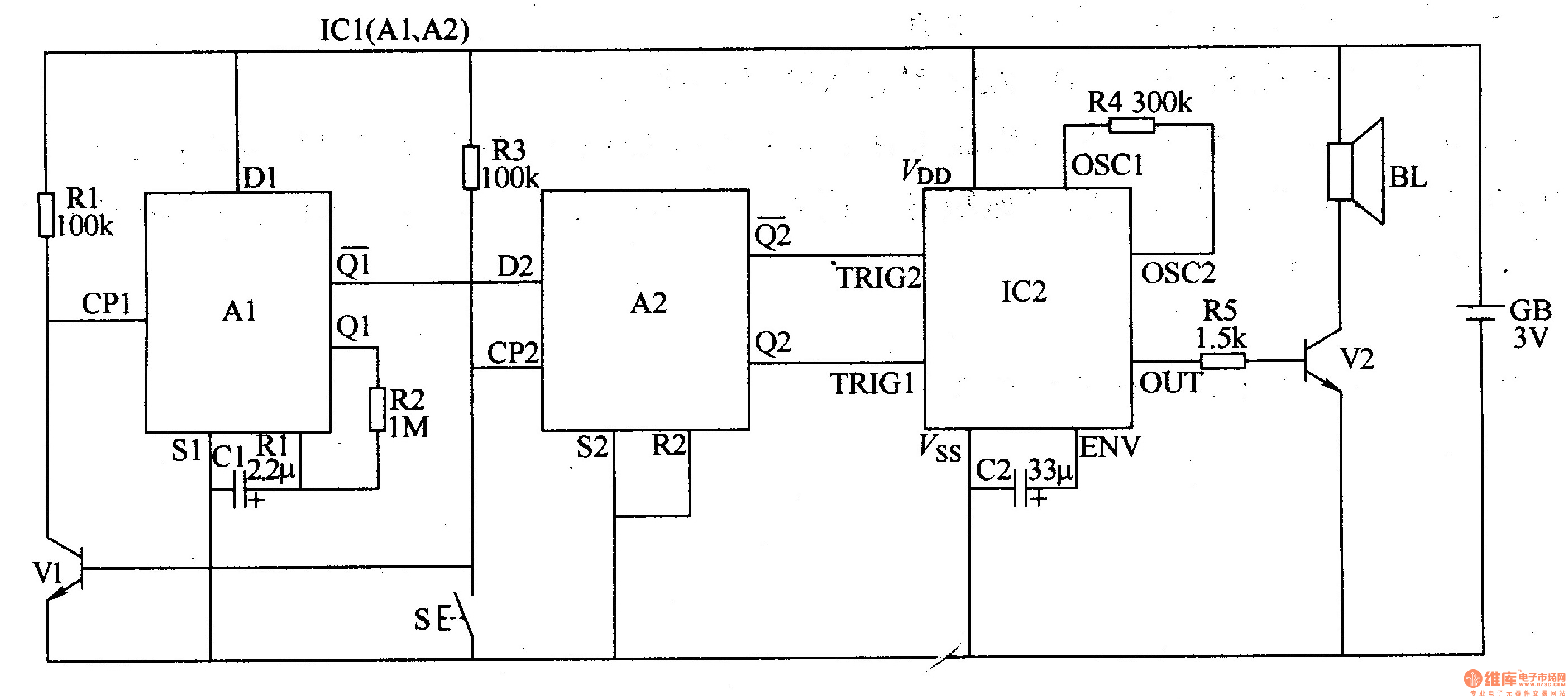
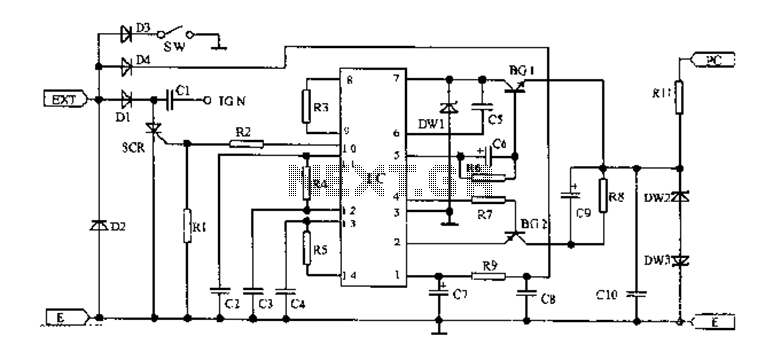
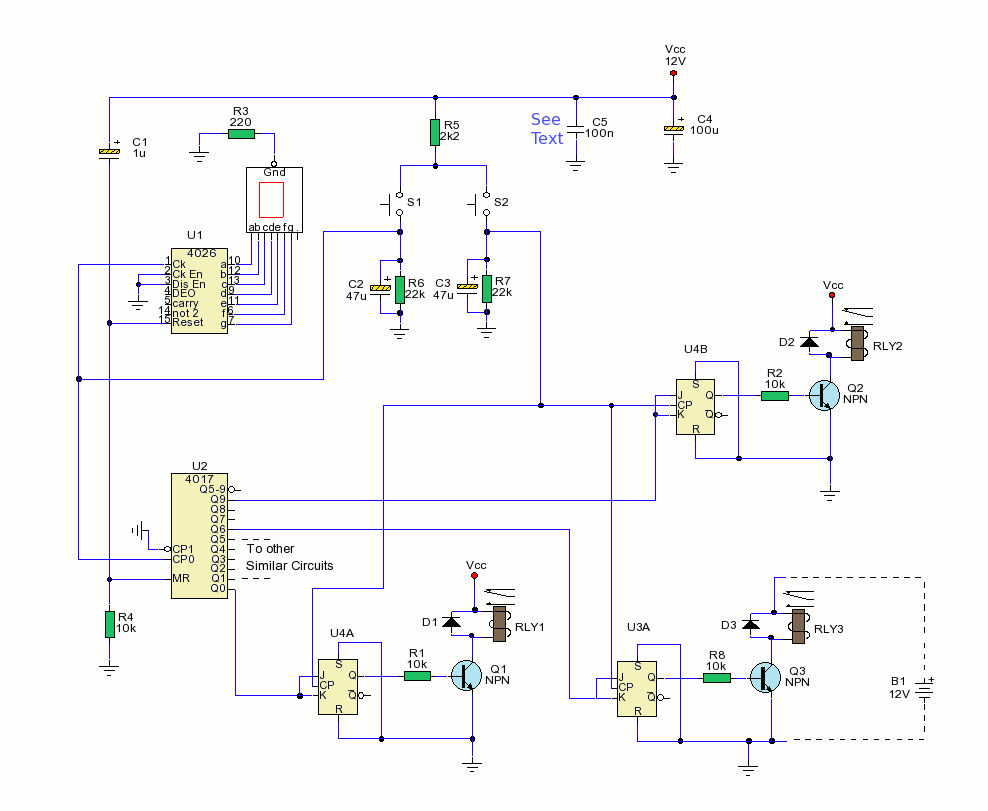
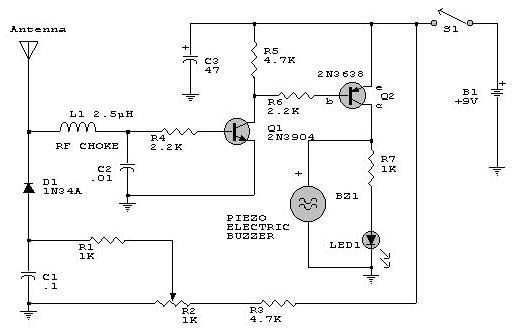
electronic dice

This beginner's breadboard circuit simulates the action of throwing a dice. By pressing a button, the circuit generates a random output, lighting up one of six LEDs to represent the result of the throw.
The circuit utilizes a microcontroller or a simple 555 timer-based design to achieve the randomization effect. When the button is pressed, it triggers the circuit to produce a random number between 1 and 6, which corresponds to the lighting of one of the six LEDs.
The components typically involved in such a circuit include:
1. **Microcontroller or Timer IC**: The 555 timer can be configured in astable mode to create a pulse output, while a microcontroller can be programmed to generate random numbers.
2. **Push Button Switch**: This input device allows the user to initiate the dice throw by closing the circuit momentarily.
3. **LEDs**: Six LEDs are used, each representing a face of the dice. They should be connected in such a way that only one LED lights up at a time based on the random output.
4. **Current-Limiting Resistors**: Resistors are necessary to prevent excessive current from flowing through the LEDs, thereby protecting them from damage.
5. **Power Supply**: A suitable power source, such as batteries or a DC power supply, is required to energize the circuit.
The circuit can be assembled on a breadboard for easy prototyping. Connections should be made carefully to ensure that the push button connects to the input of the microcontroller or timer, which in turn controls the output to the LEDs.
In summary, this circuit serves as an educational tool for beginners to learn about random number generation and basic circuit design while simulating a dice throw. The simplicity of the components involved makes it an excellent project for those new to electronics.This beginner`s breadboard circuit simulates a dice being thrown. Pressing the button throws the dice. One of six LEDs will light up after the throw.. 🔗 External reference
The circuit utilizes a microcontroller or a simple 555 timer-based design to achieve the randomization effect. When the button is pressed, it triggers the circuit to produce a random number between 1 and 6, which corresponds to the lighting of one of the six LEDs.
The components typically involved in such a circuit include:
1. **Microcontroller or Timer IC**: The 555 timer can be configured in astable mode to create a pulse output, while a microcontroller can be programmed to generate random numbers.
2. **Push Button Switch**: This input device allows the user to initiate the dice throw by closing the circuit momentarily.
3. **LEDs**: Six LEDs are used, each representing a face of the dice. They should be connected in such a way that only one LED lights up at a time based on the random output.
4. **Current-Limiting Resistors**: Resistors are necessary to prevent excessive current from flowing through the LEDs, thereby protecting them from damage.
5. **Power Supply**: A suitable power source, such as batteries or a DC power supply, is required to energize the circuit.
The circuit can be assembled on a breadboard for easy prototyping. Connections should be made carefully to ensure that the push button connects to the input of the microcontroller or timer, which in turn controls the output to the LEDs.
In summary, this circuit serves as an educational tool for beginners to learn about random number generation and basic circuit design while simulating a dice throw. The simplicity of the components involved makes it an excellent project for those new to electronics.This beginner`s breadboard circuit simulates a dice being thrown. Pressing the button throws the dice. One of six LEDs will light up after the throw.. 🔗 External reference